
The two ends A and B of a uniform rod of length l=1m are moving with velocities ${{V}_{A}}$ and ${{V}_{B}}$ as shown.
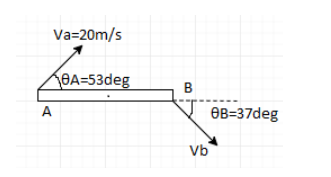
The velocity ${{V}_{B}}$ is:
A: 25m/s
B: 15m/s
C:20m/s
D: 50m/s

Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint: According to the problem, the length of the rod is given, velocities are also given. We have to resolve the velocities along the required directions and deduce the necessary value from the resultant forces and the components. Since one value of velocity and the angles are given, we can easily find the other values as well.
Complete step by step solution:
We take a purely geometric method to approach this question. We don’t need to look into any pre-existing formulae. Instead, we can resolve the given vector quantities into components.
The reconstructed diagram is as follows:
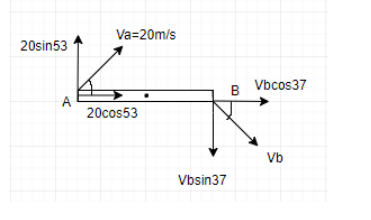
We have resolved ${{V}_{A}}$ and ${{V}_{B}}$to its horizontal and vertical components along the x and y axis.
We’re given that velocity at A is 20m/s and velocity at B is ${{V}_{B}}$
Horizontal component of ${{V}_{A}}$ is given by ${{V}_{A}}\cos 53=20\times \dfrac{3}{5}=12m/s$
Horizontal component of ${{V}_{B}}$ is given by
$
{{V}_{B}}\cos 37 = {{V}_{B}}\times \dfrac{4}{5} \\
$
Equating both components,
$
12=\dfrac{4{{V}_{B}}}{5} \\
\Rightarrow {{V}_{B}}=\dfrac{60}{4}=15m/s \\
$
Hence the value of velocity acting at the point B is 15m/s.
Therefore, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note: For any vector, there are two rectangular components: the horizontal component and the vertical component and these two vectors add up to give the resultant value of the vector. The horizontal component is along the x axis and the vertical component is along the y axis. In other words we can say that if the light is shining from above, then the shadow that forms down is the horizontal component and if the light is from the side, the shadow formed on the opposite side is the vertical component.
Complete step by step solution:
We take a purely geometric method to approach this question. We don’t need to look into any pre-existing formulae. Instead, we can resolve the given vector quantities into components.
The reconstructed diagram is as follows:

We have resolved ${{V}_{A}}$ and ${{V}_{B}}$to its horizontal and vertical components along the x and y axis.
We’re given that velocity at A is 20m/s and velocity at B is ${{V}_{B}}$
Horizontal component of ${{V}_{A}}$ is given by ${{V}_{A}}\cos 53=20\times \dfrac{3}{5}=12m/s$
Horizontal component of ${{V}_{B}}$ is given by
$
{{V}_{B}}\cos 37 = {{V}_{B}}\times \dfrac{4}{5} \\
$
Equating both components,
$
12=\dfrac{4{{V}_{B}}}{5} \\
\Rightarrow {{V}_{B}}=\dfrac{60}{4}=15m/s \\
$
Hence the value of velocity acting at the point B is 15m/s.
Therefore, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note: For any vector, there are two rectangular components: the horizontal component and the vertical component and these two vectors add up to give the resultant value of the vector. The horizontal component is along the x axis and the vertical component is along the y axis. In other words we can say that if the light is shining from above, then the shadow that forms down is the horizontal component and if the light is from the side, the shadow formed on the opposite side is the vertical component.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




