
The vertices of $\Delta ABC$ are $A(4,6),B(1,5),C(7,2)$. A line is drawn to intersect sides $AB$ and $AC$ at $D$ and $E$ respectively such that $\dfrac{{AD}}{{AB}} = \dfrac{{AE}}{{AC}} = \dfrac{1}{4}$. Calculate the area of the $\Delta ADE$ and compare it with the area of $\Delta ABC$.

Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: Since $\dfrac{{AD}}{{AB}} = \dfrac{{AE}}{{AC}} = \dfrac{1}{4}$, therefore by solving this equation and then by applying the section formula we will get the vertices and we can find the area of $\Delta ADE$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
From the above equation we get-
$\dfrac{{AE}}{{AC}} = \dfrac{1}{4}$………..(i)
$\dfrac{{AD}}{{AB}} = \dfrac{1}{4}$………..(ii)
By solving equation (i) we get-
$4AE = AC$
From the diagram we can easily understood that $AC = AE + EC$
Now we can write, $4AE = AE + EC$
Taking RHS \[{\text{AE}}\]has LHS, we get
$4AE - AE = EC$
On subtracting we get,
$3AE = EC$
We can write the above step in fraction type,
$\dfrac{{AE}}{{EC}} = \dfrac{1}{3}$
So it is clear the point $E$ divides the line $AC$ in the ratio of $1:3$ internally.
Now, we have to find the coordinates of E, by using section formula,
That is $\left( {\dfrac{{{m_1}{x_2} + {m_2}{x_1}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}},\dfrac{{{m_1}{y_2} + {m_2}{y_1}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}}} \right)$
Here $\left( {{{\text{m}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{:}}{{\text{m}}_{\text{2}}}} \right) = \left( {1:3} \right)$
$\left( {{x_{\text{1}}}{\text{,}}{{\text{y}}_1}} \right) = \left( {4,6} \right)$
$\left( {{x_2}{\text{,}}{{\text{y}}_2}} \right) = \left( {7,2} \right)$
Coordinates of $E = \left( {\dfrac{{1(7) + (3)(4)}}{{1 + 3}},\dfrac{{1(2) + 3(6)}}{{1 + 3}}} \right)$
On some simplification we get,
$ = \left( {\dfrac{{7 + 12}}{4},\dfrac{{2 + 18}}{4}} \right)$
Let us add the numerator term we get,
$ = \left( {\dfrac{{19}}{4},\dfrac{{20}}{4}} \right)$
Divided the terms we get,
$ = {\text{E}}\left( {\dfrac{{19}}{4},5} \right)$
Also we have to find Coordinates of $D$by using the section formula,
Here $\left( {{{\text{m}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{:}}{{\text{m}}_{\text{2}}}} \right) = \left( {1:3} \right)$
$\left( {{x_{\text{1}}}{\text{,}}{{\text{y}}_1}} \right) = \left( {4,6} \right)$
$\left( {{x_2}{\text{,}}{{\text{y}}_2}} \right) = \left( {1,5} \right)$
Putting the values in the section formula we can write,
Coordinates of $D$$ = \left( {\dfrac{{1(1) + 3(4)}}{{1 + 3}},\dfrac{{1(5) + 3(6)}}{{1 + 3}}} \right)$
On some simplification we get,
$ = \left( {\dfrac{{1 + 12}}{4},\dfrac{{5 + 18}}{4}} \right)$
Let us add the numerator term we get,
$ = D\left( {\dfrac{{13}}{4},\dfrac{{23}}{4}} \right)$
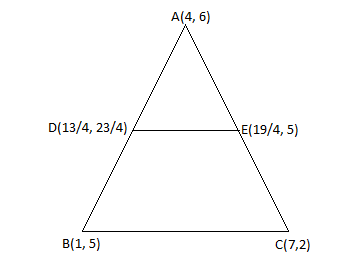
Here the diagram for the vertices of the D and E as follows
Now, we have to find out the area of ∆ADE and ∆ABC, we will apply the formula of area of triangle of vertices, i.e., $\dfrac{1}{2}[{x_1}({y_2} - {y_3}) + {x_2}({y_3} - {y_1}) + {x_3}({y_1} - {y_2})]$
First we find that the area of triangle \[\Delta {\text{ADE}}\]
Here the vertices of the \[\Delta {\text{ADE}}\],
$\left( {{x_{\text{1}}}{\text{,}}{{\text{y}}_1}} \right) = \left( {4,6} \right)$
$\left( {{x_2}{\text{,}}{{\text{y}}_2}} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{13}}{4},\dfrac{{23}}{4}} \right)$
$\left( {{x_3}{\text{,}}{{\text{y}}_3}} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{19}}{4},5} \right)$
Substitute the value in the formula for area of triangle, we get
$ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {4\left( {\dfrac{{23}}{4} - \dfrac{{20}}{4}} \right) + \dfrac{{13}}{4}\left( {\dfrac{{20}}{4} - 6} \right) + \dfrac{{19}}{4}\left( {6 - \dfrac{{23}}{4}} \right)} \right]$
On some simplification we get,
$ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {4\left( {\dfrac{3}{4}} \right) + \dfrac{{13}}{4}\left( {\dfrac{{20 - 24}}{4}} \right) + \dfrac{{19}}{4}\left( {\dfrac{{24 - 23}}{4}} \right)} \right]$
Let us subtract the terms we get,
$ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {4\left( {\dfrac{3}{4}} \right) + \dfrac{{13}}{4}\left( { - \dfrac{4}{4}} \right) + \dfrac{{19}}{4}\left( {\dfrac{1}{4}} \right)} \right]$
On multiply the terms we get,
$ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {3 - \dfrac{{52}}{{16}} + \dfrac{{19}}{{16}}} \right)$
Taking the LCM of the above terms we get,
$ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {\dfrac{{48 - 52 + 19}}{{16}}} \right)$
On some simplification we get,
$ = \dfrac{{15}}{{32}}$
Also we have to find area of triangle \[\Delta {\text{ABC}}\]
Here the vertices are,
$\left( {{x_{\text{1}}}{\text{,}}{{\text{y}}_1}} \right) = \left( {4,6} \right)$
$\left( {{x_2}{\text{,}}{{\text{y}}_2}} \right) = \left( {1,5} \right)$
$\left( {{x_3}{\text{,}}{{\text{y}}_3}} \right) = \left( {7,2} \right)$
Substitute the value in the formula for area of triangle, we get
$ = \dfrac{1}{2}[4(5 - 2) + 1(2 - 6) + 7(6 - 5)]$
On some simplification we get,
$ = \dfrac{1}{2}[12 - 4 + 7]$
On adding the terms we get,
$ = \dfrac{{15}}{2}$
So, \[\dfrac{{{\text{Area of Triangle ADE}}}}{{{\text{Area of Triangle ABC}}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{15}}{{32}}}}{{\dfrac{{15}}{2}}}\]
$ = \dfrac{{15}}{{32}}x\dfrac{2}{{15}}$
$\dfrac{{{\text{Area of Triangle ADE}}}}{{{\text{Area of Triangle ABC}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{16}}$
Also hence Area of $\Delta ADE$=$\dfrac{{15}}{{32}}$.
Note: In this type of problems you need to solve the equation at the very first when in the question it is mentioned that a line has intersected the sides of the triangle at the point D and E respectively.
It is to be noted that when any point divides the line internally then the formula which is applicable is $\left( {\dfrac{{{m_1}{x_2} + {m_2}{x_1}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}},\dfrac{{{m_1}{y_2} + {m_2}{y_1}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}}} \right)$, but if the point divides the line externally then the formula which is applicable is $\left( {\dfrac{{{m_1}{x_2} - {m_2}{x_1}}}{{{m_1} - {m_2}}},\dfrac{{{m_1}{y_2} - {m_2}{y_1}}}{{{m_1} - {m_2}}}} \right)$
The key point in these questions is to check whether the point is dividing the line internally or externally or it is the midpoint.
Complete step-by-step answer:
From the above equation we get-
$\dfrac{{AE}}{{AC}} = \dfrac{1}{4}$………..(i)
$\dfrac{{AD}}{{AB}} = \dfrac{1}{4}$………..(ii)
By solving equation (i) we get-
$4AE = AC$
From the diagram we can easily understood that $AC = AE + EC$
Now we can write, $4AE = AE + EC$
Taking RHS \[{\text{AE}}\]has LHS, we get
$4AE - AE = EC$
On subtracting we get,
$3AE = EC$
We can write the above step in fraction type,
$\dfrac{{AE}}{{EC}} = \dfrac{1}{3}$
So it is clear the point $E$ divides the line $AC$ in the ratio of $1:3$ internally.
Now, we have to find the coordinates of E, by using section formula,
That is $\left( {\dfrac{{{m_1}{x_2} + {m_2}{x_1}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}},\dfrac{{{m_1}{y_2} + {m_2}{y_1}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}}} \right)$
Here $\left( {{{\text{m}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{:}}{{\text{m}}_{\text{2}}}} \right) = \left( {1:3} \right)$
$\left( {{x_{\text{1}}}{\text{,}}{{\text{y}}_1}} \right) = \left( {4,6} \right)$
$\left( {{x_2}{\text{,}}{{\text{y}}_2}} \right) = \left( {7,2} \right)$
Coordinates of $E = \left( {\dfrac{{1(7) + (3)(4)}}{{1 + 3}},\dfrac{{1(2) + 3(6)}}{{1 + 3}}} \right)$
On some simplification we get,
$ = \left( {\dfrac{{7 + 12}}{4},\dfrac{{2 + 18}}{4}} \right)$
Let us add the numerator term we get,
$ = \left( {\dfrac{{19}}{4},\dfrac{{20}}{4}} \right)$
Divided the terms we get,
$ = {\text{E}}\left( {\dfrac{{19}}{4},5} \right)$
Also we have to find Coordinates of $D$by using the section formula,
Here $\left( {{{\text{m}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{:}}{{\text{m}}_{\text{2}}}} \right) = \left( {1:3} \right)$
$\left( {{x_{\text{1}}}{\text{,}}{{\text{y}}_1}} \right) = \left( {4,6} \right)$
$\left( {{x_2}{\text{,}}{{\text{y}}_2}} \right) = \left( {1,5} \right)$
Putting the values in the section formula we can write,
Coordinates of $D$$ = \left( {\dfrac{{1(1) + 3(4)}}{{1 + 3}},\dfrac{{1(5) + 3(6)}}{{1 + 3}}} \right)$
On some simplification we get,
$ = \left( {\dfrac{{1 + 12}}{4},\dfrac{{5 + 18}}{4}} \right)$
Let us add the numerator term we get,
$ = D\left( {\dfrac{{13}}{4},\dfrac{{23}}{4}} \right)$
Here the diagram for the vertices of the D and E as follows

Now, we have to find out the area of ∆ADE and ∆ABC, we will apply the formula of area of triangle of vertices, i.e., $\dfrac{1}{2}[{x_1}({y_2} - {y_3}) + {x_2}({y_3} - {y_1}) + {x_3}({y_1} - {y_2})]$
First we find that the area of triangle \[\Delta {\text{ADE}}\]
Here the vertices of the \[\Delta {\text{ADE}}\],
$\left( {{x_{\text{1}}}{\text{,}}{{\text{y}}_1}} \right) = \left( {4,6} \right)$
$\left( {{x_2}{\text{,}}{{\text{y}}_2}} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{13}}{4},\dfrac{{23}}{4}} \right)$
$\left( {{x_3}{\text{,}}{{\text{y}}_3}} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{19}}{4},5} \right)$
Substitute the value in the formula for area of triangle, we get
$ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {4\left( {\dfrac{{23}}{4} - \dfrac{{20}}{4}} \right) + \dfrac{{13}}{4}\left( {\dfrac{{20}}{4} - 6} \right) + \dfrac{{19}}{4}\left( {6 - \dfrac{{23}}{4}} \right)} \right]$
On some simplification we get,
$ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {4\left( {\dfrac{3}{4}} \right) + \dfrac{{13}}{4}\left( {\dfrac{{20 - 24}}{4}} \right) + \dfrac{{19}}{4}\left( {\dfrac{{24 - 23}}{4}} \right)} \right]$
Let us subtract the terms we get,
$ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {4\left( {\dfrac{3}{4}} \right) + \dfrac{{13}}{4}\left( { - \dfrac{4}{4}} \right) + \dfrac{{19}}{4}\left( {\dfrac{1}{4}} \right)} \right]$
On multiply the terms we get,
$ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {3 - \dfrac{{52}}{{16}} + \dfrac{{19}}{{16}}} \right)$
Taking the LCM of the above terms we get,
$ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {\dfrac{{48 - 52 + 19}}{{16}}} \right)$
On some simplification we get,
$ = \dfrac{{15}}{{32}}$
Also we have to find area of triangle \[\Delta {\text{ABC}}\]
Here the vertices are,
$\left( {{x_{\text{1}}}{\text{,}}{{\text{y}}_1}} \right) = \left( {4,6} \right)$
$\left( {{x_2}{\text{,}}{{\text{y}}_2}} \right) = \left( {1,5} \right)$
$\left( {{x_3}{\text{,}}{{\text{y}}_3}} \right) = \left( {7,2} \right)$
Substitute the value in the formula for area of triangle, we get
$ = \dfrac{1}{2}[4(5 - 2) + 1(2 - 6) + 7(6 - 5)]$
On some simplification we get,
$ = \dfrac{1}{2}[12 - 4 + 7]$
On adding the terms we get,
$ = \dfrac{{15}}{2}$
So, \[\dfrac{{{\text{Area of Triangle ADE}}}}{{{\text{Area of Triangle ABC}}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{15}}{{32}}}}{{\dfrac{{15}}{2}}}\]
$ = \dfrac{{15}}{{32}}x\dfrac{2}{{15}}$
$\dfrac{{{\text{Area of Triangle ADE}}}}{{{\text{Area of Triangle ABC}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{16}}$
Also hence Area of $\Delta ADE$=$\dfrac{{15}}{{32}}$.
Note: In this type of problems you need to solve the equation at the very first when in the question it is mentioned that a line has intersected the sides of the triangle at the point D and E respectively.
It is to be noted that when any point divides the line internally then the formula which is applicable is $\left( {\dfrac{{{m_1}{x_2} + {m_2}{x_1}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}},\dfrac{{{m_1}{y_2} + {m_2}{y_1}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}}} \right)$, but if the point divides the line externally then the formula which is applicable is $\left( {\dfrac{{{m_1}{x_2} - {m_2}{x_1}}}{{{m_1} - {m_2}}},\dfrac{{{m_1}{y_2} - {m_2}{y_1}}}{{{m_1} - {m_2}}}} \right)$
The key point in these questions is to check whether the point is dividing the line internally or externally or it is the midpoint.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




