
The substituent which is predominantly ortho-para directing but deactivating in aromatic electrophilic substitution reaction is:
A.) $ - N{O_2}$
B.) $ - OC{H_3}$
C.) $ - C{H_3}$
D.) $ - Cl$
Answer
542.4k+ views
Hint: The ortho- para directing groups are those in which the substituents are placed at ortho and para position and generally electron donating groups are ortho para directing. Also, the deactivating groups are groups which withdraw the electrons from the ring.
Complete answer:
As we know that the ortho-para directing groups are those groups which favors the attack of electrophile at ortho and para position in the aromatic electrophilic substitution reaction and the meta directing groups favors the attack of electrophile at meta position in the aromatic electrophilic substitution reaction.
Also, the deactivating groups are those groups which deactivate the ring by the inductive effect in the presence of an electronegative group. This is because the electronegative group attracts the electrons away from the ring and makes the ring less stable.
In case of Chlorine ($Cl$) , due to its electronegative nature, it shows negative inductive effect ($ - I$) and withdraws the electrons away from the ring thus it makes the ring deactivating towards aromatic electrophilic substitution .
Also, the Chlorine group has a lone pair on it. Chlorine donate its lone pair to the aromatic ring and hence increase the electron density at ortho and para position. Therefore, chlorine is a deactivating group. The resonating structures of chlorobenzene can be shown as:
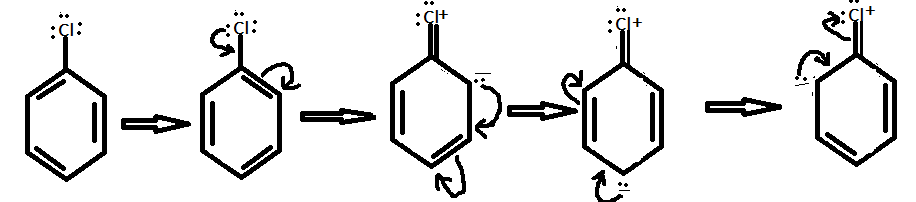
Hence, option (D) is the correct option.
Note:
Always remember that chlorine is an electronegative element due to which it attracts the electrons from the ring and deactivates the ring to which it is attached and also it has a lone pair and by donating that lone pair it makes the ring predominantly ortho para directing.
Complete answer:
As we know that the ortho-para directing groups are those groups which favors the attack of electrophile at ortho and para position in the aromatic electrophilic substitution reaction and the meta directing groups favors the attack of electrophile at meta position in the aromatic electrophilic substitution reaction.
Also, the deactivating groups are those groups which deactivate the ring by the inductive effect in the presence of an electronegative group. This is because the electronegative group attracts the electrons away from the ring and makes the ring less stable.
In case of Chlorine ($Cl$) , due to its electronegative nature, it shows negative inductive effect ($ - I$) and withdraws the electrons away from the ring thus it makes the ring deactivating towards aromatic electrophilic substitution .
Also, the Chlorine group has a lone pair on it. Chlorine donate its lone pair to the aromatic ring and hence increase the electron density at ortho and para position. Therefore, chlorine is a deactivating group. The resonating structures of chlorobenzene can be shown as:

Hence, option (D) is the correct option.
Note:
Always remember that chlorine is an electronegative element due to which it attracts the electrons from the ring and deactivates the ring to which it is attached and also it has a lone pair and by donating that lone pair it makes the ring predominantly ortho para directing.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




