
The wings of an insect and a bat exhibit
A. Homology
B. Analogy
C. Atavism
D. Connecting link
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: Comparative study of the morphology and anatomy of animals and plants show that certain structural features are basically similar.
These features include body organization, gradual modification, homologous organs, and analogous organs, connecting links, vestigial organs, and atavism.
Complete answer: The organs which have the same function and superficially alike but are quite different in fundamental structure and embryonic origins are called analogous organs.
1. The analogy is based on convergent evolution.
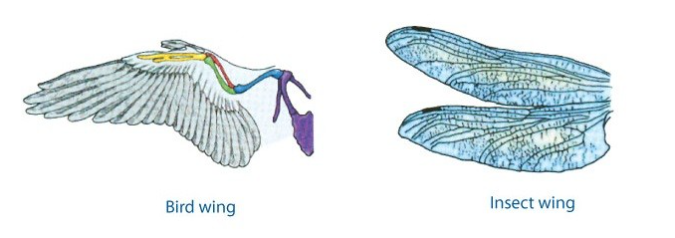
2. Insect and birdwings: The wing of an insect and the wing of a bird are analogous organs. Both these organs are used for flying in the air, but they are very different in structure.
3. An insect wing is an extension of the integument, whereas s birdwing is formed of limb bones covered with flesh, skin, and feathers.
4. The adaptations to flying rather than to inheritance from a common ancestor.
Each has evolved from a separate ancestral population as a means of a more efficient mode of locomotion. Similarly developed in distantly related groups as an adaptation for the same is called analogy, or convergent evolution
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional Information: Homologous organs: The organs of different species of common descent which look different and perform a different function, but have a similar basic structure similar topographic relationship, and similar embryonic origin are called homologous organs.
Connecting link: The living organisms which possess characters of two different groups of organisms are known as the connecting links.
Vestigial organs: The organs which occur in reduced form and are useless to the possession, but are homologous to fully developed, functional organs of related animals are called vestigial organs.
Atavism: Atavism, also called reversion or throwback, is the reappearance of a certain ancestral, not parental, a structure which have either completely disappeared or greatly reduced.
Note: Other examples of analogy include:
1. Fins and flippers: The pectoral fins of fishes and the flippers of dolphins are flattened organs used for swimming.
2. Cephalopod and vertebrate eyes: Eyes of cephalopods (octopus, sepia) and vertebrates have many morphological features in common besides the same function.
3. Leaves and cladodes: Leaves of the plant and stem modification called cladodes of Rucus are also analogous organs.
These features include body organization, gradual modification, homologous organs, and analogous organs, connecting links, vestigial organs, and atavism.
Complete answer: The organs which have the same function and superficially alike but are quite different in fundamental structure and embryonic origins are called analogous organs.
1. The analogy is based on convergent evolution.
2. Insect and birdwings: The wing of an insect and the wing of a bird are analogous organs. Both these organs are used for flying in the air, but they are very different in structure.
3. An insect wing is an extension of the integument, whereas s birdwing is formed of limb bones covered with flesh, skin, and feathers.
4. The adaptations to flying rather than to inheritance from a common ancestor.
Each has evolved from a separate ancestral population as a means of a more efficient mode of locomotion. Similarly developed in distantly related groups as an adaptation for the same is called analogy, or convergent evolution

So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional Information: Homologous organs: The organs of different species of common descent which look different and perform a different function, but have a similar basic structure similar topographic relationship, and similar embryonic origin are called homologous organs.
Connecting link: The living organisms which possess characters of two different groups of organisms are known as the connecting links.
Vestigial organs: The organs which occur in reduced form and are useless to the possession, but are homologous to fully developed, functional organs of related animals are called vestigial organs.
Atavism: Atavism, also called reversion or throwback, is the reappearance of a certain ancestral, not parental, a structure which have either completely disappeared or greatly reduced.
Note: Other examples of analogy include:
1. Fins and flippers: The pectoral fins of fishes and the flippers of dolphins are flattened organs used for swimming.
2. Cephalopod and vertebrate eyes: Eyes of cephalopods (octopus, sepia) and vertebrates have many morphological features in common besides the same function.
3. Leaves and cladodes: Leaves of the plant and stem modification called cladodes of Rucus are also analogous organs.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




