
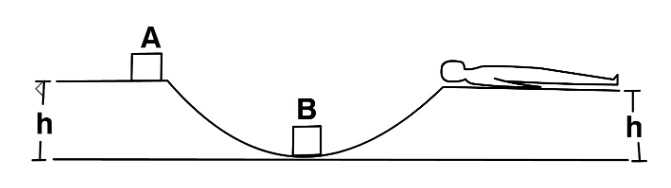
The track shown in figure is frictionless. The block B of mass 2m is lying at rest and the block A of mass m is pushed along the truck with some speed. The collision between A and B is perfectly elastic. With what velocity should the block A be started to get the sleeping man awakened.

Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: The kinetic energy is defined as the energy of a body by the virtue of its motion. The potential energy is the energy of the body by the virtue of its height. Conservation of momentum says that the sum of momentum of two bodies will be conserved before and after the collision.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given in the problem that the track is frictionless, the block B of mass 2m is lying at rest and the block A of mass m is pushed along the truck with some speed. The collision between A and B is perfectly elastic. We need to tell with what velocity should the block A be started to get the sleeping man awakened.
Let the initial velocity of the block A is${u_1}$, the velocity of block A after collision be${u_2}$, the initial velocity of the block B be${v_1}$, the velocity of the block A after collision is $v'$.
The change in the potential energy will equal the kinetic energy of block A.
$ \Rightarrow mgh + \dfrac{1}{2}m \times {u_1}^2 = \dfrac{1}{2}m \times {u_2}^2$
The mass of the block A is m and the initial and final velocity of the block A is ${u_1}$ and${u_2}$.
$ \Rightarrow mgh = \dfrac{1}{2}m \times {u_2}^2 - \dfrac{1}{2}m \times {u_1}^2$
$ \Rightarrow {u_2}^2 = {u_1}^2 + 2gh$
$ \Rightarrow {u_2} = \sqrt {{u_1}^2 + 2gh} $………eq. (1)
For motion of block B.
The kinetic energy of the block will get converted into potential energy.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} \times 2m \times {v_1}^2 = 2m \times g \times h$
$ \Rightarrow {v_1}^2 = 2 \times g \times h$
$ \Rightarrow {v_1} = \sqrt {2gh} $………eq. (2)
Applying conservation of energy for the collision of block A and B.
$ \Rightarrow m{u_2} = mv' + 2m \times {v_1}$
$ \Rightarrow {u_2} = v' + 2 \times {v_1}$………eq. (3)
Replacing equation (1) in equation (3)
$ \Rightarrow {u_2} = v' + 2 \times \sqrt {2gh} $
$ \Rightarrow {u_2} - v' = 2 \times \sqrt {2gh} $………eq. (4)
The kinetic energy of the block A and B before and after the collision.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}m \times {u_2}^2 = \dfrac{1}{2}m \times {\left( {v'} \right)^2} + \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {2m} \right) \times {v_1}^2$
$ \Rightarrow {u_2}^2 = {\left( {v'} \right)^2} + 2 \times {v_1}^2$
$ \Rightarrow {u_2}^2 - {\left( {v'} \right)^2} = + 2 \times {v_1}^2$………eq. (5)
Replacing the value of equation (2) in equation (5) we get.
$ \Rightarrow {u_2}^2 - {\left( {v'} \right)^2} = + 2 \times {\left( {\sqrt {2gh} } \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {u_2}^2 - {\left( {v'} \right)^2} = + 2 \times 2gh$
$ \Rightarrow {u_2}^2 - {\left( {v'} \right)^2} = 4gh$………eq. (6)
Dividing equation (6) by equation (4).
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{u_2}^2 - {{\left( {v'} \right)}^2}}}{{{u_2} - v'}} = \dfrac{{4gh}}{{2\sqrt {2gh} }}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\left( {{u_2} - v'} \right) \times \left( {{u_2} + v'} \right)}}{{{u_2} - v'}} = \sqrt {2gh} $
$ \Rightarrow {u_2} + v' = \sqrt {2gh} $………eq. (7)
Adding equation (4) and equation (7) we get.
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{u_2} - v'} \right) + \left( {{u_2} + v'} \right) = 2 \times \sqrt {2gh} + \sqrt {2gh} $
$ \Rightarrow 2 \times {u_2} = 3 \times \sqrt {2gh} $
$ \Rightarrow {u_2} = \dfrac{3}{2} \times \sqrt {2gh} $………eq. (8)
Equating equation (1) and equation (8) we get.
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{u_1}^2 + 2gh} = \dfrac{3}{2} \times \sqrt {2gh} $
squaring on both sides we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {\sqrt {{u_1}^2 + 2gh} } \right)^2} = \dfrac{9}{4} \times {\left( {\sqrt {2gh} } \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {u_1}^2 + 2gh = \dfrac{9}{4} \times \left( {2gh} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {u_1}^2 + 2gh = \dfrac{9}{2} \times \left( {gh} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 2\left( {{u_1}^2 + 2gh} \right) = 9gh$
$ \Rightarrow 2{u_1}^2 + 4gh = 9gh$
$ \Rightarrow 2{u_1}^2 = 5gh$
$ \Rightarrow {u_1} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{5gh}}{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow {u_1} = \sqrt {2 \cdot 5gh} $.
The velocity with which the block A should be pushed is equal to
${u_1} = \sqrt {2 \cdot 5gh} $.
Note: It is advisable for the students to remember and understand the concept of conservation of energy students should also remember the formula of the kinetic and potential energy. Whenever an object falls from a height then the kinetic energy gets converted into potential energy of the object.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given in the problem that the track is frictionless, the block B of mass 2m is lying at rest and the block A of mass m is pushed along the truck with some speed. The collision between A and B is perfectly elastic. We need to tell with what velocity should the block A be started to get the sleeping man awakened.
Let the initial velocity of the block A is${u_1}$, the velocity of block A after collision be${u_2}$, the initial velocity of the block B be${v_1}$, the velocity of the block A after collision is $v'$.
The change in the potential energy will equal the kinetic energy of block A.
$ \Rightarrow mgh + \dfrac{1}{2}m \times {u_1}^2 = \dfrac{1}{2}m \times {u_2}^2$
The mass of the block A is m and the initial and final velocity of the block A is ${u_1}$ and${u_2}$.
$ \Rightarrow mgh = \dfrac{1}{2}m \times {u_2}^2 - \dfrac{1}{2}m \times {u_1}^2$
$ \Rightarrow {u_2}^2 = {u_1}^2 + 2gh$
$ \Rightarrow {u_2} = \sqrt {{u_1}^2 + 2gh} $………eq. (1)
For motion of block B.
The kinetic energy of the block will get converted into potential energy.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} \times 2m \times {v_1}^2 = 2m \times g \times h$
$ \Rightarrow {v_1}^2 = 2 \times g \times h$
$ \Rightarrow {v_1} = \sqrt {2gh} $………eq. (2)
Applying conservation of energy for the collision of block A and B.
$ \Rightarrow m{u_2} = mv' + 2m \times {v_1}$
$ \Rightarrow {u_2} = v' + 2 \times {v_1}$………eq. (3)
Replacing equation (1) in equation (3)
$ \Rightarrow {u_2} = v' + 2 \times \sqrt {2gh} $
$ \Rightarrow {u_2} - v' = 2 \times \sqrt {2gh} $………eq. (4)
The kinetic energy of the block A and B before and after the collision.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}m \times {u_2}^2 = \dfrac{1}{2}m \times {\left( {v'} \right)^2} + \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {2m} \right) \times {v_1}^2$
$ \Rightarrow {u_2}^2 = {\left( {v'} \right)^2} + 2 \times {v_1}^2$
$ \Rightarrow {u_2}^2 - {\left( {v'} \right)^2} = + 2 \times {v_1}^2$………eq. (5)
Replacing the value of equation (2) in equation (5) we get.
$ \Rightarrow {u_2}^2 - {\left( {v'} \right)^2} = + 2 \times {\left( {\sqrt {2gh} } \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {u_2}^2 - {\left( {v'} \right)^2} = + 2 \times 2gh$
$ \Rightarrow {u_2}^2 - {\left( {v'} \right)^2} = 4gh$………eq. (6)
Dividing equation (6) by equation (4).
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{u_2}^2 - {{\left( {v'} \right)}^2}}}{{{u_2} - v'}} = \dfrac{{4gh}}{{2\sqrt {2gh} }}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\left( {{u_2} - v'} \right) \times \left( {{u_2} + v'} \right)}}{{{u_2} - v'}} = \sqrt {2gh} $
$ \Rightarrow {u_2} + v' = \sqrt {2gh} $………eq. (7)
Adding equation (4) and equation (7) we get.
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{u_2} - v'} \right) + \left( {{u_2} + v'} \right) = 2 \times \sqrt {2gh} + \sqrt {2gh} $
$ \Rightarrow 2 \times {u_2} = 3 \times \sqrt {2gh} $
$ \Rightarrow {u_2} = \dfrac{3}{2} \times \sqrt {2gh} $………eq. (8)
Equating equation (1) and equation (8) we get.
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{u_1}^2 + 2gh} = \dfrac{3}{2} \times \sqrt {2gh} $
squaring on both sides we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {\sqrt {{u_1}^2 + 2gh} } \right)^2} = \dfrac{9}{4} \times {\left( {\sqrt {2gh} } \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {u_1}^2 + 2gh = \dfrac{9}{4} \times \left( {2gh} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {u_1}^2 + 2gh = \dfrac{9}{2} \times \left( {gh} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 2\left( {{u_1}^2 + 2gh} \right) = 9gh$
$ \Rightarrow 2{u_1}^2 + 4gh = 9gh$
$ \Rightarrow 2{u_1}^2 = 5gh$
$ \Rightarrow {u_1} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{5gh}}{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow {u_1} = \sqrt {2 \cdot 5gh} $.
The velocity with which the block A should be pushed is equal to
${u_1} = \sqrt {2 \cdot 5gh} $.
Note: It is advisable for the students to remember and understand the concept of conservation of energy students should also remember the formula of the kinetic and potential energy. Whenever an object falls from a height then the kinetic energy gets converted into potential energy of the object.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




