
Three charges$ + 4q$, $Q$ and $q$ are placed in the straight line of $l$ at the point of distances at $0$, $\dfrac{1}{2}$, $1$ respectively. What should be $Q$ in order to make the net force on $q$ to be zero
a. $ - q$
b. $ - 2q$
c. $ - \dfrac{q}{2}$
d. $4q$
Answer
566.4k+ views
Hint: To solve the given problem first, we need to calculate the force between $ + 4q$ and $q$, then we need to calculate the force between $Q$ and $q$. If we add the answers, we will get the resultant force.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{d^2}}}$
Where ${q_1},{q_2}$are two forces, $d$is the distance.
Complete step by step answer:
The values of the three charges are given that is three charges $ + 4q$, $Q$ and $q$ are placed in the straight line of $l$ at the point of distances at $0$, $\dfrac{1}{2}$, $1$. We can represent the given data in the diagram.
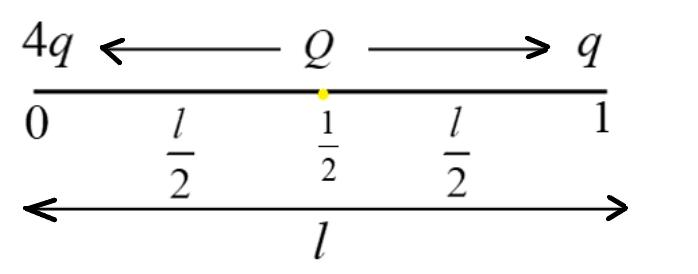
We have three charges$ + 4q$, $Q$ and $q$ that are placed in the distance of $0$,$\dfrac{1}{2}$, $1$ in a straight line.
We can solve the given problem with the help of Coulomb's law. According to Coulomb's law the force or attraction or repulsion between two charged bodies is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. That is,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{d^2}}}$
Where ${q_1},{q_2}$are two forces, $d$ is the distance.
To solve the given problem we need to calculate the force between $ + 4q$ and $q$, then we need to calculate the force between $Q$ and $q$. If we add the answers, we will get the resultant force.
Calculate${F_1}$, that is the force between the $ + 4q$ and $q$. That is,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{d^2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow {F_1} = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{{4q \times q}}{{{l^2}}}$
Calculate ${F_1}$, that is the force between $Q$ and $q$. That is,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{d^2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow {F_2} = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{{Q \times q}}{{\dfrac{l}{2}}}$
Add the two forces we get,
$ \Rightarrow {F_1} + {F_2} = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{{4q \times q}}{{{l^2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{{Q \times q}}{{\dfrac{l}{2}}}$
Simplify the given equation as,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{4{q^2}}}{{{l^2}}} = \dfrac{{4Qq}}{{{l^2}}}$
We can even simplify the equation to get the answer.
$ \Rightarrow q = Q$
We need $Q$ in order to make the net force $q$ to be zero.
$\therefore Q = - q$
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: There are some limitations of the coulomb’s law. It is difficult to implement where the law charges in arbitrary shape because we cannot determine the distance between the charges in such cases.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{d^2}}}$
Where ${q_1},{q_2}$are two forces, $d$is the distance.
Complete step by step answer:
The values of the three charges are given that is three charges $ + 4q$, $Q$ and $q$ are placed in the straight line of $l$ at the point of distances at $0$, $\dfrac{1}{2}$, $1$. We can represent the given data in the diagram.
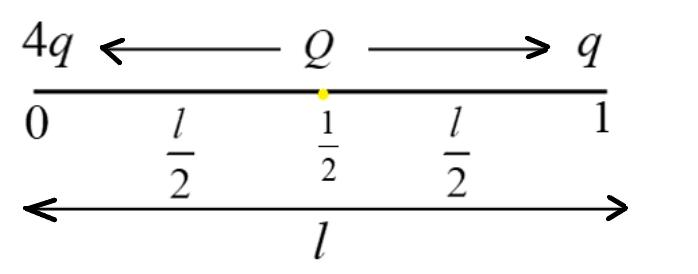
We have three charges$ + 4q$, $Q$ and $q$ that are placed in the distance of $0$,$\dfrac{1}{2}$, $1$ in a straight line.
We can solve the given problem with the help of Coulomb's law. According to Coulomb's law the force or attraction or repulsion between two charged bodies is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. That is,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{d^2}}}$
Where ${q_1},{q_2}$are two forces, $d$ is the distance.
To solve the given problem we need to calculate the force between $ + 4q$ and $q$, then we need to calculate the force between $Q$ and $q$. If we add the answers, we will get the resultant force.
Calculate${F_1}$, that is the force between the $ + 4q$ and $q$. That is,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{d^2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow {F_1} = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{{4q \times q}}{{{l^2}}}$
Calculate ${F_1}$, that is the force between $Q$ and $q$. That is,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{d^2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow {F_2} = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{{Q \times q}}{{\dfrac{l}{2}}}$
Add the two forces we get,
$ \Rightarrow {F_1} + {F_2} = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{{4q \times q}}{{{l^2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{{Q \times q}}{{\dfrac{l}{2}}}$
Simplify the given equation as,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{4{q^2}}}{{{l^2}}} = \dfrac{{4Qq}}{{{l^2}}}$
We can even simplify the equation to get the answer.
$ \Rightarrow q = Q$
We need $Q$ in order to make the net force $q$ to be zero.
$\therefore Q = - q$
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: There are some limitations of the coulomb’s law. It is difficult to implement where the law charges in arbitrary shape because we cannot determine the distance between the charges in such cases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




