
The stem of Turmeric is
(a)Corm
(b)Bulb
(c)Rhizome
(d)Tuber
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: It is an underground stem, which bears nodes and internodes and is fleshy due to the storage of food. It shows branching and is placed horizontally into the soil.
Complete answer:
Turmeric stem is an example of a rhizome. These give the appearance of sympodial axis rhizome, which means the lateral branches appear opposite to the leaves. The rhizome is also known as rootstock. Edible canna, ginger, and water lily are also rhizomes. The branching of rhizomes may be monopodial or sympodial.
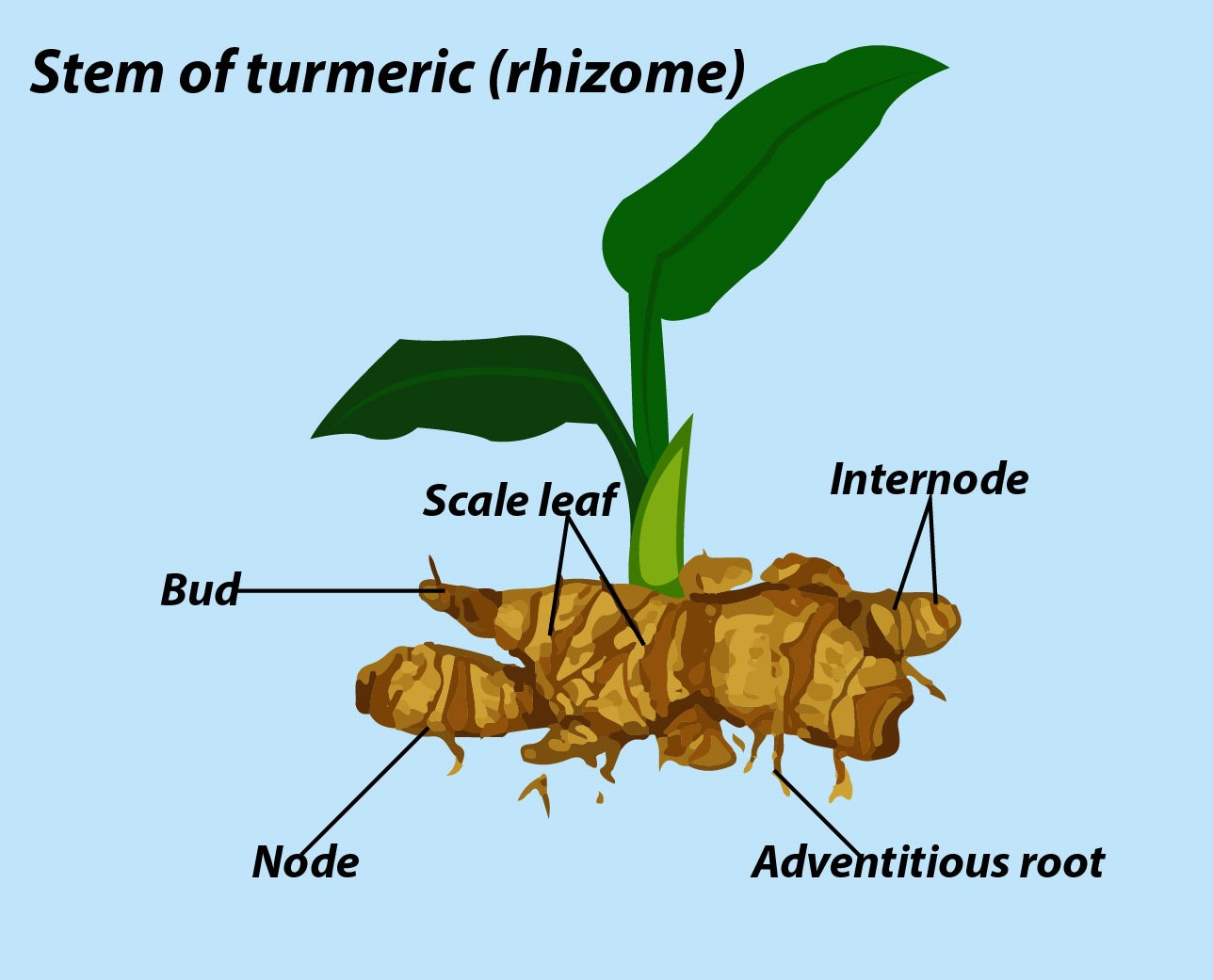
Additional Information:
-A corm is short, thick, and unbranched. The corm bears buds at its nodes. Alocasia, Gladiolus, Colocasia, Crocus, Colchicum, and Freesia are examples of the corm. A Corm is covered by thin sheathing leaves called scales.
-A bulb may be regarded as a short underground with a fleshy leaf base called scales. A bulb contains a reduced and disc-like stem. The discoidal shape of the bulb is convex or conical in shape that bears highly compressed internodes.
-Potato is an example of a tuber. When the underground stem becomes enlarged at the growing tips by the accumulation of stored food, commonly starch, it is called a tuber. In potato, several lenticels are present for gaseous exchange. Cyperus, Helianthus, Stachys are examples of tubers. In tubers, eye buds develop into small shoots, and from its base, adventitious roots develop.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Rhizome.’
Note: -Turmeric is yellow colored due to the presence of a compound called curcumin. It is a common Indian spice. The scientific name of turmeric is Curcuma longa.
-A bulb is of two types: tunicated and scaly. In the tunicated type, concentric layers are present and in scaly type, a series of angular scales are present.
Complete answer:
Turmeric stem is an example of a rhizome. These give the appearance of sympodial axis rhizome, which means the lateral branches appear opposite to the leaves. The rhizome is also known as rootstock. Edible canna, ginger, and water lily are also rhizomes. The branching of rhizomes may be monopodial or sympodial.

Additional Information:
-A corm is short, thick, and unbranched. The corm bears buds at its nodes. Alocasia, Gladiolus, Colocasia, Crocus, Colchicum, and Freesia are examples of the corm. A Corm is covered by thin sheathing leaves called scales.
-A bulb may be regarded as a short underground with a fleshy leaf base called scales. A bulb contains a reduced and disc-like stem. The discoidal shape of the bulb is convex or conical in shape that bears highly compressed internodes.
-Potato is an example of a tuber. When the underground stem becomes enlarged at the growing tips by the accumulation of stored food, commonly starch, it is called a tuber. In potato, several lenticels are present for gaseous exchange. Cyperus, Helianthus, Stachys are examples of tubers. In tubers, eye buds develop into small shoots, and from its base, adventitious roots develop.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Rhizome.’
Note: -Turmeric is yellow colored due to the presence of a compound called curcumin. It is a common Indian spice. The scientific name of turmeric is Curcuma longa.
-A bulb is of two types: tunicated and scaly. In the tunicated type, concentric layers are present and in scaly type, a series of angular scales are present.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




