
Three arrangements are shown for the complex, ${{[Co(en){{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}B{{r}_{2}}]}^{+}}$. Which one is the wrong statement?
(I)
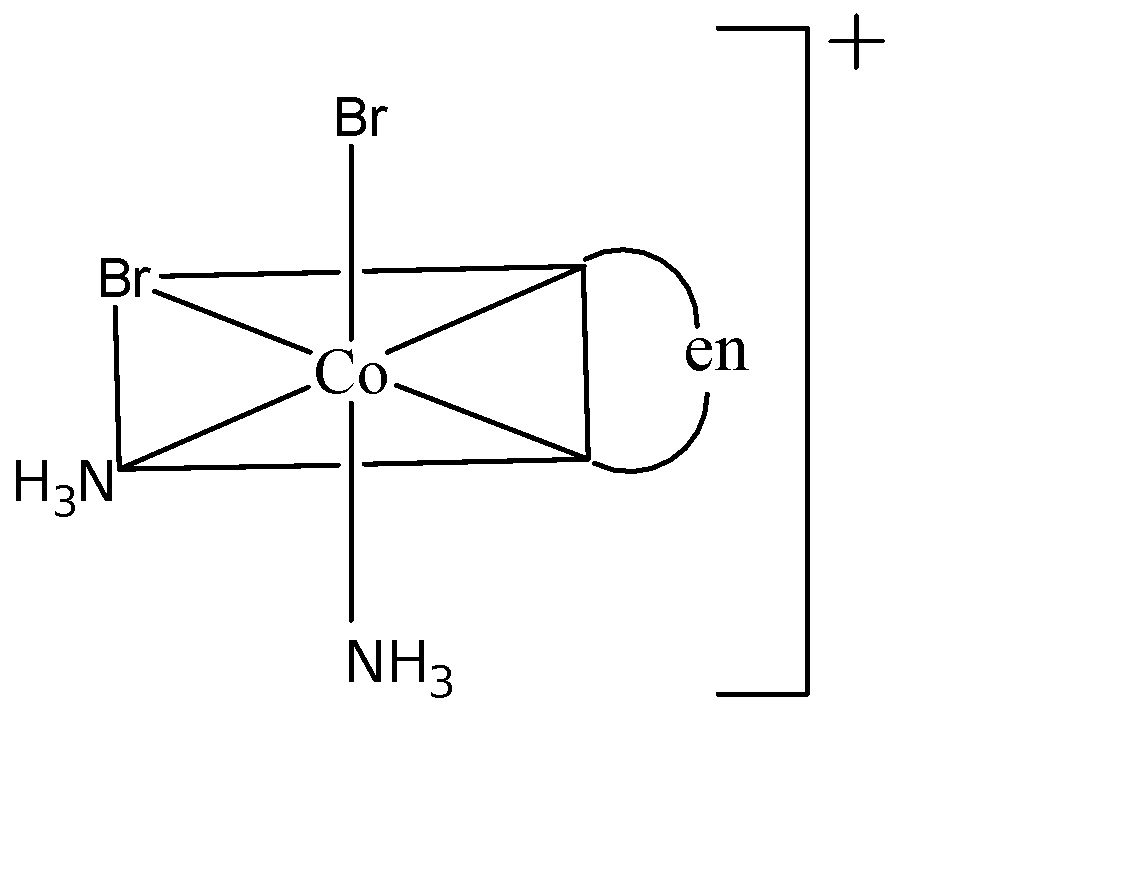
(II)
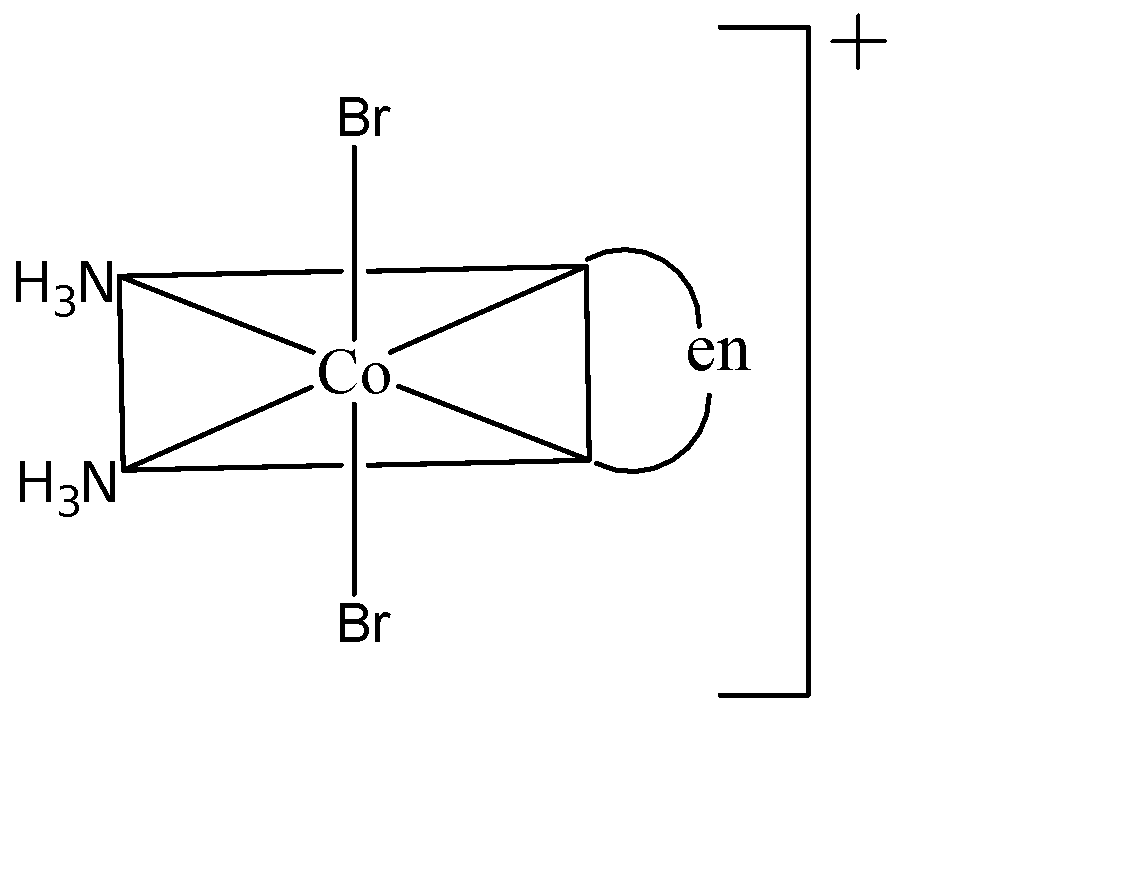
(III)
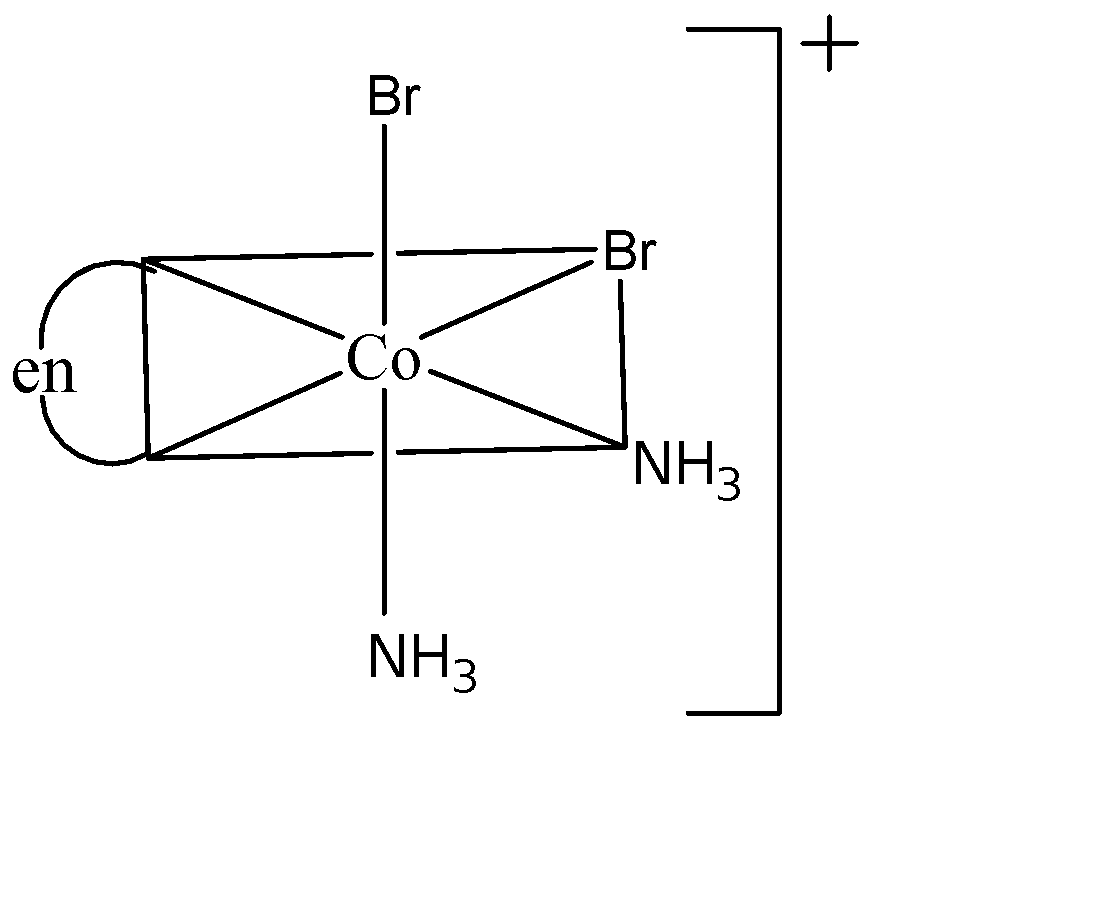
(A) I and II are geometrical isomers
(B) II and III are optical isomers
(C) I and III are optical isomers
(D) II and III are geometrical isomers



Answer
531.6k+ views
Hint: As we know that isomers are the molecules with identical molecular formulas i.e., same number of atoms of each element but different arrangements of atoms in space. First of all try to understand the basic definition of geometrical and optical isomers. Then attempt this question by applying those definitions to the given pairs of the three arrangements given in the question.
Complete answer:
Let us first begin with the definition of geometrical and optical isomers:-
-Geometrical isomers: Molecules are called geometrical isomers when they have the same empirical formula but atoms are arranged in different manner. Also atom to atom bonds can be different. These are usually classified as cis and trans isomers.
-Optical isomers: These are the molecules which have the same molecular formula and atom to atom bonds are also same but the way of their arrangement in space is different. These isomers are generally non-superimposable images of each other and are categorized as enantiomers.
Now let us apply these definitions to the given statements in the question:-
(A) I and II are geometrical isomers: I is cis since both Br atoms are adjacent to each other and II is trans since both Br atoms are opposite to each other. Hence this statement is true.
(B) II and III are optical isomers: Both II and III aren’t non-superimposable images of each other which means they are not optical isomers. Also, II is not optically active. Therefore this statement is false.
(C) I and III are optical isomers: Both I and III non-superimposable images of each other which means they are enantiomeric pairs and hence they are optical isomers. Therefore this statement is true.
(D) II and III are geometrical isomers: III is cis since both Br atoms are adjacent to each other and II is trans since both Br atoms are opposite to each other. Hence this statement is true.
-From the above data we conclude that the wrong statement is (B) II and III are optical isomers.
Note:
Few tips which are helpful in questions of isomerism of coordination compounds:-
-Optical activity can also be checked by finding whether the compound has any symmetry or not. If the compound does not have any symmetry then it is optically active and if the compound has symmetry then it is optically inactive.
-In case of tetrahedral complexes, there is no geometrical isomerism since all the angles are the same between the bonds.
-In case of square planar complexes, there is no optical isomerism since there is always a plane of symmetry.
Complete answer:
Let us first begin with the definition of geometrical and optical isomers:-
-Geometrical isomers: Molecules are called geometrical isomers when they have the same empirical formula but atoms are arranged in different manner. Also atom to atom bonds can be different. These are usually classified as cis and trans isomers.
-Optical isomers: These are the molecules which have the same molecular formula and atom to atom bonds are also same but the way of their arrangement in space is different. These isomers are generally non-superimposable images of each other and are categorized as enantiomers.
Now let us apply these definitions to the given statements in the question:-
(A) I and II are geometrical isomers: I is cis since both Br atoms are adjacent to each other and II is trans since both Br atoms are opposite to each other. Hence this statement is true.
(B) II and III are optical isomers: Both II and III aren’t non-superimposable images of each other which means they are not optical isomers. Also, II is not optically active. Therefore this statement is false.
(C) I and III are optical isomers: Both I and III non-superimposable images of each other which means they are enantiomeric pairs and hence they are optical isomers. Therefore this statement is true.
(D) II and III are geometrical isomers: III is cis since both Br atoms are adjacent to each other and II is trans since both Br atoms are opposite to each other. Hence this statement is true.
-From the above data we conclude that the wrong statement is (B) II and III are optical isomers.
Note:
Few tips which are helpful in questions of isomerism of coordination compounds:-
-Optical activity can also be checked by finding whether the compound has any symmetry or not. If the compound does not have any symmetry then it is optically active and if the compound has symmetry then it is optically inactive.
-In case of tetrahedral complexes, there is no geometrical isomerism since all the angles are the same between the bonds.
-In case of square planar complexes, there is no optical isomerism since there is always a plane of symmetry.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




