
The vertical angle of a cone of maximum volume and given slant height is?
A. \[{\tan ^{ - 1}}\sqrt 2 \]
B. \[2{\tan ^{ - 1}}\sqrt 2 \]
C. \[{\tan ^{ - 1}}\sqrt 3 \]
D. \[2{\tan ^{ - 1}}\sqrt 3 \]
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: To find the vertical angle of a cone, we need to establish a relation between the radius and height of the cone to its slant height. We express the height and radius of the cone in terms of its slant height using the formula of volume of a cone and by applying Pythagoras theorem on one half of the cone and making a relation. Maximum volume is obtained by differentiating the volume.
Complete step by step answer:
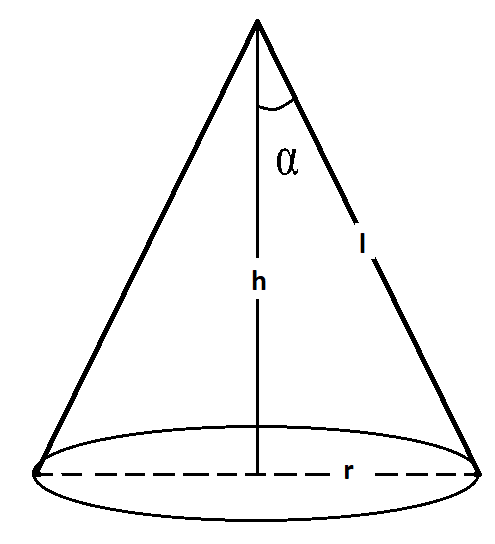
Given that,
Let r be the radius and h be the height and $\alpha $ be the vertical angle of the cone.
Slant height, l is given, i.e.
l is constant.
From the figure, we can see that
By applying Pythagoras theorem in $\vartriangle OAB$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {AB} \right)^2} = {\left( {OA} \right)^2} + {\left( {OB} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {l^2} = {h^2} + {r^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {r^2} = {l^2} - {h^2}$ ……… (i)
We have to show that the volume of the cone is maximum and find the vertical angle $\alpha $
We know that,
Volume of the cone, V = $\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h$
Putting the value of r from equation (i),
\[ \Rightarrow V = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( {{l^2} - {h^2}} \right)h\] ………… (ii)
Here, we can see that slant height, l is constant (given), so we will differentiate equation (ii) both sides with respect to h, we will get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dV}}{{dh}} = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi \dfrac{d}{{dh}}\left( {{l^2}h - {h^3}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dV}}{{dh}} = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( {{l^2} - 3{h^2}} \right)\] ……… (iii)
As we know that,
$\dfrac{{dV}}{{dh}} = 0$ [for maxima and minima].
So, by equating $\dfrac{{dV}}{{dh}} = 0$, we will get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( {{l^2} - 3{h^2}} \right) = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow {l^2} = 3{h^2}\]
Putting the value of l here, we will get
\[ \Rightarrow {h^2} + {r^2} = 3{h^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {r^2} = 2{h^2}\]
Taking square root on both sides, we will get
\[ \Rightarrow r = \sqrt 2 h\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{r}{h} = \sqrt 2 \] ……… (iv)
From $\vartriangle OAB$, we can see that
$ \Rightarrow \tan \alpha = \dfrac{{OB}}{{OA}}$
$ \Rightarrow \tan \alpha = \dfrac{r}{h}$
Putting this value in equation (iv), we will get
$ \Rightarrow \tan \alpha = \sqrt 2 $
\[ \Rightarrow \alpha = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\sqrt 2 } \right)\]
Hence, we get vertical angle, \[\alpha = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\sqrt 2 } \right)\]
Now, from equation (iii), we have
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dV}}{{dh}} = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( {{l^2} - 3{h^2}} \right)\]
Again, differentiate equation (iii) both sides with respect to h, we will get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}V}}{{d{h^2}}} = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi \dfrac{d}{{dh}}\left( {{l^2} - 3{h^2}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}V}}{{d{h^2}}} = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( { - 6h} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}V}}{{d{h^2}}} = - 2\pi h\]
Here we can see that, \[\dfrac{{{d^2}V}}{{d{h^2}}} = - 2\pi h < 0\]
So, we can say that the volume of the cone, V is maximum.
Hence, the vertical angle of the cone with maximum volume and given slant height is \[\alpha = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\sqrt 2 } \right)\]
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: In order to solve this type of questions the key is to know the formula of volume of a cone and the concept of Pythagoras theorem. Using these two we establish a relation between its length, radius and slant height.
It is an important step to know that the differentiation of a term gives its maximum value. Also, the basic differentiation forms of algebraic terms to be known.
To know the value of trigonometric and inverse trigonometric terms of tan function we refer to its trigonometric table.
Complete step by step answer:

Given that,
Let r be the radius and h be the height and $\alpha $ be the vertical angle of the cone.
Slant height, l is given, i.e.
l is constant.
From the figure, we can see that
By applying Pythagoras theorem in $\vartriangle OAB$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {AB} \right)^2} = {\left( {OA} \right)^2} + {\left( {OB} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {l^2} = {h^2} + {r^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {r^2} = {l^2} - {h^2}$ ……… (i)
We have to show that the volume of the cone is maximum and find the vertical angle $\alpha $
We know that,
Volume of the cone, V = $\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h$
Putting the value of r from equation (i),
\[ \Rightarrow V = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( {{l^2} - {h^2}} \right)h\] ………… (ii)
Here, we can see that slant height, l is constant (given), so we will differentiate equation (ii) both sides with respect to h, we will get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dV}}{{dh}} = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi \dfrac{d}{{dh}}\left( {{l^2}h - {h^3}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dV}}{{dh}} = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( {{l^2} - 3{h^2}} \right)\] ……… (iii)
As we know that,
$\dfrac{{dV}}{{dh}} = 0$ [for maxima and minima].
So, by equating $\dfrac{{dV}}{{dh}} = 0$, we will get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( {{l^2} - 3{h^2}} \right) = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow {l^2} = 3{h^2}\]
Putting the value of l here, we will get
\[ \Rightarrow {h^2} + {r^2} = 3{h^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {r^2} = 2{h^2}\]
Taking square root on both sides, we will get
\[ \Rightarrow r = \sqrt 2 h\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{r}{h} = \sqrt 2 \] ……… (iv)
From $\vartriangle OAB$, we can see that
$ \Rightarrow \tan \alpha = \dfrac{{OB}}{{OA}}$
$ \Rightarrow \tan \alpha = \dfrac{r}{h}$
Putting this value in equation (iv), we will get
$ \Rightarrow \tan \alpha = \sqrt 2 $
\[ \Rightarrow \alpha = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\sqrt 2 } \right)\]
Hence, we get vertical angle, \[\alpha = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\sqrt 2 } \right)\]
Now, from equation (iii), we have
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dV}}{{dh}} = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( {{l^2} - 3{h^2}} \right)\]
Again, differentiate equation (iii) both sides with respect to h, we will get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}V}}{{d{h^2}}} = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi \dfrac{d}{{dh}}\left( {{l^2} - 3{h^2}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}V}}{{d{h^2}}} = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( { - 6h} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}V}}{{d{h^2}}} = - 2\pi h\]
Here we can see that, \[\dfrac{{{d^2}V}}{{d{h^2}}} = - 2\pi h < 0\]
So, we can say that the volume of the cone, V is maximum.
Hence, the vertical angle of the cone with maximum volume and given slant height is \[\alpha = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\sqrt 2 } \right)\]
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: In order to solve this type of questions the key is to know the formula of volume of a cone and the concept of Pythagoras theorem. Using these two we establish a relation between its length, radius and slant height.
It is an important step to know that the differentiation of a term gives its maximum value. Also, the basic differentiation forms of algebraic terms to be known.
To know the value of trigonometric and inverse trigonometric terms of tan function we refer to its trigonometric table.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




