
The structure of diborane $({B_2}{H_6})$ contains:
A.Four 2C-2e bonds and two 3C-2e bonds
B.Two 2C-2e bonds and 3C-2e bonds
C.Two 2C-2e bonds and four 3C-2e bonds
D.Four 2C-2e bonds and four 3C-2e bonds.
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: Diborane is a chemical compound that consists of boron and hydrogen atoms. Its molecular formula is $({B_2}{H_6})$. The structure of diborane is based on hybridization.
Complete step by step answer:
Since the atomic number of boron is 5 and the electronic configuration of boron is in the ground state is $1{s^2},2{s^2},2{p^1}$. In the excited state, the electron from 2s orbital jumps in 2p orbital hence in the excited state the electronic configuration is $1{s^2},2{s^1},2p{}_x^1,2p_y^1,2p_z^0$ and it undergoes $s{p^3}$ hybridization.
The two half-filled hybrid orbitals of each boron atom overlap with the half-filled orbitals of hydrogen atom forming a normal covalent bond whereas third half-filled hybrid orbital of boron atom and vacant hybrid orbital of second boron atom overlap simultaneously with the half-filled orbital of H- atom, thus the electron cloud contain two electrons but spread over three atoms that why this bond is called three centres electron-pair bond. The structure of diborane.
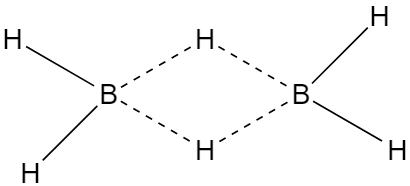
The bond length of terminal B-H bond is 119pm. And the distance between two boron atoms is 178pm.
Hence the correct answer is option A.
Note:
Alternatively, according to X-ray diffraction studies, there are two types of hydrogen atoms i.e., four-terminal hydrogen atoms and two bridge hydrogen atoms. The four-terminal hydrogen atom forms a normal covalent bond with boron hence it is quite strong whereas each bridge hydrogen atom is bonded to two boron atoms by a pair of electrons. In other words there are three centre electron-pair bonds and due to resemblance with bananas, it is also known as a banana bond. The three centre electron-pair bond is quite different from the normal covalent bond hence it is a weak bond.
Complete step by step answer:
Since the atomic number of boron is 5 and the electronic configuration of boron is in the ground state is $1{s^2},2{s^2},2{p^1}$. In the excited state, the electron from 2s orbital jumps in 2p orbital hence in the excited state the electronic configuration is $1{s^2},2{s^1},2p{}_x^1,2p_y^1,2p_z^0$ and it undergoes $s{p^3}$ hybridization.
The two half-filled hybrid orbitals of each boron atom overlap with the half-filled orbitals of hydrogen atom forming a normal covalent bond whereas third half-filled hybrid orbital of boron atom and vacant hybrid orbital of second boron atom overlap simultaneously with the half-filled orbital of H- atom, thus the electron cloud contain two electrons but spread over three atoms that why this bond is called three centres electron-pair bond. The structure of diborane.

The bond length of terminal B-H bond is 119pm. And the distance between two boron atoms is 178pm.
Hence the correct answer is option A.
Note:
Alternatively, according to X-ray diffraction studies, there are two types of hydrogen atoms i.e., four-terminal hydrogen atoms and two bridge hydrogen atoms. The four-terminal hydrogen atom forms a normal covalent bond with boron hence it is quite strong whereas each bridge hydrogen atom is bonded to two boron atoms by a pair of electrons. In other words there are three centre electron-pair bonds and due to resemblance with bananas, it is also known as a banana bond. The three centre electron-pair bond is quite different from the normal covalent bond hence it is a weak bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




