
The wavelength of red light is \[7.5\times {{10}^{-5}}cm\] and that of the blue light is \[5.0\times {{10}^{-5}}cm\]. The value of n for which \[{{(n+1)}^{th}}\] blue bright band coincides with the \[{{n}^{th}}\]red band is–
A) 8
B) 4
C) 2
D) 1
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: We need to find the point on the screen when two lights with different wavelengths coincide at a point on the screen after interference. We can equate the distances from the origin of the screen to both colours to find the required fringe order.
Complete answer:
Let us consider the interference of two white light beams in the Young’s double slit experiment. We know that after interference of two beams from a white light source interfere and produce spectrum on the screen.
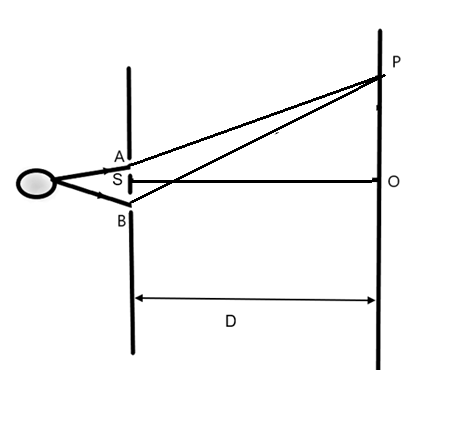
We can assume a point on the screen at a distance D from the slits of slit width ‘d’ to be the point where the blue and red colour bands coincide for the first time. Let the fringe order for blue be ‘m’ and the fringe order for red be ‘n’ at the point.
But it is given that the point we require has to be the one where the \[{{(n+1)}^{th}}\] band of blue light and \[{{n}^{th}}\] band of red light coincide. Let this be the point P.
Now, we know the formula to calculate the distance OP in terms of the wavelengths of both blue and red light as –
\[\begin{align}
& O{{P}_{blue}}=\dfrac{(n+1){{\lambda }_{blue}}D}{d} \\
& \text{and,} \\
& O{{P}_{red}}=\dfrac{n{{\lambda }_{red}}D}{d} \\
\end{align}\]
But both the distances are same and we can equate them as –
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \text{ }\dfrac{(n+1){{\lambda }_{blue}}D}{d}=\dfrac{n{{\lambda }_{red}}D}{d} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }(n+1){{\lambda }_{blue}}=n{{\lambda }_{red}} \\
\end{align}\]
Given that,
\[\begin{align}
& {{\lambda }_{red}}=7.5\times {{10}^{-5}}cm \\
& {{\lambda }_{blue}}=5.0\times {{10}^{-5}}cm \\
\end{align}\]
Substituting these in the above relation gives –
\[\begin{align}
& \text{ }(n+1){{\lambda }_{blue}}=n{{\lambda }_{red}} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }\dfrac{(n+1)}{n}=\dfrac{{{\lambda }_{red}}}{{{\lambda }_{blue}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }\dfrac{1}{n}=\dfrac{{{\lambda }_{red}}}{{{\lambda }_{blue}}}-1 \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }n=\dfrac{{{\lambda }_{blue}}}{{{\lambda }_{red}}-{{\lambda }_{blue}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }n=\dfrac{5.0\times {{10}^{-7}}}{7.5\times {{10}^{-7}}-5.0\times {{10}^{-7}}} \\
& \therefore \text{ }n=2 \\
\end{align}\]
From the above calculations, we find that the fringe order of red band is 2 and that of blue is 3.
The required solution is \[n=2\]
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
The spectrum formed by the interference pattern can be theoretically determined using the similar method we have used here. The dependence of the wavelength on the pattern of the spectrum in the interference is relevant from these observations.
Complete answer:
Let us consider the interference of two white light beams in the Young’s double slit experiment. We know that after interference of two beams from a white light source interfere and produce spectrum on the screen.

We can assume a point on the screen at a distance D from the slits of slit width ‘d’ to be the point where the blue and red colour bands coincide for the first time. Let the fringe order for blue be ‘m’ and the fringe order for red be ‘n’ at the point.
But it is given that the point we require has to be the one where the \[{{(n+1)}^{th}}\] band of blue light and \[{{n}^{th}}\] band of red light coincide. Let this be the point P.
Now, we know the formula to calculate the distance OP in terms of the wavelengths of both blue and red light as –
\[\begin{align}
& O{{P}_{blue}}=\dfrac{(n+1){{\lambda }_{blue}}D}{d} \\
& \text{and,} \\
& O{{P}_{red}}=\dfrac{n{{\lambda }_{red}}D}{d} \\
\end{align}\]
But both the distances are same and we can equate them as –
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \text{ }\dfrac{(n+1){{\lambda }_{blue}}D}{d}=\dfrac{n{{\lambda }_{red}}D}{d} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }(n+1){{\lambda }_{blue}}=n{{\lambda }_{red}} \\
\end{align}\]
Given that,
\[\begin{align}
& {{\lambda }_{red}}=7.5\times {{10}^{-5}}cm \\
& {{\lambda }_{blue}}=5.0\times {{10}^{-5}}cm \\
\end{align}\]
Substituting these in the above relation gives –
\[\begin{align}
& \text{ }(n+1){{\lambda }_{blue}}=n{{\lambda }_{red}} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }\dfrac{(n+1)}{n}=\dfrac{{{\lambda }_{red}}}{{{\lambda }_{blue}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }\dfrac{1}{n}=\dfrac{{{\lambda }_{red}}}{{{\lambda }_{blue}}}-1 \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }n=\dfrac{{{\lambda }_{blue}}}{{{\lambda }_{red}}-{{\lambda }_{blue}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }n=\dfrac{5.0\times {{10}^{-7}}}{7.5\times {{10}^{-7}}-5.0\times {{10}^{-7}}} \\
& \therefore \text{ }n=2 \\
\end{align}\]
From the above calculations, we find that the fringe order of red band is 2 and that of blue is 3.
The required solution is \[n=2\]
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
The spectrum formed by the interference pattern can be theoretically determined using the similar method we have used here. The dependence of the wavelength on the pattern of the spectrum in the interference is relevant from these observations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




