
The value of $\sin [{\cot ^{ - 1}}\left\{ {\cos \left( {{{\tan }^{ - 1}}} \right)} \right\}]$ is
A. $\dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 2} }}$
B. $\dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} }}$
C. $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 2} }}$
D. $\dfrac{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} }}{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 2} }}$
Answer
478.8k+ views
Hint: In this question, we can see that we have inverse trigonometric expressions. We will try to simplify this by using trigonometric formulas and identities. We will first assume ${\tan ^{ - 1}}x = \theta $ . After this, we will draw the right angle triangle and by using the Pythagoras theorem we will solve this.
Complete step-by-step answer:
According to the question we have:
$\sin [{\cot ^{ - 1}}\left\{ {\cos \left( {{{\tan }^{ - 1}}} \right)} \right\}]$
Let us assume ${\tan ^{ - 1}}x = \theta $ . We can write the expression as
$x = \tan \theta $ .
We know that the trigonometric ratio of tangent can be written as
$\tan = \dfrac{p}{b}$ .
Let us draw the diagram of a triangle and try to solve:
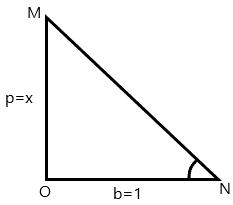
In the above triangle, we have $\angle MNO = \theta $ .
Now we will apply the Pythagoras theorem and find the value of MN, so we have:
$MN = \sqrt {M{O^2} + O{P^2}} $
By putting the values we have;
$ \Rightarrow MN = h = \sqrt {{x^2} + 1} $
Now we have assumed ${\tan ^{ - 1}}x = \theta $ , so we can write the expression as:
$\sin [{\cot ^{ - 1}}\left\{ {\cos \theta } \right\}]$.
Again we can find $\cos \theta $ from the above triangle, we know that $\cos \theta = \dfrac{b}{h}$ .
By putting the value from the above we have the value
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{b}{h} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} }}$ .
WE can directly put the value in the expression and it gives us;
$\sin [{\cot ^{ - 1}}\left\{ {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} }}} \right\}]$.
Let us assume again that
${\cot ^{ - 1}}\left\{ {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} }}} \right\} = \phi $.
So we have a new expression as $\sin \phi $
We can simplify this also as above and we have:
$ \Rightarrow \left\{ {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} }}} \right\} = \cot \phi $.
We know that the ratio of cotangent is: $\dfrac{b}{p}$
By comparing we have :
$b = 1,p = \sqrt {{x^2} + 1} $ .
We can calculate the hypotenuse from the above values:
$ \Rightarrow h = \sqrt {{p^2} + {b^2}} $
By putting the values in the equation, we have:
$ \Rightarrow h = \sqrt {{{\left( {\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} } \right)}^2} + {1^2}} $
$ \Rightarrow h = \sqrt {{x^2} + 1 + 1} $
Therefore we have:
$h = \sqrt {{x^2} + 2} $ .
So we can calculate the value of the sine function as, we know that
$\sin \phi = \dfrac{p}{h}$
By substituting the values, we have;
$\sin \phi = \dfrac{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} }}{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 2} }}$
This gives us the value of the required equation.
Hence the correct option is (d) $\dfrac{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} }}{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 2} }}$ .
Note: We should know the basic trigonometric functions and ratios along with inverse trigonometric functions to solve this kind of question. Sine and cosine functions are the most basic trigonometric ratio. We should know that the value of trigonometric ratio changes with different angles but it remains the same with certain angles such as $90^\circ ,180^\circ ,270^\circ $ and $360^\circ $ .
Complete step-by-step answer:
According to the question we have:
$\sin [{\cot ^{ - 1}}\left\{ {\cos \left( {{{\tan }^{ - 1}}} \right)} \right\}]$
Let us assume ${\tan ^{ - 1}}x = \theta $ . We can write the expression as
$x = \tan \theta $ .
We know that the trigonometric ratio of tangent can be written as
$\tan = \dfrac{p}{b}$ .
Let us draw the diagram of a triangle and try to solve:

In the above triangle, we have $\angle MNO = \theta $ .
Now we will apply the Pythagoras theorem and find the value of MN, so we have:
$MN = \sqrt {M{O^2} + O{P^2}} $
By putting the values we have;
$ \Rightarrow MN = h = \sqrt {{x^2} + 1} $
Now we have assumed ${\tan ^{ - 1}}x = \theta $ , so we can write the expression as:
$\sin [{\cot ^{ - 1}}\left\{ {\cos \theta } \right\}]$.
Again we can find $\cos \theta $ from the above triangle, we know that $\cos \theta = \dfrac{b}{h}$ .
By putting the value from the above we have the value
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{b}{h} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} }}$ .
WE can directly put the value in the expression and it gives us;
$\sin [{\cot ^{ - 1}}\left\{ {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} }}} \right\}]$.
Let us assume again that
${\cot ^{ - 1}}\left\{ {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} }}} \right\} = \phi $.
So we have a new expression as $\sin \phi $
We can simplify this also as above and we have:
$ \Rightarrow \left\{ {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} }}} \right\} = \cot \phi $.
We know that the ratio of cotangent is: $\dfrac{b}{p}$
By comparing we have :
$b = 1,p = \sqrt {{x^2} + 1} $ .
We can calculate the hypotenuse from the above values:
$ \Rightarrow h = \sqrt {{p^2} + {b^2}} $
By putting the values in the equation, we have:
$ \Rightarrow h = \sqrt {{{\left( {\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} } \right)}^2} + {1^2}} $
$ \Rightarrow h = \sqrt {{x^2} + 1 + 1} $
Therefore we have:
$h = \sqrt {{x^2} + 2} $ .
So we can calculate the value of the sine function as, we know that
$\sin \phi = \dfrac{p}{h}$
By substituting the values, we have;
$\sin \phi = \dfrac{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} }}{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 2} }}$
This gives us the value of the required equation.
Hence the correct option is (d) $\dfrac{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} }}{{\sqrt {{x^2} + 2} }}$ .
Note: We should know the basic trigonometric functions and ratios along with inverse trigonometric functions to solve this kind of question. Sine and cosine functions are the most basic trigonometric ratio. We should know that the value of trigonometric ratio changes with different angles but it remains the same with certain angles such as $90^\circ ,180^\circ ,270^\circ $ and $360^\circ $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




