
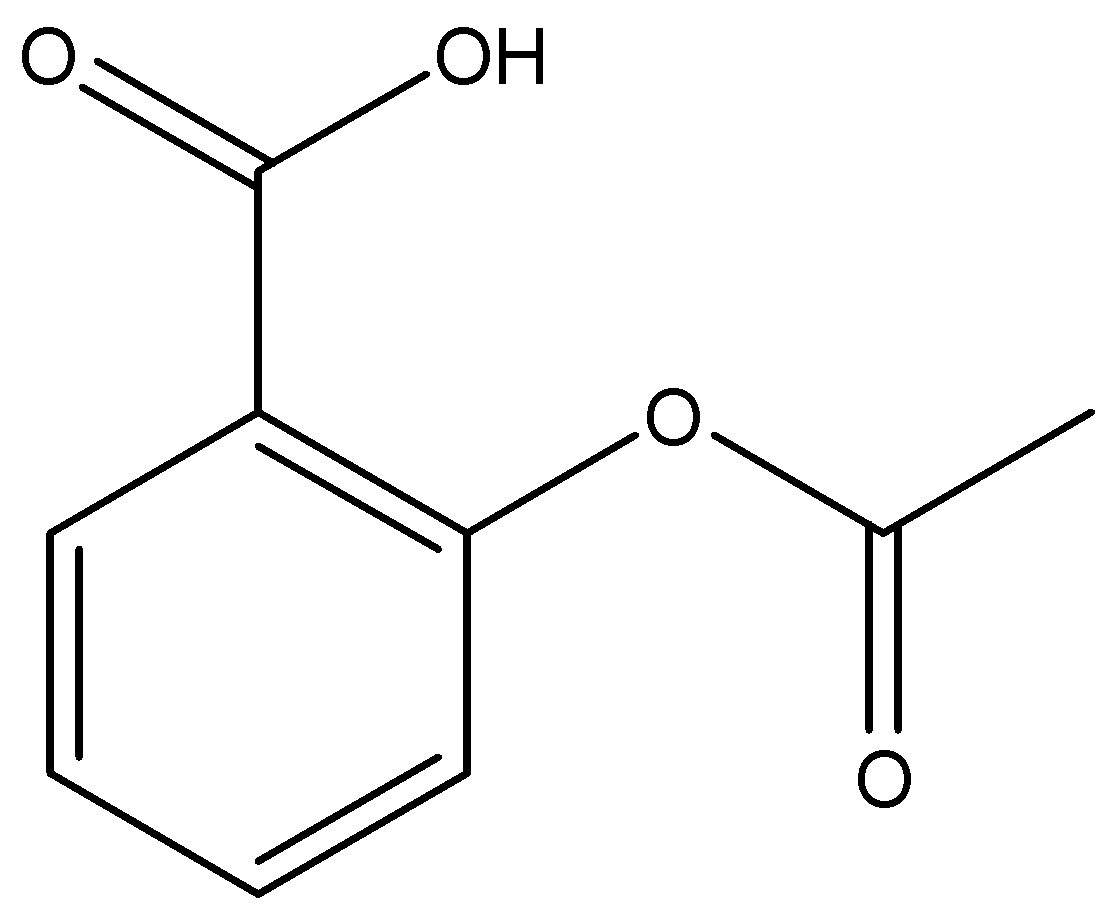
The structure of Aspirin is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)




Answer
588k+ views
Hint: The compound is a derivative of the carbonyl group. The structure consists of two functional groups attached to the benzene ring out of which one functional group is present which indicates sweet odour in general.
Complete step by step answer:
Aspirin has a chemical name as acetylsalicylic acid. Aspirin is used in medication. This drug reduces the pain, fever and inflammation. Aspirin is also used in the treatment of Kawasaki disease. Aspirin is useful for long term prevention of heart attack, blood clots and ischemic strokes. Aspirin is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug.
Preparation of Aspirin:
The preparation of aspirin is an esterification reaction. Esterification is the reaction when an alcohol reacts with carboxylic acid to give ester and water. Esters are the compounds having sweet odour because of which they are used in perfumes and in cosmetics. Esterification can be done by three methods:
1) From acid anhydride and alcohol
2) From acid chloride and alcohol
3) From carboxylic acid and alcohol.
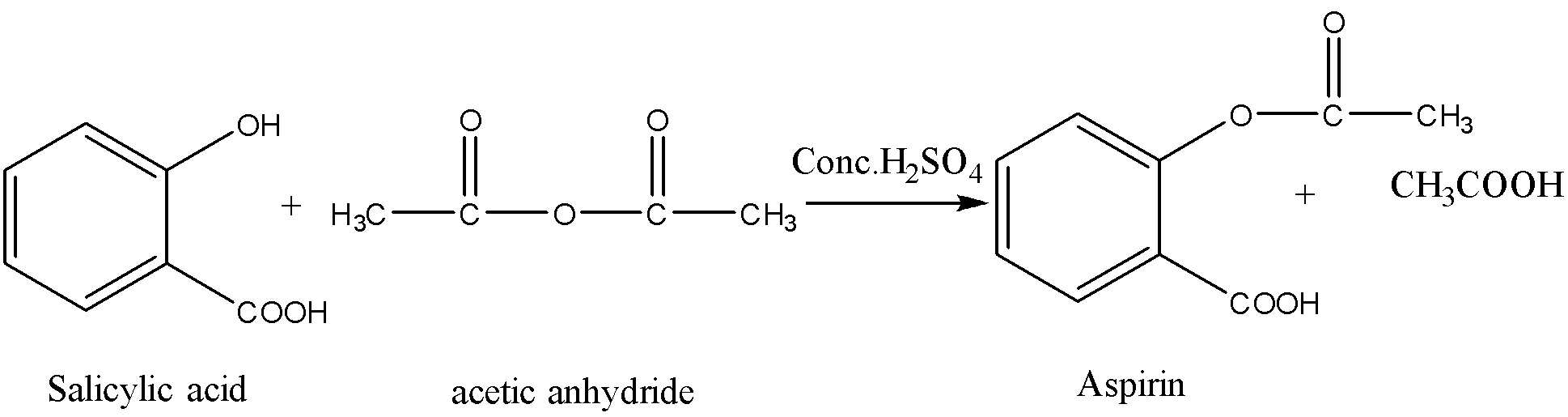
Aspirin is prepared by using the first method. That is from acid anhydride and alcohol. Here the role of alcohol is fulfilled by salicylic acid. Salicylic acid consists of two functional groups – phenol and carboxylic acid. Among both the groups only phenolic groups take part in this reaction.
Aspirin can be prepared from salicylic acid. Salicylic acid on reaction with acetic anhydride in presence of concentrated sulphuric acid gives aspirin. Salicylic acid is a phenolic acid. Here the hydroxyl group of salicylic acid is converted to the ester group. Acetic acid is the byproduct. Sulfuric acid in small amounts is used as a catalyst.
Physical properties of Aspirin: Aspirin is white, crystalline and weakly acidic substance.
Chemical properties of Aspirin: Aspirin decomposes in ammonium acetate, carbonates, hydroxides of alkali metal and citrates. It is stable in dry air but gets hydrolysed in presence of moisture. Formation of high concentrated aspirin smells like vinegar.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Due to the addition of a small amount of acid in the reaction, the carbon of one of the carbonyl groups of anhydride is more positive. Because of this the nucleophilic strength of the phenolic group becomes more dominant. Also the reaction of acid anhydride with alcohol is slower as compared with acid chloride.
Complete step by step answer:
Aspirin has a chemical name as acetylsalicylic acid. Aspirin is used in medication. This drug reduces the pain, fever and inflammation. Aspirin is also used in the treatment of Kawasaki disease. Aspirin is useful for long term prevention of heart attack, blood clots and ischemic strokes. Aspirin is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug.
Preparation of Aspirin:
The preparation of aspirin is an esterification reaction. Esterification is the reaction when an alcohol reacts with carboxylic acid to give ester and water. Esters are the compounds having sweet odour because of which they are used in perfumes and in cosmetics. Esterification can be done by three methods:
1) From acid anhydride and alcohol
2) From acid chloride and alcohol
3) From carboxylic acid and alcohol.
Aspirin is prepared by using the first method. That is from acid anhydride and alcohol. Here the role of alcohol is fulfilled by salicylic acid. Salicylic acid consists of two functional groups – phenol and carboxylic acid. Among both the groups only phenolic groups take part in this reaction.
Aspirin can be prepared from salicylic acid. Salicylic acid on reaction with acetic anhydride in presence of concentrated sulphuric acid gives aspirin. Salicylic acid is a phenolic acid. Here the hydroxyl group of salicylic acid is converted to the ester group. Acetic acid is the byproduct. Sulfuric acid in small amounts is used as a catalyst.

Physical properties of Aspirin: Aspirin is white, crystalline and weakly acidic substance.
Chemical properties of Aspirin: Aspirin decomposes in ammonium acetate, carbonates, hydroxides of alkali metal and citrates. It is stable in dry air but gets hydrolysed in presence of moisture. Formation of high concentrated aspirin smells like vinegar.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Due to the addition of a small amount of acid in the reaction, the carbon of one of the carbonyl groups of anhydride is more positive. Because of this the nucleophilic strength of the phenolic group becomes more dominant. Also the reaction of acid anhydride with alcohol is slower as compared with acid chloride.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




