
The value of ‘a’ for which $a{{x}^{2}}+{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( {{x}^{2}}-2x+2 \right)+{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( {{x}^{2}}-2x+2 \right)=0$ has real solution is.
Answer
598.5k+ views
Hint: We will write $\left( {{x}^{2}}-2x+2 \right)$ as ${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{2}}+1$. We know that the value of sin varies from -1 to 1, thus we will get, $-1\le {{\left( x-1 \right)}^{2}}+1\le 1$. We will solve this further to get x=1. In the final step, we will put x=1 in the given equation to get the value of ‘a’.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given in the question that we have to find the value of ‘a’ for which $a{{x}^{2}}+{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( {{x}^{2}}-2x+2 \right)+{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( {{x}^{2}}-2x+2 \right)=0$ has real solution.
We can write $\left( {{x}^{2}}-2x+2 \right)$ as $\left[ {{x}^{2}}-2\left( x \right)\left( 1 \right)+1 \right]+1$, so we will get, ${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{2}}+1$.
We know that the value of sin varies from -1 to 1. So, we can represent it graphically as follows.
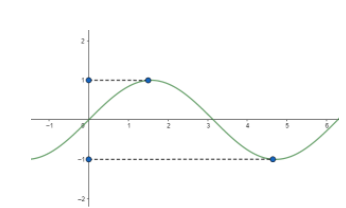
So, from this we can limit ${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{2}}+1$ between -1 and 1. So, we can write it as,
$-1\le {{\left( x-1 \right)}^{2}}+1\le 1$
But we know that ${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{2}}+1$ is already greater than 1, so in order to satisfy $-1\le {{\left( x-1 \right)}^{2}}+1\le 1$, we have to make the term ${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{2}}+1$ equal to 1, so we get,
${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{2}}+1=1$
We know that ${{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}-2ab+{{b}^{2}}$, so we get,
${{x}^{2}}-2x+2=1$
On transposing 1 from RHS to LHS, we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}-2x+2-1=0 \\
& {{x}^{2}}-2x+1=0 \\
\end{align}$
We can write -2x as –x –x, so we will get,
$\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}-x-x+1=0 \\
& x\left( x-1 \right)-1\left( x-1 \right)=0 \\
& \left( x-1 \right)\left( x-1 \right)=0 \\
& x=1 \\
\end{align}$
On putting the value of x as 1 in the equation $a{{x}^{2}}+{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( {{x}^{2}}-2x+2 \right)+{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( {{x}^{2}}-2x+2 \right)=0$, we get,
$\begin{align}
& a{{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}+{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( {{1}^{2}}-2\left( 1 \right)+2 \right)+{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( {{1}^{2}}-2\left( 1 \right)+2 \right)=0 \\
& a+{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)+{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)=0 \\
\end{align}$
We know that, ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ and ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)=0$.
So, we can substitute these values in the equation, so we will get,
$\begin{align}
& a+\dfrac{\pi }{2}+0=0 \\
& a+\dfrac{\pi }{2}=0 \\
\end{align}$
On transposing $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ from the LHS to the RHS, we get,
$a=-\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
Thus, the value of ‘a‘ is $-\dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
Note: Most of the students make mistake while taking the value of ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)$ and ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)$. They may take ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)$ as 0 and ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)$ as $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$. They may get the exact same answer, that is $-\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ but the solution is wrong conceptually and due to this they may get less marks.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given in the question that we have to find the value of ‘a’ for which $a{{x}^{2}}+{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( {{x}^{2}}-2x+2 \right)+{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( {{x}^{2}}-2x+2 \right)=0$ has real solution.
We can write $\left( {{x}^{2}}-2x+2 \right)$ as $\left[ {{x}^{2}}-2\left( x \right)\left( 1 \right)+1 \right]+1$, so we will get, ${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{2}}+1$.
We know that the value of sin varies from -1 to 1. So, we can represent it graphically as follows.

So, from this we can limit ${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{2}}+1$ between -1 and 1. So, we can write it as,
$-1\le {{\left( x-1 \right)}^{2}}+1\le 1$
But we know that ${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{2}}+1$ is already greater than 1, so in order to satisfy $-1\le {{\left( x-1 \right)}^{2}}+1\le 1$, we have to make the term ${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{2}}+1$ equal to 1, so we get,
${{\left( x-1 \right)}^{2}}+1=1$
We know that ${{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}-2ab+{{b}^{2}}$, so we get,
${{x}^{2}}-2x+2=1$
On transposing 1 from RHS to LHS, we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}-2x+2-1=0 \\
& {{x}^{2}}-2x+1=0 \\
\end{align}$
We can write -2x as –x –x, so we will get,
$\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}-x-x+1=0 \\
& x\left( x-1 \right)-1\left( x-1 \right)=0 \\
& \left( x-1 \right)\left( x-1 \right)=0 \\
& x=1 \\
\end{align}$
On putting the value of x as 1 in the equation $a{{x}^{2}}+{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( {{x}^{2}}-2x+2 \right)+{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( {{x}^{2}}-2x+2 \right)=0$, we get,
$\begin{align}
& a{{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}+{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( {{1}^{2}}-2\left( 1 \right)+2 \right)+{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( {{1}^{2}}-2\left( 1 \right)+2 \right)=0 \\
& a+{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)+{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)=0 \\
\end{align}$
We know that, ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ and ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)=0$.
So, we can substitute these values in the equation, so we will get,
$\begin{align}
& a+\dfrac{\pi }{2}+0=0 \\
& a+\dfrac{\pi }{2}=0 \\
\end{align}$
On transposing $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ from the LHS to the RHS, we get,
$a=-\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
Thus, the value of ‘a‘ is $-\dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
Note: Most of the students make mistake while taking the value of ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)$ and ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)$. They may take ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)$ as 0 and ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)$ as $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$. They may get the exact same answer, that is $-\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ but the solution is wrong conceptually and due to this they may get less marks.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




