
The time taken by an A.C current of 50 Hz in reaching from zero to the maximum value is?
\[
{\text{A}}{\text{. 50 }} \times {\text{ 1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 3}}{\text{s}} \\
{\text{B}}{\text{. 5 }} \times {\text{ 1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 3}}{\text{s}} \\
{\text{C}}{\text{. 1 }} \times {\text{ 1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 3}}{\text{s}} \\
{\text{D}}{\text{. 2 }} \times {\text{ 1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 3}}{\text{s}} \\
\]
Answer
603.6k+ views
- Hint: To find the time taken to reach the maximum value, we figure out which type of a wave an AC current is attributed to and apply the formula of its time period. An AC current is a sinusoidal waveform.
Formula Used:
Time period ${\text{T = }}\dfrac{1}{{\text{f}}}$, where f is the frequency of the wave.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Given data, f = 50 Hz
The graph of an AC current is obtained when a change of voltage or current is calculated with respect to time. The graph plotted with voltage or current against time gives us the graph of an AC current.
The graph of an AC current is a sinusoidal waveform or simply a sine wave.
It is as follows:
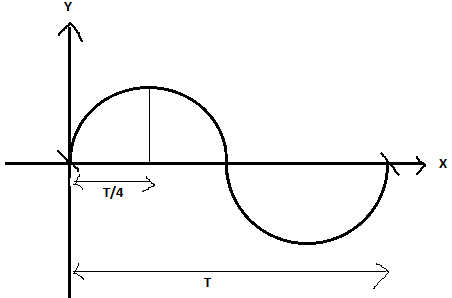
It begins with an initial value ‘zero’, reaches its maximum magnitude and becomes zero at one point. Then it progresses in the same way with respect to the magnitude but in the opposite direction as shown in the figure.
The time taken for the wave to complete this entire process is said to be its time period, i.e. the time taken for the wave to make one full cycle.
In this process the wave reaches its maximum value two times but with different polarities.
The time period of a wave for one complete cycle is denoted by ‘T’.
Hence from the figure the time taken by the wave to reach its first maximum value is $\dfrac{{\text{T}}}{4}$.
Now we know the formula of the time period of a sine wave is given by, ${\text{T = }}\dfrac{1}{{\text{f}}}$
$
\Rightarrow {\text{T = }}\dfrac{1}{{50}}{\text{ }}\left( {\because {\text{f = 50}}} \right) \\
{\text{Now, }}\dfrac{{\text{T}}}{4}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{{50}}} \right)}}{4} = \dfrac{1}{{200}} = 0.005{\text{s}} \\
$
Hence, the time taken by an A.C current of 50 Hz in reaching from zero to the maximum value is ${\text{5 }} \times {\text{ 1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 3}}{\text{s}}$.
Option B is the correct answer.
Note – In order to answer this type of question the key is to identify that the waveform of an AC current wave is similar to that of a sine wave. Having knowledge of the graph of a sine wave and its properties helps in figuring this out soon.
A sine wave is always changing its value, throughout one complete cycle, the value or amplitude of the wave is always different. Amplitude is the maximum value a wave particle can reach throughout one cycle.
Frequency is the number of cycles a wave can do per unit time.
Formula Used:
Time period ${\text{T = }}\dfrac{1}{{\text{f}}}$, where f is the frequency of the wave.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Given data, f = 50 Hz
The graph of an AC current is obtained when a change of voltage or current is calculated with respect to time. The graph plotted with voltage or current against time gives us the graph of an AC current.
The graph of an AC current is a sinusoidal waveform or simply a sine wave.
It is as follows:

It begins with an initial value ‘zero’, reaches its maximum magnitude and becomes zero at one point. Then it progresses in the same way with respect to the magnitude but in the opposite direction as shown in the figure.
The time taken for the wave to complete this entire process is said to be its time period, i.e. the time taken for the wave to make one full cycle.
In this process the wave reaches its maximum value two times but with different polarities.
The time period of a wave for one complete cycle is denoted by ‘T’.
Hence from the figure the time taken by the wave to reach its first maximum value is $\dfrac{{\text{T}}}{4}$.
Now we know the formula of the time period of a sine wave is given by, ${\text{T = }}\dfrac{1}{{\text{f}}}$
$
\Rightarrow {\text{T = }}\dfrac{1}{{50}}{\text{ }}\left( {\because {\text{f = 50}}} \right) \\
{\text{Now, }}\dfrac{{\text{T}}}{4}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{{50}}} \right)}}{4} = \dfrac{1}{{200}} = 0.005{\text{s}} \\
$
Hence, the time taken by an A.C current of 50 Hz in reaching from zero to the maximum value is ${\text{5 }} \times {\text{ 1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 3}}{\text{s}}$.
Option B is the correct answer.
Note – In order to answer this type of question the key is to identify that the waveform of an AC current wave is similar to that of a sine wave. Having knowledge of the graph of a sine wave and its properties helps in figuring this out soon.
A sine wave is always changing its value, throughout one complete cycle, the value or amplitude of the wave is always different. Amplitude is the maximum value a wave particle can reach throughout one cycle.
Frequency is the number of cycles a wave can do per unit time.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




