
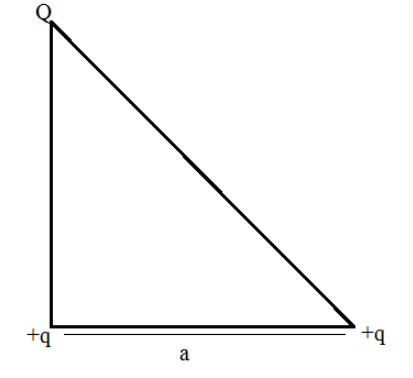
Three charges Q, +q and +q are placed at the vertices of a right angled isosceles triangle as shown. The net electronic energy of configuration is zero if Q is equal to:
(A) $\dfrac{{ - q}}{{1 + \sqrt 2 }}$
(B) $\dfrac{{ - q\sqrt 2 }}{{1 + \sqrt 2 }}$
(C) $ - 2q$
(D) $ + q$

Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: In this question, we need to determine the value of the charge “Q” such that the net electronic energy of the configuration of the charges shown in the figure is equivalent to zero. For this, we will use Coulomb's law and substitute the given values in the coulomb’s formula. Write the formula for net potential (electrostatic) energy of the system and put it equal to zero.
Complete step by step answer:
Applying the Pythagoras theorem to determine the distance between the charges +Q and +q.
$\left( {{d_{Qq}}} \right) = \sqrt {{{\left( {{d_{qq}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{d_{qq}}} \right)}^2}} $
Substituting the values of the ${d_{qq}}$ as ‘a’ in the equation $\left( {{d_{Qq}}} \right) = {\left( {{d_{qq}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{d_{qq}}} \right)^2}$ to determine the distance between the charges +Q and +q.
$
\left( {{d_{Qq}}} \right) = \sqrt {{{\left( {{d_{qq}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{d_{qq}}} \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow\left( {{d_{Qq}}} \right) = \sqrt {{{\left( a \right)}^2} + {{\left( a \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow\left( {{d_{Qq}}} \right) = \sqrt {2{a^2}} \\
\Rightarrow\left( {{d_{Qq}}} \right) = \sqrt 2 a \\
$
Potential energy $U = K\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{r}$, where \[K{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{4\pi \varepsilon }}\].
Net potential energy of the system is given by $U = K\dfrac{{Qq}}{a} + K\dfrac{{qq}}{a} + K\dfrac{{qQ}}{{a\sqrt 2 }}$
Given that net potential energy is 0. So,
$
U = 0 \\
\Rightarrow K\dfrac{{Qq}}{a} + K\dfrac{{qq}}{a} + K\dfrac{{qQ}}{{a\sqrt 2 }} = 0 \\
$
Now solve the equation for Q,
$
\dfrac{{Kq}}{a}\left( {Q + q + \dfrac{Q}{2}} \right) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow Q + \dfrac{Q}{{\sqrt 2 }} = - q \\
\Rightarrow\dfrac{{Q\sqrt 2 + Q}}{{\sqrt 2 }} = - q \\
\Rightarrow Q\left( {1 + \sqrt 2 } \right) = - q\sqrt 2 \\
\therefore Q = \dfrac{{ - q\sqrt 2 }}{{\left( {1 + \sqrt 2 } \right)}} \\
$
Hence, value of the charge “Q” such that the net electronic energy of the configuration of the charges shown in the figure is equivalent to zero is $\dfrac{{ - q\sqrt 2 }}{{\left( {1 + \sqrt 2 } \right)}}$.
Hence,option B is correct.
Note: It is to be worth noting here that, the distance between the charges can be found by using the Pythagoras theorem as the charges are situated at the vertices of the isosceles triangles.
Complete step by step answer:
Applying the Pythagoras theorem to determine the distance between the charges +Q and +q.
$\left( {{d_{Qq}}} \right) = \sqrt {{{\left( {{d_{qq}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{d_{qq}}} \right)}^2}} $
Substituting the values of the ${d_{qq}}$ as ‘a’ in the equation $\left( {{d_{Qq}}} \right) = {\left( {{d_{qq}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{d_{qq}}} \right)^2}$ to determine the distance between the charges +Q and +q.
$
\left( {{d_{Qq}}} \right) = \sqrt {{{\left( {{d_{qq}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{d_{qq}}} \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow\left( {{d_{Qq}}} \right) = \sqrt {{{\left( a \right)}^2} + {{\left( a \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow\left( {{d_{Qq}}} \right) = \sqrt {2{a^2}} \\
\Rightarrow\left( {{d_{Qq}}} \right) = \sqrt 2 a \\
$
Potential energy $U = K\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{r}$, where \[K{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{4\pi \varepsilon }}\].
Net potential energy of the system is given by $U = K\dfrac{{Qq}}{a} + K\dfrac{{qq}}{a} + K\dfrac{{qQ}}{{a\sqrt 2 }}$
Given that net potential energy is 0. So,
$
U = 0 \\
\Rightarrow K\dfrac{{Qq}}{a} + K\dfrac{{qq}}{a} + K\dfrac{{qQ}}{{a\sqrt 2 }} = 0 \\
$
Now solve the equation for Q,
$
\dfrac{{Kq}}{a}\left( {Q + q + \dfrac{Q}{2}} \right) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow Q + \dfrac{Q}{{\sqrt 2 }} = - q \\
\Rightarrow\dfrac{{Q\sqrt 2 + Q}}{{\sqrt 2 }} = - q \\
\Rightarrow Q\left( {1 + \sqrt 2 } \right) = - q\sqrt 2 \\
\therefore Q = \dfrac{{ - q\sqrt 2 }}{{\left( {1 + \sqrt 2 } \right)}} \\
$
Hence, value of the charge “Q” such that the net electronic energy of the configuration of the charges shown in the figure is equivalent to zero is $\dfrac{{ - q\sqrt 2 }}{{\left( {1 + \sqrt 2 } \right)}}$.
Hence,option B is correct.
Note: It is to be worth noting here that, the distance between the charges can be found by using the Pythagoras theorem as the charges are situated at the vertices of the isosceles triangles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




