
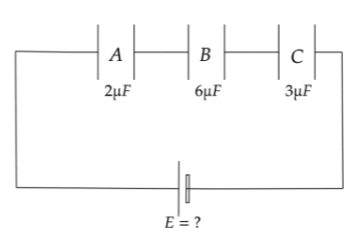
What should be the value of applied voltage (E) so all the capacitors can work properly. Also find out the value of applied voltage if only Capacitor B is replaced by a capacitor having $ V_B = 1.5KV $ and Capacitance $ 6\mu F $
$ V_A = 4KV $ $ V_B = 3KV $ $ V_C = 3KV $
 $ V_B \to $ Breaking voltage
$ V_B \to $ Breaking voltage
$ \left( A \right)8KV,8KV $
$ \left( B \right)6KV,8KV $
$ \left( C \right)8KV,6KV $
$ \left( D \right)6KV,6KV $

Answer
493.2k+ views
Hint: First we will find the charge on each of the capacitors. Then we will find the total voltage present in the circuit with the help of the charge and capacitance of each capacitor. Now if we replace the capacitor B by a capacitor of $ V_B = 1.5KV $ and $ 6\mu F $ then the net voltage changes hence similarly with the help of previous formula we can find the new applied village.
Complete answer:
As per the figure given we need to calculate the applied voltage so that all the capacitors can work properly.
We know,
$ V_A = 4KV,C_A = 2\mu F $
$ V_B = 3KV,C_B = 6\mu F $
$ V_C = 3KV,C_C = 3\mu F $
Now with the help of the given values we can calculate the change on each of the capacitors.
$ Q = V_C $
Where,
Q is the change on the capacitor.
V is the voltage across the capacitor.
C is the capacitance.
So we can write,
$ Q_A = V_AC_A $
Now putting the known values we will get,
$ Q_A = 4KV \times 2\mu F $
Convert the term in its SI unit we will get,
$ Q_A = 4 \times {10^3}V \times 2 \times {10^{ - 6}}F $
$ Q_A = 8 \times {10^{ - 3}}C $
Similarly,
$ Q_B = V_BC_B $
Now putting the known values we will get,
$ Q_B = 3KV \times 6\mu F $
Convert the term in its SI unit we will get,
$ Q_B = 3 \times {10^3}V \times 6 \times {10^{ - 6}}F $
$ Q_B = 18 \times {10^{ - 3}}C $
For C,
$ Q_C = V_CC_C $
Now putting the known values we will get,
$ Q_C = 3KV \times 3\mu F $
Convert the term in its SI unit we will get,
$ Q_C = 3 \times {10^3}V \times 3 \times {10^{ - 6}}F $
$ Q_C = 9 \times {10^{ - 3}}C $
Hence $ Q_A $ is lower.
Now the total voltage applied will be,
$ V = V_1 + V_2 + V_3 $
We know,
$ V = \dfrac{Q}{C} $
Now putting this,
$ V = \dfrac{{Q_A}}{{C_A}} + \dfrac{{Q_A}}{{C_B}} + \dfrac{{Q_A}}{{C_C}} $
Putting the respective values we will get,
$ V = \dfrac{{8 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}C}}{{2 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}F}} + \dfrac{{8 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}C}}{{6 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}F}} + \dfrac{{8 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}C}}{{3 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}F}} $
$ \Rightarrow V = 4 \times {10^3}V + \dfrac{4}{3} \times {10^3}V + \dfrac{8}{3} \times {10^3}V $
On further solving we will get,
$ V = 4 \times {10^3}V + \dfrac{{4 + 8}}{3} \times {10^3}V $
$ \Rightarrow V = 4 \times {10^3}V + 4 \times {10^3}V = 8 \times {10^3}V $
Hene the applied voltage will be,
$ V = 8KV $
Now if we replace the capacitor B by a capacitor of $ V_B = 1.5KV $ and $ 6\mu F $ then the net voltage will be,
$ Q_B = V_BC_B $
Now putting the known values we will get,
$ Q_B = 1.5KV \times 6\mu F $
Convert the term in its SI unit we will get,
$ Q_B = 1.5 \times {10^3}V \times 6 \times {10^{ - 6}}F $
$ Q_B = 9 \times {10^{ - 3}}C $
Now also $ Q_A $ is lower.
Now the total voltage applied will be,
$ V = V_1 + V_2 + V_3 $
We know,
$ V = \dfrac{Q}{C} $
Now putting this,
$ V = \dfrac{{Q_A}}{{C_A}} + \dfrac{{Q_A}}{{C_B}} + \dfrac{{Q_A}}{{C_C}} $
Putting the respective values we will get,
$ V = \dfrac{{8 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}C}}{{2 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}F}} + \dfrac{{8 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}C}}{{6 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}F}} + \dfrac{{8 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}C}}{{3 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}F}} $
$ \Rightarrow V = 4 \times {10^3}V + \dfrac{4}{3} \times {10^3}V + \dfrac{8}{3} \times {10^3}V $
On further solving we will get,
$ V = 4 \times {10^3}V + \dfrac{{4 + 8}}{3} \times {10^3}V $
$ \Rightarrow V = 4 \times {10^3}V + 4 \times {10^3}V = 8 \times {10^3}V $
Hene the applied voltage will be,
$ V = 8KV $
Therefore the correct option is $ \left( A \right) $ .
Note:
Here keep in mind we have to choose such a capacitor whose charge is lower than the other so as to get the maximum applied voltage which must be greater than the breakdown voltage so that all the capacitors present in circuit should work properly. To check if our solution is current or not we can check it by comparing the breakdown voltage and the applied voltage.
Complete answer:
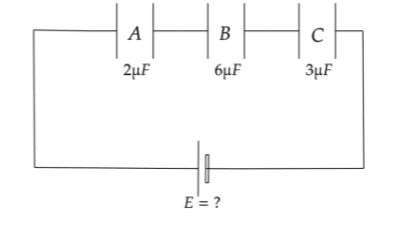
As per the figure given we need to calculate the applied voltage so that all the capacitors can work properly.

We know,
$ V_A = 4KV,C_A = 2\mu F $
$ V_B = 3KV,C_B = 6\mu F $
$ V_C = 3KV,C_C = 3\mu F $
Now with the help of the given values we can calculate the change on each of the capacitors.
$ Q = V_C $
Where,
Q is the change on the capacitor.
V is the voltage across the capacitor.
C is the capacitance.
So we can write,
$ Q_A = V_AC_A $
Now putting the known values we will get,
$ Q_A = 4KV \times 2\mu F $
Convert the term in its SI unit we will get,
$ Q_A = 4 \times {10^3}V \times 2 \times {10^{ - 6}}F $
$ Q_A = 8 \times {10^{ - 3}}C $
Similarly,
$ Q_B = V_BC_B $
Now putting the known values we will get,
$ Q_B = 3KV \times 6\mu F $
Convert the term in its SI unit we will get,
$ Q_B = 3 \times {10^3}V \times 6 \times {10^{ - 6}}F $
$ Q_B = 18 \times {10^{ - 3}}C $
For C,
$ Q_C = V_CC_C $
Now putting the known values we will get,
$ Q_C = 3KV \times 3\mu F $
Convert the term in its SI unit we will get,
$ Q_C = 3 \times {10^3}V \times 3 \times {10^{ - 6}}F $
$ Q_C = 9 \times {10^{ - 3}}C $
Hence $ Q_A $ is lower.
Now the total voltage applied will be,
$ V = V_1 + V_2 + V_3 $
We know,
$ V = \dfrac{Q}{C} $
Now putting this,
$ V = \dfrac{{Q_A}}{{C_A}} + \dfrac{{Q_A}}{{C_B}} + \dfrac{{Q_A}}{{C_C}} $
Putting the respective values we will get,
$ V = \dfrac{{8 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}C}}{{2 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}F}} + \dfrac{{8 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}C}}{{6 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}F}} + \dfrac{{8 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}C}}{{3 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}F}} $
$ \Rightarrow V = 4 \times {10^3}V + \dfrac{4}{3} \times {10^3}V + \dfrac{8}{3} \times {10^3}V $
On further solving we will get,
$ V = 4 \times {10^3}V + \dfrac{{4 + 8}}{3} \times {10^3}V $
$ \Rightarrow V = 4 \times {10^3}V + 4 \times {10^3}V = 8 \times {10^3}V $
Hene the applied voltage will be,
$ V = 8KV $
Now if we replace the capacitor B by a capacitor of $ V_B = 1.5KV $ and $ 6\mu F $ then the net voltage will be,
$ Q_B = V_BC_B $
Now putting the known values we will get,
$ Q_B = 1.5KV \times 6\mu F $
Convert the term in its SI unit we will get,
$ Q_B = 1.5 \times {10^3}V \times 6 \times {10^{ - 6}}F $
$ Q_B = 9 \times {10^{ - 3}}C $
Now also $ Q_A $ is lower.
Now the total voltage applied will be,
$ V = V_1 + V_2 + V_3 $
We know,
$ V = \dfrac{Q}{C} $
Now putting this,
$ V = \dfrac{{Q_A}}{{C_A}} + \dfrac{{Q_A}}{{C_B}} + \dfrac{{Q_A}}{{C_C}} $
Putting the respective values we will get,
$ V = \dfrac{{8 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}C}}{{2 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}F}} + \dfrac{{8 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}C}}{{6 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}F}} + \dfrac{{8 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}C}}{{3 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}F}} $
$ \Rightarrow V = 4 \times {10^3}V + \dfrac{4}{3} \times {10^3}V + \dfrac{8}{3} \times {10^3}V $
On further solving we will get,
$ V = 4 \times {10^3}V + \dfrac{{4 + 8}}{3} \times {10^3}V $
$ \Rightarrow V = 4 \times {10^3}V + 4 \times {10^3}V = 8 \times {10^3}V $
Hene the applied voltage will be,
$ V = 8KV $
Therefore the correct option is $ \left( A \right) $ .
Note:
Here keep in mind we have to choose such a capacitor whose charge is lower than the other so as to get the maximum applied voltage which must be greater than the breakdown voltage so that all the capacitors present in circuit should work properly. To check if our solution is current or not we can check it by comparing the breakdown voltage and the applied voltage.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




