
The tangents drawn from a point P to the ellipse make an angle ${{\theta }_{1}}$ and ${{\theta }_{2}}$ with the major axis; find the locus of P when,
$\tan {{\theta }_{1}}-\tan {{\theta }_{2}}$ is constant $=d$
Answer
543.6k+ views
Hint: First write down the general equation of the ellipse and then the standard equation of tangent for ellipse for the tangent $y=mx\pm \sqrt{{{a}^{2}}{{m}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}$ , Let there be a point $P\left( h,k \right)$ that lies on that tangent. Now rewrite the tangent equation for the point $P\left( h,k \right)$ and then evaluate to form a quadratic expression in ‘m’ and proceed further to find the sum of roots, $\tan {{\theta }_{1}}+\tan {{\theta }_{2}}$ and then from there find the value of $\tan {{\theta }_{1}}-\tan {{\theta }_{2}}$
Complete step by step solution:
Let us write the general equation for an ellipse.
It is given by,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ considered that $\left( a>b \right)$
Hence, X-axis is the major axis.
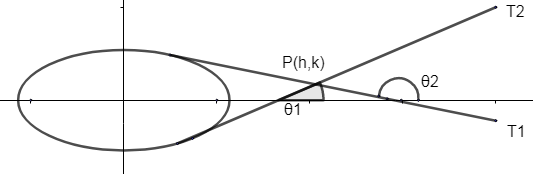
As we have the equation of tangent drawn from an external point with given slope is
$y=mx\pm \sqrt{{{a}^{2}}{{m}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}$
The slope of the tangent ${{T}_{1}}=\tan {{\theta }_{1}}$
And the slope of the tangent ${{T}_{2}}=\tan {{\theta }_{2}}$
Let us consider a point $P\left( h,k \right)$ that lies on this tangent.
We can rewrite the tangent equation as,
$\Rightarrow k=mh\pm \sqrt{{{a}^{2}}{{m}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\left( k-mh \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}{{m}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{k}^{2}}+{{m}^{2}}{{h}^{2}}-2mkh={{a}^{2}}{{m}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{m}^{2}}\left( {{h}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}} \right)-2mhk+{{k}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}=0$
As m is a quadratic function, hence it has two roots or two tangents passing through P are there with slopes $\tan {{\theta }_{1}}$ and $\tan {{\theta }_{2}}$
Hence, $\tan {{\theta }_{1}}$ and $\tan {{\theta }_{2}}$ are roots of quadratic obtained.
The sum of roots for the quadratic equation is given by,
The Sum of roots is given by $=\dfrac{-b}{a}$ in $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$
$\Rightarrow \tan {{\theta }_{1}}+\tan {{\theta }_{2}}=\dfrac{2hk}{{{h}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}}$
And the product of roots is given by,
Product of roots is given by $\dfrac{c}{a}$ in $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$
$\Rightarrow \tan {{\theta }_{1}}\tan {{\theta }_{2}}=\dfrac{{{k}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}}{{{h}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}}$
We also know that,
$\Rightarrow {{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}={{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}+4ab$
Substituting the slopes, we get,
$\Rightarrow {{\left( \tan {{\theta }_{1}}-\tan {{\theta }_{2}} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \tan {{\theta }_{1}}+\tan {{\theta }_{2}} \right)}^{2}}+4\tan {{\theta }_{1}}\tan {{\theta }_{2}}$
As $\tan {{\theta }_{1}}-\tan {{\theta }_{2}}=d$ (given)
$\Rightarrow {{d}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{2hk}{{{h}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}} \right)}^{2}}+4\left( \dfrac{{{k}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}}{{{h}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}} \right)$
On further evaluating we get,
$\Rightarrow {{d}^{2}}=\dfrac{4{{h}^{2}}{{k}^{2}}}{{{\left( {{h}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}} \right)}^{2}}}+4\left( \dfrac{{{k}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}}{{{h}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{d}^{2}}=\dfrac{4{{h}^{2}}{{k}^{2}}-4\left( {{h}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}} \right)\left( {{k}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}} \right)}{{{\left( {{h}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}} \right)}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{d}^{2}}{{\left( {{h}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}} \right)}^{2}}=4{{h}^{2}}{{k}^{2}}+4\left( {{k}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}} \right)\left( {{h}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{d}^{2}}{{\left( {{h}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}} \right)}^{2}}=4\left( {{h}^{2}}{{k}^{2}}-{{h}^{2}}{{k}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}{{k}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}} \right)$
On simplifying,
$\Rightarrow {{d}^{2}}{{\left( {{h}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}} \right)}^{2}}=4\left( {{a}^{2}}{{k}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}} \right)$
Replacing (h, k) by (x, y) to get locus: -
$\Rightarrow {{d}^{2}}{{\left( {{x}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}} \right)}^{2}}=4\left( {{x}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}} \right)\left( {{y}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}} \right)+4{{x}^{2}}{{y}^{2}}$
Now the required locus is ${{d}^{2}}{{\left( {{x}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}} \right)}^{2}}=4\left( {{x}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}} \right)\left( {{y}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}} \right)+4{{x}^{2}}{{y}^{2}}$
Note: Eliminating ${{\theta }_{1}}\And {{\theta }_{2}}$ by using the given relation ${{\tan }^{2}}{{\theta }_{1}}+{{\tan }^{2}}{{\theta }_{1}}=\lambda$ with the help of quadratic formed in ‘m’ i.e. $y=mx\pm \sqrt{{{a}^{2}}{{m}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}$ or ${{\left( y-mx \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}{{m}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}$ by using properties of roots is the key point of this equation.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us write the general equation for an ellipse.
It is given by,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ considered that $\left( a>b \right)$
Hence, X-axis is the major axis.

As we have the equation of tangent drawn from an external point with given slope is
$y=mx\pm \sqrt{{{a}^{2}}{{m}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}$
The slope of the tangent ${{T}_{1}}=\tan {{\theta }_{1}}$
And the slope of the tangent ${{T}_{2}}=\tan {{\theta }_{2}}$
Let us consider a point $P\left( h,k \right)$ that lies on this tangent.
We can rewrite the tangent equation as,
$\Rightarrow k=mh\pm \sqrt{{{a}^{2}}{{m}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\left( k-mh \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}{{m}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{k}^{2}}+{{m}^{2}}{{h}^{2}}-2mkh={{a}^{2}}{{m}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{m}^{2}}\left( {{h}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}} \right)-2mhk+{{k}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}=0$
As m is a quadratic function, hence it has two roots or two tangents passing through P are there with slopes $\tan {{\theta }_{1}}$ and $\tan {{\theta }_{2}}$
Hence, $\tan {{\theta }_{1}}$ and $\tan {{\theta }_{2}}$ are roots of quadratic obtained.
The sum of roots for the quadratic equation is given by,
The Sum of roots is given by $=\dfrac{-b}{a}$ in $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$
$\Rightarrow \tan {{\theta }_{1}}+\tan {{\theta }_{2}}=\dfrac{2hk}{{{h}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}}$
And the product of roots is given by,
Product of roots is given by $\dfrac{c}{a}$ in $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$
$\Rightarrow \tan {{\theta }_{1}}\tan {{\theta }_{2}}=\dfrac{{{k}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}}{{{h}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}}$
We also know that,
$\Rightarrow {{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}={{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}+4ab$
Substituting the slopes, we get,
$\Rightarrow {{\left( \tan {{\theta }_{1}}-\tan {{\theta }_{2}} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \tan {{\theta }_{1}}+\tan {{\theta }_{2}} \right)}^{2}}+4\tan {{\theta }_{1}}\tan {{\theta }_{2}}$
As $\tan {{\theta }_{1}}-\tan {{\theta }_{2}}=d$ (given)
$\Rightarrow {{d}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{2hk}{{{h}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}} \right)}^{2}}+4\left( \dfrac{{{k}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}}{{{h}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}} \right)$
On further evaluating we get,
$\Rightarrow {{d}^{2}}=\dfrac{4{{h}^{2}}{{k}^{2}}}{{{\left( {{h}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}} \right)}^{2}}}+4\left( \dfrac{{{k}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}}{{{h}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{d}^{2}}=\dfrac{4{{h}^{2}}{{k}^{2}}-4\left( {{h}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}} \right)\left( {{k}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}} \right)}{{{\left( {{h}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}} \right)}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{d}^{2}}{{\left( {{h}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}} \right)}^{2}}=4{{h}^{2}}{{k}^{2}}+4\left( {{k}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}} \right)\left( {{h}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{d}^{2}}{{\left( {{h}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}} \right)}^{2}}=4\left( {{h}^{2}}{{k}^{2}}-{{h}^{2}}{{k}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}{{k}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}} \right)$
On simplifying,
$\Rightarrow {{d}^{2}}{{\left( {{h}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}} \right)}^{2}}=4\left( {{a}^{2}}{{k}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}} \right)$
Replacing (h, k) by (x, y) to get locus: -
$\Rightarrow {{d}^{2}}{{\left( {{x}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}} \right)}^{2}}=4\left( {{x}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}} \right)\left( {{y}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}} \right)+4{{x}^{2}}{{y}^{2}}$
Now the required locus is ${{d}^{2}}{{\left( {{x}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}} \right)}^{2}}=4\left( {{x}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}} \right)\left( {{y}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}} \right)+4{{x}^{2}}{{y}^{2}}$
Note: Eliminating ${{\theta }_{1}}\And {{\theta }_{2}}$ by using the given relation ${{\tan }^{2}}{{\theta }_{1}}+{{\tan }^{2}}{{\theta }_{1}}=\lambda$ with the help of quadratic formed in ‘m’ i.e. $y=mx\pm \sqrt{{{a}^{2}}{{m}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}$ or ${{\left( y-mx \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}{{m}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}$ by using properties of roots is the key point of this equation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




