
The truth table given in the figure represents:
A B Y 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1
A. AND - Gate
B. NOR – Gate
C. NAND – Gate
D. OR - Gate
| A | B | Y |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
Answer
599.7k+ views
Hint: Knowledge of the basic logic gates operations is required to solve this question. The corresponding truth tables creation is essential for this question too.
Step by step solution:
In digital electronics, we have 3 basic gates known as AND gate, OR gate and NOT gate.
Combination of these gates produce advanced gates such as NAND gate, NOR gate and X-OR gate.
Each of the
basic gates work on a certain logic earning them the name of basic logic gates.
Each of these logic gates may have one or two inputs depending on the kind of logical operation but all of them have a single output.
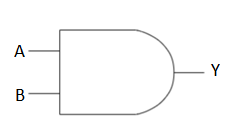
Let’s discuss the logical operations of AND gate:
AND gate has 2 input terminals and single output terminal. If we consider the inputs to be A and B and the output to be Y, then the logical operation of A AND B is equivalent to A.B or multiplicative operation. Therefore, Y=A.B
The graphical representation and its corresponding truth table is as follows:
Moving on to the NOT gate:
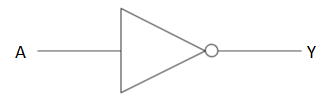
NOT gate has a single input terminal and a single output terminal as well. If we consider the input as A and output as Y, then the logical operation of NOT on A is equivalent to $\overline{A}$ or conjugate/opposite of the input value operation.
The graphical representation and its corresponding truth table is as follows:
Moving on to OR gate:
OR gate has 2 input terminals and single output terminal. If we consider the inputs to be A and B and the output to be Y, then the logical operation of A OR B is equivalent to A+B or additive operation. Therefore, Y=A+B
The graphical representation is:
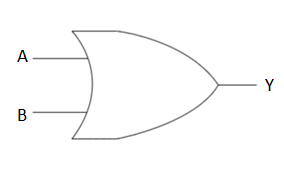
This truth table is the same as the one asked in the question. Therefore, the truth table mentioned in the question belongs to the OR gate.
Note: In digital electronics there are only 2 kinds of states High and Low also known digitally as 1 and 0 respectively. So, don’t consider the OR operation of 1 OR 1 = 2, as this isn’t possible.
Step by step solution:
In digital electronics, we have 3 basic gates known as AND gate, OR gate and NOT gate.
Combination of these gates produce advanced gates such as NAND gate, NOR gate and X-OR gate.
Each of the
basic gates work on a certain logic earning them the name of basic logic gates.
Each of these logic gates may have one or two inputs depending on the kind of logical operation but all of them have a single output.
Let’s discuss the logical operations of AND gate:
AND gate has 2 input terminals and single output terminal. If we consider the inputs to be A and B and the output to be Y, then the logical operation of A AND B is equivalent to A.B or multiplicative operation. Therefore, Y=A.B
The graphical representation and its corresponding truth table is as follows:
| A | B | Y=A.B |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |

Moving on to the NOT gate:
NOT gate has a single input terminal and a single output terminal as well. If we consider the input as A and output as Y, then the logical operation of NOT on A is equivalent to $\overline{A}$ or conjugate/opposite of the input value operation.
The graphical representation and its corresponding truth table is as follows:

| A | $Y=\overline{A}$ |
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 |
Moving on to OR gate:
OR gate has 2 input terminals and single output terminal. If we consider the inputs to be A and B and the output to be Y, then the logical operation of A OR B is equivalent to A+B or additive operation. Therefore, Y=A+B
The graphical representation is:

| A | B | Y=A+B |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
This truth table is the same as the one asked in the question. Therefore, the truth table mentioned in the question belongs to the OR gate.
Note: In digital electronics there are only 2 kinds of states High and Low also known digitally as 1 and 0 respectively. So, don’t consider the OR operation of 1 OR 1 = 2, as this isn’t possible.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




