
The wall-thickening material in tracheids and vessels are
A. Cutin and suberin
B. Cellulose and cutin
C. Suberin and cellulose
D. Lignin and cellulose
Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint:The cell walls of plant cells such as tracheids and vessels (elements of xylem) necessarily undergo additional secondary thickening or deposition of new hard materials. This hard thickening material is secreted by cytoplasm.
Complete answer: The cells cease to increase in size and become mature. At this stage, the tracheids and vessels undergo modification depending on the specialized function they have to perform. During this entire process of their maturation, the cells undergo additional or secondary thickening deposition of new materials such as cellulose, lignin, suberin, cutin, etc.; vessel elements and tracheids are no exception. The cells of certain parts of the plant including the pericycle, phloem, as well as xylem, undergo heavy thickening of their walls. The thickening materials of the cells are secreted by the protoplasm. These materials, (typically lignin and cellulose) are deposited within the cell walls in such a manner that their cell walls become stratified in appearance. The cells which ultimately develop into vessels, tracheids, and fibers show the thickening of the cell wall in prominent ways. This thickening takes place due to the deposition of a hard substance, called lignin, on the inner surface of the cell wall.
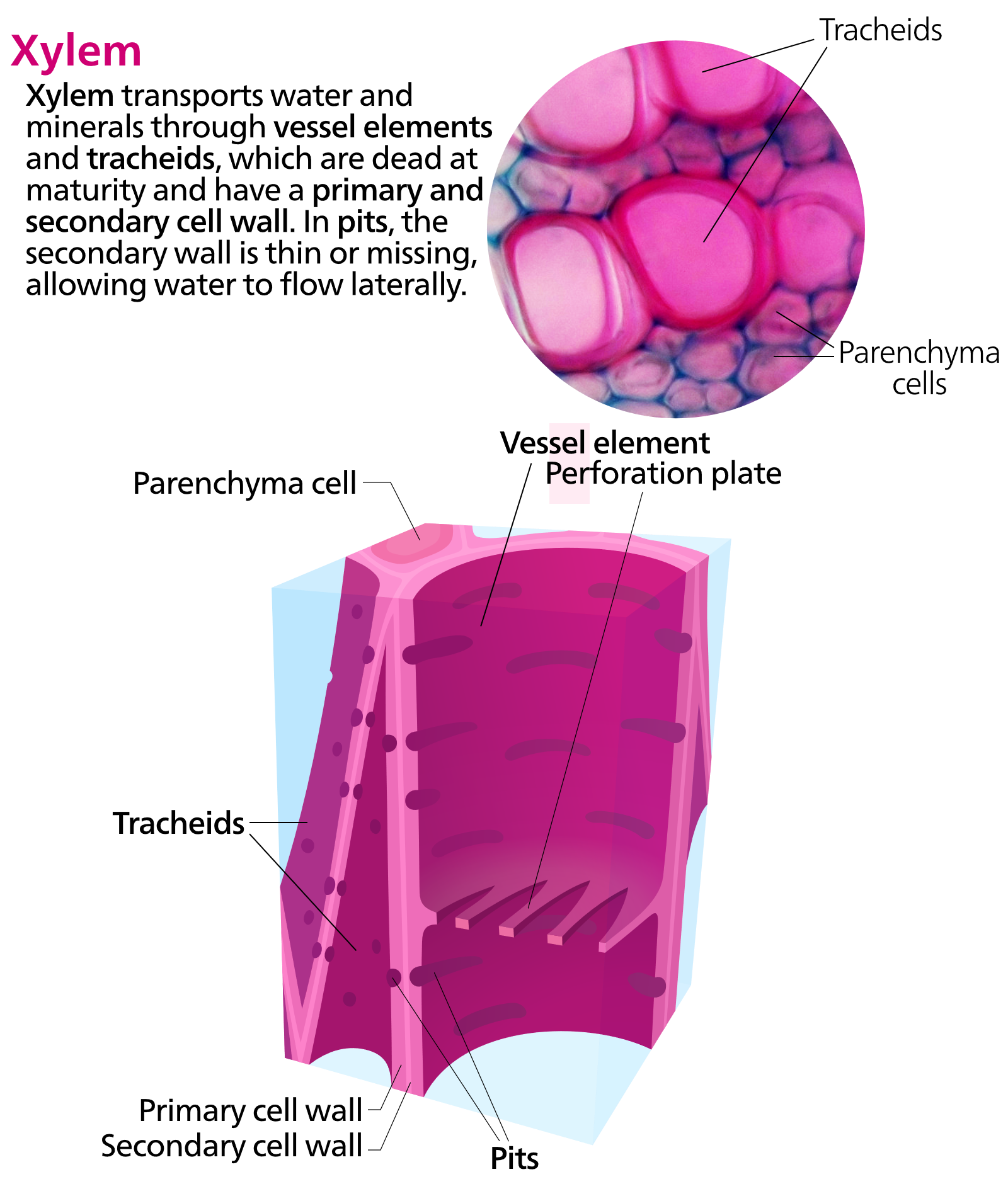
Thus, the correct answer is option D. Lignin and cellulose.
Note:It is noteworthy that usually the thickening material (e.g., lignin) of the secondary wall is not laid down in uniform thickness but it may form special patterns such as annular, spiral, scalariform, reticulate, and pitted.
Complete answer: The cells cease to increase in size and become mature. At this stage, the tracheids and vessels undergo modification depending on the specialized function they have to perform. During this entire process of their maturation, the cells undergo additional or secondary thickening deposition of new materials such as cellulose, lignin, suberin, cutin, etc.; vessel elements and tracheids are no exception. The cells of certain parts of the plant including the pericycle, phloem, as well as xylem, undergo heavy thickening of their walls. The thickening materials of the cells are secreted by the protoplasm. These materials, (typically lignin and cellulose) are deposited within the cell walls in such a manner that their cell walls become stratified in appearance. The cells which ultimately develop into vessels, tracheids, and fibers show the thickening of the cell wall in prominent ways. This thickening takes place due to the deposition of a hard substance, called lignin, on the inner surface of the cell wall.

Thus, the correct answer is option D. Lignin and cellulose.
Note:It is noteworthy that usually the thickening material (e.g., lignin) of the secondary wall is not laid down in uniform thickness but it may form special patterns such as annular, spiral, scalariform, reticulate, and pitted.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




