
The sun is ${{60^\circ }}$ above the horizon. A ray of sunlight on refraction at a surface of water (refractive index, 4/3) will suffer a deviation of-
A. ${{60^\circ - si}}{{{n}}^{{{ - 1}}}}\left( {\dfrac{{{3}}}{{{8}}}}
\right)$
B. ${{30^\circ - si}}{{{n}}^{{{ - 1}}}}\left( {\dfrac{{{{3}}\sqrt {{3}}
}}{{{8}}}} \right)$
C. ${{30^\circ - si}}{{{n}}^{{{ - 1}}}}\left( {\dfrac{{{3}}}{{{8}}}}
\right)$
D. ${{60^\circ - si}}{{{n}}^{{{ - 1}}}}\left( {\dfrac{{{{3}}\sqrt {{3}}
}}{{{8}}}} \right)$
Answer
574.5k+ views
Hint: As value of refractive index is given in this question, ${{\mu = }}\dfrac{{{4}}}{{{3}}}$ . For finding the deviation of ray of sunlight on a surface of water, firstly consider one right angle triangle by considering that the sun is ${{60^\circ }}$above the horizon. After finding the sides of a triangle, we can easily find out the value of all angles of triangles. We will get two equations, by comparing those two we can easily find the deviation.
Complete step by step solution:
Given: the sun is ${{60^\circ }}$above the horizon.
${{\mu = }}\dfrac{{{4}}}{{{3}}}$
Since the sun is ${{60^\circ }}$above the horizon, we can draw a right angled triangle and consider the base of the triangle is horizon whereas the hypotenuse of the triangle and the horizon is making angle of ${{60^\circ }}$ represents the sun is ${{60^\circ }}$ above the horizon,
In the following diagram A is sun, BC is horizon.
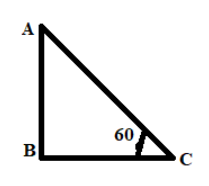
Hence when a ray of sunlight enters into water, the refraction at a surface water takes place. Where the refractive index of water is $\dfrac{{{4}}}{{{3}}}$
Hence ,$\dfrac{{{1}}}{{{\mu }}}{{ = }}\dfrac{{{3}}}{{{4}}}$ ………(I)
Since there is total refraction takes place at the surface of the water,
${{d = }}\dfrac{{{1}}}{{{{2\mu }}}}{{ = }}\dfrac{{{3}}}{{{8}}}$
Now if we consider AB = 4 and BC = 3 according to pythagoras theorem,
${{AC = }}\sqrt {{{{{(AB)}}}^{^{{2}}}}{{ + (BC}}{{{)}}^{{2}}}} $
${{AC = }}\sqrt {{{{{(4)}}}^{^{{2}}}}{{ + (3}}{{{)}}^{{2}}}} {{ = 5}}$
Since sum of all angles of a triangle is equals to ${{180^\circ }}$,
If \[\angle {{C = 60^\circ }}\] and $\angle {{B = 90^\circ }}$then $\angle {{A = 30^\circ }}$
\[{{Sin 30^\circ = }}\dfrac{{{{BC}}}}{{{{AB}}}}\]
\[\therefore {{Sin 30^\circ = }}\dfrac{{{3}}}{{{4}}}\] ……………….(II)
Now from equation (I) and (II),
$\dfrac{{{1}}}{{{\mu }}}{{ = sin30^\circ }}$
$\therefore {{\mu = }}\dfrac{{{1}}}{{{{sin30^\circ }}}}$
${{d = 30^\circ - si}}{{{n}}^{{{ - 1}}}}{{(}}\dfrac{{{3}}}{{{8}}}{{)}}$
Hence option (C) is the correct answer.
Note: It must be noted that while taking the angles in a triangle care should be taken that for what angle we are taking sin and cos must be the corresponding one only. The Pythagorean theorem consists of a formula ${{{x}}^{{2}}}{{ + }}{{{y}}^{{2}}}{{ = }}{{{z}}^{{2}}}$ which is used to figure out the value of (mostly) the hypotenuse side in a right angled triangle. The $x$ and$y$ are the $2$ "non-hypotenuse" sides of the triangle (Opposite side and Adjacent side), and z is the hypotenuse side opposite to right angle.
Complete step by step solution:
Given: the sun is ${{60^\circ }}$above the horizon.
${{\mu = }}\dfrac{{{4}}}{{{3}}}$
Since the sun is ${{60^\circ }}$above the horizon, we can draw a right angled triangle and consider the base of the triangle is horizon whereas the hypotenuse of the triangle and the horizon is making angle of ${{60^\circ }}$ represents the sun is ${{60^\circ }}$ above the horizon,
In the following diagram A is sun, BC is horizon.

Hence when a ray of sunlight enters into water, the refraction at a surface water takes place. Where the refractive index of water is $\dfrac{{{4}}}{{{3}}}$
Hence ,$\dfrac{{{1}}}{{{\mu }}}{{ = }}\dfrac{{{3}}}{{{4}}}$ ………(I)
Since there is total refraction takes place at the surface of the water,
${{d = }}\dfrac{{{1}}}{{{{2\mu }}}}{{ = }}\dfrac{{{3}}}{{{8}}}$
Now if we consider AB = 4 and BC = 3 according to pythagoras theorem,
${{AC = }}\sqrt {{{{{(AB)}}}^{^{{2}}}}{{ + (BC}}{{{)}}^{{2}}}} $
${{AC = }}\sqrt {{{{{(4)}}}^{^{{2}}}}{{ + (3}}{{{)}}^{{2}}}} {{ = 5}}$
Since sum of all angles of a triangle is equals to ${{180^\circ }}$,
If \[\angle {{C = 60^\circ }}\] and $\angle {{B = 90^\circ }}$then $\angle {{A = 30^\circ }}$
\[{{Sin 30^\circ = }}\dfrac{{{{BC}}}}{{{{AB}}}}\]
\[\therefore {{Sin 30^\circ = }}\dfrac{{{3}}}{{{4}}}\] ……………….(II)
Now from equation (I) and (II),
$\dfrac{{{1}}}{{{\mu }}}{{ = sin30^\circ }}$
$\therefore {{\mu = }}\dfrac{{{1}}}{{{{sin30^\circ }}}}$
${{d = 30^\circ - si}}{{{n}}^{{{ - 1}}}}{{(}}\dfrac{{{3}}}{{{8}}}{{)}}$
Hence option (C) is the correct answer.
Note: It must be noted that while taking the angles in a triangle care should be taken that for what angle we are taking sin and cos must be the corresponding one only. The Pythagorean theorem consists of a formula ${{{x}}^{{2}}}{{ + }}{{{y}}^{{2}}}{{ = }}{{{z}}^{{2}}}$ which is used to figure out the value of (mostly) the hypotenuse side in a right angled triangle. The $x$ and$y$ are the $2$ "non-hypotenuse" sides of the triangle (Opposite side and Adjacent side), and z is the hypotenuse side opposite to right angle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




