
The type of magnetism exhibited by ${{[Mn{{({{H}_{2}}O)}_{6}}]}^{2+}}$ion is ----
A. Anti-ferromagnetism
B. Diamagnetism
C. Ferromagnetism
D. Paramagnetism
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: Solid substances having different numbers of electrons (paired or unpaired) will have different types of magnetic properties. And these alignment of the electrons (that is unpaired or full) in the configuration of an element help us to say about what type of magnetism it will possess.
Complete step by step solution:
Given that,
We have to find out the magnetism exhibited by ${{[Mn{{({{H}_{2}}O)}_{6}}]}^{2+}}$ion.
So, here the oxidation state of manganese (Mn) is $M{{n}^{2+}}$, which means it has lost two electrons from its orbital.
As we know, the atomic number of manganese is 25 i.e. it has 25 electrons in total.
But, the oxidised manganese i.e. $M{{n}^{2+}}$will lose two electrons from its configuration.
So, now it has 23 electrons in total.
We know that the configuration of manganese is$[Ar]3{{d}^{7}}$.
But, after losing two electrons the configuration of manganese i.e. $M{{n}^{2+}}$ will be $[Ar]3{{d}^{5}}$as shown in the figure,
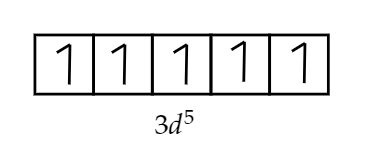
As we can see, the configuration has five unpaired electrons which will be responsible for the paramagnetic nature manganese ion.
So,
The presence of these five unpaired electrons will result in the paramagnetic nature of $M{{n}^{2+}}$.
Hence, the correct option is D.
Additional Information:
On the basis of magnetic properties, solids can be classified as follows:
- Diamagnetic: They are weakly repelled by the magnetic fields. Diamagnetic materials have all the paired electrons i.e. the electrons occupy the same orbital of an atom but orbiting and spinning in the same direction.
- Paramagnetic: They are weakly attracted by the magnetic fields. Paramagnetic materials have more unpaired electrons i.e. the electron occupies the orbital of an atom singly rather than a pair.
- Ferromagnetic: They are strongly attracted by the magnetic field. These materials have some unpaired electrons.
- Anti-ferromagnetic: They have net magnetic moment zero. In these materials, the alignment of electrons is a combination of both parallel and antiparallel.
- Ferrimagnetic: These possess small net magnetic moments. In ferrimagnetic materials, atoms have opposing magnetic moments i.e. electrons are arranged in an antiparallel way.
Note: The magnetic property of materials depends upon the alignment of the electrons. On the basis of magnetic property, solids are classified to various types i.e. diamagnetic, paramagnetic, anti-ferromagnetic, etc.
Complete step by step solution:
Given that,
We have to find out the magnetism exhibited by ${{[Mn{{({{H}_{2}}O)}_{6}}]}^{2+}}$ion.
So, here the oxidation state of manganese (Mn) is $M{{n}^{2+}}$, which means it has lost two electrons from its orbital.
As we know, the atomic number of manganese is 25 i.e. it has 25 electrons in total.
But, the oxidised manganese i.e. $M{{n}^{2+}}$will lose two electrons from its configuration.
So, now it has 23 electrons in total.
We know that the configuration of manganese is$[Ar]3{{d}^{7}}$.
But, after losing two electrons the configuration of manganese i.e. $M{{n}^{2+}}$ will be $[Ar]3{{d}^{5}}$as shown in the figure,

As we can see, the configuration has five unpaired electrons which will be responsible for the paramagnetic nature manganese ion.
So,
The presence of these five unpaired electrons will result in the paramagnetic nature of $M{{n}^{2+}}$.
Hence, the correct option is D.
Additional Information:
On the basis of magnetic properties, solids can be classified as follows:
- Diamagnetic: They are weakly repelled by the magnetic fields. Diamagnetic materials have all the paired electrons i.e. the electrons occupy the same orbital of an atom but orbiting and spinning in the same direction.
- Paramagnetic: They are weakly attracted by the magnetic fields. Paramagnetic materials have more unpaired electrons i.e. the electron occupies the orbital of an atom singly rather than a pair.
- Ferromagnetic: They are strongly attracted by the magnetic field. These materials have some unpaired electrons.
- Anti-ferromagnetic: They have net magnetic moment zero. In these materials, the alignment of electrons is a combination of both parallel and antiparallel.
- Ferrimagnetic: These possess small net magnetic moments. In ferrimagnetic materials, atoms have opposing magnetic moments i.e. electrons are arranged in an antiparallel way.
Note: The magnetic property of materials depends upon the alignment of the electrons. On the basis of magnetic property, solids are classified to various types i.e. diamagnetic, paramagnetic, anti-ferromagnetic, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




