
The structure of Lactic acid is shown.
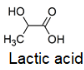
Which esters might form when lactic acid is heated?
$1.$$C{{H}_{3}}CH\left( OH \right)C{{O}_{2}}CH\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)COOH$
$2.$
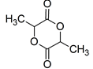
$3.$$C{{H}_{3}}CH\left( OH \right)C{{O}_{2}}CH\left( OH \right)C{{H}_{3}}$
A. $1,2$ and $3$ are correct.
B. $1\And 2$ are only correct.
C. $2\And 3$ are correct.
D. $1$ only is correct.


Answer
546.3k+ views
Hint: The question given to us states that what products are formed when lactic acid is heated. We know that Lactic acid is a carboxylic acid. So, the reaction that carboxylic acid shows on heating, the same reaction will be shown by lactic acid even. But we need to keep in mind the type of carboxylic acid lactic acid is, as different types of carboxylic acids give different products on heating.
Complete step-by-step answer:We know that carbonyl compounds containing the $-COOH$groups are termed as carboxylic acids.
Before, we solve the question it is important to know about the types of carboxylic acids
There are different types of carboxylic acids depending on the position of the hydroxyl group. These are as follows:
1. $2$-hydroxycarboxylic acids
2. $3$-hydroxycarboxylic acids
3. $4$-hydroxycarboxylic acids
4. $5$-hydroxycarboxylic acids.
Now, let us see what types of reactions they show on heating.
The $2-,3-,4-,\And 5-$ hydroxycarboxylic acids all lose water upon heating, although the products are not the same.
The $2-$ hydroxycarboxylic acids form cyclic dimeric esters (formed by the esterification of two molecules of the acids) called lactides whereas,
The $3-\And 4-$ hydroxy acids undergo intramolecular esterification to give cyclic esters called lactones.
Now, if we see the structure of lactic acid from the question, we see that the $-OH$ group is present on the 2nd carbon atom of the chain, and hence it is $2-$hydroxycarboxylic acid.
We have already seen above that 2-hydroxycarboxylic acids undergo dimerization forms lactides on heating. This means lactic acid on heating will dimerize and form the lactide, which is represented by the structure given on image 2 in question.
The reaction can be represented as follows:
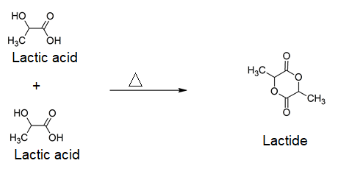
It should be noted that when lactic acid gets heated, apart from 2-hydroxycarboxylic acid (lactic acid), $C{{H}_{3}}CH\left( OH \right)C{{O}_{2}}CH\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)COOH$ is also formed along with it as a minor product.
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note: The above reaction takes place so readily and quickly. If suppose we want to stop lactic acid to form cyclic esters after heating, then the only way is to convert them to their sodium or potassium salts. As a fact we should note that Lactides are used in the manufacturing of the biodegradable polymers which are eco-friendly.
Complete step-by-step answer:We know that carbonyl compounds containing the $-COOH$groups are termed as carboxylic acids.
Before, we solve the question it is important to know about the types of carboxylic acids
There are different types of carboxylic acids depending on the position of the hydroxyl group. These are as follows:
1. $2$-hydroxycarboxylic acids
2. $3$-hydroxycarboxylic acids
3. $4$-hydroxycarboxylic acids
4. $5$-hydroxycarboxylic acids.
Now, let us see what types of reactions they show on heating.
The $2-,3-,4-,\And 5-$ hydroxycarboxylic acids all lose water upon heating, although the products are not the same.
The $2-$ hydroxycarboxylic acids form cyclic dimeric esters (formed by the esterification of two molecules of the acids) called lactides whereas,
The $3-\And 4-$ hydroxy acids undergo intramolecular esterification to give cyclic esters called lactones.
Now, if we see the structure of lactic acid from the question, we see that the $-OH$ group is present on the 2nd carbon atom of the chain, and hence it is $2-$hydroxycarboxylic acid.
We have already seen above that 2-hydroxycarboxylic acids undergo dimerization forms lactides on heating. This means lactic acid on heating will dimerize and form the lactide, which is represented by the structure given on image 2 in question.
The reaction can be represented as follows:

It should be noted that when lactic acid gets heated, apart from 2-hydroxycarboxylic acid (lactic acid), $C{{H}_{3}}CH\left( OH \right)C{{O}_{2}}CH\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)COOH$ is also formed along with it as a minor product.
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note: The above reaction takes place so readily and quickly. If suppose we want to stop lactic acid to form cyclic esters after heating, then the only way is to convert them to their sodium or potassium salts. As a fact we should note that Lactides are used in the manufacturing of the biodegradable polymers which are eco-friendly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




