
The Sun subtends an angle of half a degree at the pole of a concave mirror which has a radius of curvature of $15{\text{ }}m$. Then the size (diameter) of the image of the Sun formed by the concave mirror is.
A. $7.5{\text{ }}cm$
B. $6.55{\text{ }}cm$
C. $3.7{\text{ }}cm$
D. $13.1{\text{ }}cm$
Answer
492.9k+ views
Hint: We have to first draw a diagram of the problem given. By using the concept that when an object is placed at infinity from the surface of a mirror the image forms at the focus of the mirror, we will find the construction of the diagram. Then by using trigonometric concepts we will find the answer.
Complete answer:
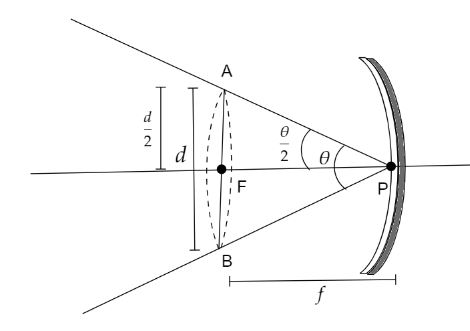
The Sun is at infinity which is the object. When an object is at infinity, the image formed due to a concave mirror after reflection from it is at the focus.The pole of the mirror is given as P and the focus as F. Let $d$ be the diameter of the image of the Sun.In the given, the radius of curvature $r = 15{\text{ }}m$
Let the focal length of the mirror be $f$.The relation between radius of curvature $r$ and focal length $f$ is $f = \dfrac{r}{2}$.
So, the focal length $f$ of the mirror$ = \dfrac{{15}}{2} = 7.5{\text{ }}m$
As per the given question, the sun is subtending ${\dfrac{1}{2}^ \circ }$ at the pole.
So, $\dfrac{\theta }{2} = {\dfrac{1}{2}^ \circ } - - - - - \left( 1 \right)$
Converting the given angle in radian we get,
${\dfrac{1}{2}^ \circ } = \dfrac{\pi }{{180}} \times \dfrac{1}{2} = \dfrac{\pi }{{360}}$ radian$ - - - - - \left( 2 \right)$
Now, from the given triangle AFP we get,
$\tan \dfrac{\theta }{2} = \dfrac{{AF}}{{FP}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{d}{2}}}{f}$
Now, as $\tan \dfrac{\theta }{2}$ is very small, so we consider $\tan \dfrac{\theta }{2} = \dfrac{\theta }{2}$
Hence, we get,
$\dfrac{\theta }{2} = \dfrac{d}{{2f}}$
From$\left( 1 \right)$we get,
${\dfrac{1}{2}^ \circ } = \dfrac{d}{{2f}}$
Again, from $\left( 2 \right)$ we get,
$\dfrac{\pi }{{360}} = \dfrac{d}{{2f}}$
Substituting the value of $f$ we get,
$\dfrac{\pi }{{360}} = \dfrac{d}{{2 \times 7.5}} = \dfrac{d}{{15}}$
$ \therefore d = \dfrac{{22}}{{7 \times 24}} = 0.131$
The diameter of the image of the Sun$ = 0.131{\text{ }}m = 13.1{\text{ }}cm$
Therefore, the correct option is D.
Note: It must be noted that when an object is placed at infinity to a concave mirror the image will always form at the focus of the mirror. The ray of the light is normally considered to be parallel as it comes from infinity. When the angle subtended is very small, then we can omit the trigonometric identity as the difference in value is almost the same.
Complete answer:

The Sun is at infinity which is the object. When an object is at infinity, the image formed due to a concave mirror after reflection from it is at the focus.The pole of the mirror is given as P and the focus as F. Let $d$ be the diameter of the image of the Sun.In the given, the radius of curvature $r = 15{\text{ }}m$
Let the focal length of the mirror be $f$.The relation between radius of curvature $r$ and focal length $f$ is $f = \dfrac{r}{2}$.
So, the focal length $f$ of the mirror$ = \dfrac{{15}}{2} = 7.5{\text{ }}m$
As per the given question, the sun is subtending ${\dfrac{1}{2}^ \circ }$ at the pole.
So, $\dfrac{\theta }{2} = {\dfrac{1}{2}^ \circ } - - - - - \left( 1 \right)$
Converting the given angle in radian we get,
${\dfrac{1}{2}^ \circ } = \dfrac{\pi }{{180}} \times \dfrac{1}{2} = \dfrac{\pi }{{360}}$ radian$ - - - - - \left( 2 \right)$
Now, from the given triangle AFP we get,
$\tan \dfrac{\theta }{2} = \dfrac{{AF}}{{FP}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{d}{2}}}{f}$
Now, as $\tan \dfrac{\theta }{2}$ is very small, so we consider $\tan \dfrac{\theta }{2} = \dfrac{\theta }{2}$
Hence, we get,
$\dfrac{\theta }{2} = \dfrac{d}{{2f}}$
From$\left( 1 \right)$we get,
${\dfrac{1}{2}^ \circ } = \dfrac{d}{{2f}}$
Again, from $\left( 2 \right)$ we get,
$\dfrac{\pi }{{360}} = \dfrac{d}{{2f}}$
Substituting the value of $f$ we get,
$\dfrac{\pi }{{360}} = \dfrac{d}{{2 \times 7.5}} = \dfrac{d}{{15}}$
$ \therefore d = \dfrac{{22}}{{7 \times 24}} = 0.131$
The diameter of the image of the Sun$ = 0.131{\text{ }}m = 13.1{\text{ }}cm$
Therefore, the correct option is D.
Note: It must be noted that when an object is placed at infinity to a concave mirror the image will always form at the focus of the mirror. The ray of the light is normally considered to be parallel as it comes from infinity. When the angle subtended is very small, then we can omit the trigonometric identity as the difference in value is almost the same.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




