
There is an electric field E is the +x direction. If the work done by the electric field in moving a charge of 0.2C through a distance of 2m along a line making an angle ${{60}^{\circ }}$ with the x-axis is 1.0J, what is the value of E in $N{{C}^{-1}}$?
Answer
534k+ views
Hint: In the question it is given that there is a uniform electric field in the positive x direction. The electric field is conservative in nature. This means that work only has to be done in order to move the charge horizontally and not vertically. Hence using the relation between work done to move the charge along the direction of the field and electric field the electric field in the region can be determined.
Formula used:
$\Delta V=\dfrac{W}{q}$
$E=\Delta Vx$
Complete step-by-step answer:
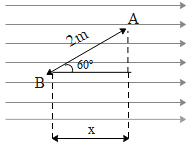
The above figure gives a brief description of moving the charge along the line making an angle ${{60}^{\circ }}$ with the x-axis i.e. from point B to A. The electric field is uniform. Therefore when charge ‘q’ is moved from B to A, there would be a change in potential difference $\Delta V$ . Therefore the work done ‘W’ in moving the charge from B to A is given by,
$\begin{align}
& \Delta V=\dfrac{W}{q} \\
& \because W=1.0J,\text{ }q=0.2C \\
& \Rightarrow \Delta V=\dfrac{1J}{0.2C}=5V \\
\end{align}$
Let us say we move a charge across a potential difference of $\Delta V$ in the direction of the field by a distance ‘x’. then the electric field ‘E’ is given by,
$E=\Delta Vx....(1)$
From the above figure using the definition of cosine the side ‘x’ is equal to,
$\begin{align}
& \cos {{60}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{x}{2m} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{2m}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
& \therefore x=1m \\
\end{align}$
Hence from equation 1, the electric field of the region is equal to,
$\begin{align}
& E=\dfrac{\Delta V}{x} \\
& \Rightarrow E=5V/(1m) \\
& \therefore E=5V/m=5Nm{{C}^{-1}}/m=5N{{C}^{-1}} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore the electric field in the space is equal to $5N{{C}^{-1}}$
Note: The electric field in a region is given as a negative gradient of the potential. In the above solution we have not considered the negative sign as the work done in moving a charge from higher to lower potential is negative. Therefore the two signs will adjust the mathematical nature of the equation.
Formula used:
$\Delta V=\dfrac{W}{q}$
$E=\Delta Vx$
Complete step-by-step answer:

The above figure gives a brief description of moving the charge along the line making an angle ${{60}^{\circ }}$ with the x-axis i.e. from point B to A. The electric field is uniform. Therefore when charge ‘q’ is moved from B to A, there would be a change in potential difference $\Delta V$ . Therefore the work done ‘W’ in moving the charge from B to A is given by,
$\begin{align}
& \Delta V=\dfrac{W}{q} \\
& \because W=1.0J,\text{ }q=0.2C \\
& \Rightarrow \Delta V=\dfrac{1J}{0.2C}=5V \\
\end{align}$
Let us say we move a charge across a potential difference of $\Delta V$ in the direction of the field by a distance ‘x’. then the electric field ‘E’ is given by,
$E=\Delta Vx....(1)$
From the above figure using the definition of cosine the side ‘x’ is equal to,
$\begin{align}
& \cos {{60}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{x}{2m} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{2m}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
& \therefore x=1m \\
\end{align}$
Hence from equation 1, the electric field of the region is equal to,
$\begin{align}
& E=\dfrac{\Delta V}{x} \\
& \Rightarrow E=5V/(1m) \\
& \therefore E=5V/m=5Nm{{C}^{-1}}/m=5N{{C}^{-1}} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore the electric field in the space is equal to $5N{{C}^{-1}}$
Note: The electric field in a region is given as a negative gradient of the potential. In the above solution we have not considered the negative sign as the work done in moving a charge from higher to lower potential is negative. Therefore the two signs will adjust the mathematical nature of the equation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




