
The species that can have trans-isomer is :
( $\text{en = ethane - 1,2 - diamine, ox = oxalate}$ )
A.) $[Pt(en)C{l_2}]$
B.) ${[Cr{(en)_2}(ox)]^ + }$
C.) $[Zn(en)C{l_2}]$
D.) ${[Pt{(en)_2}C{l_2}]^{2 + }}$
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: In the trans – isomer the same functional groups are on the same side of the carbon chain on the other hand cis-isomer is the opposite of trans isomer. In cis-isomer the same functional groups are on the different side of the carbon chain.
Complete step by step answer:
The cis- isomerism and trans isomerism are types of stereoisomerism in which ligand have same bond, but different orientation relative to one another. Here, ligands mean the ion or molecule which is attached to a metal atom by a coordinate bond.
In cis-isomerism, the two similar ligands are on the same side of the complex or at the same side of the carbon chain and in trans-isomerism, the two similar ligands are on the opposite side of the complex.
Here, in this question the $en$ that is ( $\text{ethane - 1,2 - diamine}$ ) and also $ox$ that is ( $\text{oxalate ion}$ ) both are bi-dendate ligand. Bidentate ligands are those ligands which are Lewis bases and can donate two pairs of electrons to a metal atom.
In option A.) $[Pt(en)C{l_2}]$ can be represented as follows:
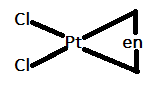
In this case, the bidentate ligand that is $en$ is coordinating at an angle of $90^\circ $. Therefore, it will not show trans isomerism.
In option B.) ${[Cr{(en)_2}(ox)]^ + }$ can be represented as:
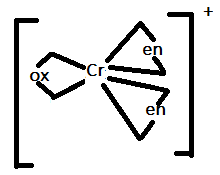
In this option, there are only three ligands present that are bidentate ligands. Therefore, it will also not show trans-isomerism.
In option C.) $[Zn(en)C{l_2}]$ can be represented as:
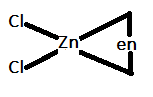
In this option, the central metal atom is $s{p^3}$ hybridized and only three ligands are attached to the central atom. Therefore, it will also not show trans-isomerism.
In option D.) ${[Pt{(en)_2}C{l_2}]^{2 + }}$ can be represented as:
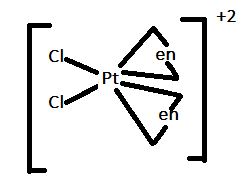
In this case, there are four ligands attached to a central metal atom. Therefore, it can show both trans-isomerism and cis-isomerism as shown above.
Hence, option D is the correct answer.
Note: Always remember that in case of trans-isomerism, if there is a central metal atom then that should have four groups attached to it whether it is a hydrogen or any other functional group with the same functional group on the same side of the carbon chain.
Complete step by step answer:
The cis- isomerism and trans isomerism are types of stereoisomerism in which ligand have same bond, but different orientation relative to one another. Here, ligands mean the ion or molecule which is attached to a metal atom by a coordinate bond.
In cis-isomerism, the two similar ligands are on the same side of the complex or at the same side of the carbon chain and in trans-isomerism, the two similar ligands are on the opposite side of the complex.
Here, in this question the $en$ that is ( $\text{ethane - 1,2 - diamine}$ ) and also $ox$ that is ( $\text{oxalate ion}$ ) both are bi-dendate ligand. Bidentate ligands are those ligands which are Lewis bases and can donate two pairs of electrons to a metal atom.
In option A.) $[Pt(en)C{l_2}]$ can be represented as follows:

In this case, the bidentate ligand that is $en$ is coordinating at an angle of $90^\circ $. Therefore, it will not show trans isomerism.
In option B.) ${[Cr{(en)_2}(ox)]^ + }$ can be represented as:

In this option, there are only three ligands present that are bidentate ligands. Therefore, it will also not show trans-isomerism.
In option C.) $[Zn(en)C{l_2}]$ can be represented as:

In this option, the central metal atom is $s{p^3}$ hybridized and only three ligands are attached to the central atom. Therefore, it will also not show trans-isomerism.
In option D.) ${[Pt{(en)_2}C{l_2}]^{2 + }}$ can be represented as:

In this case, there are four ligands attached to a central metal atom. Therefore, it can show both trans-isomerism and cis-isomerism as shown above.
Hence, option D is the correct answer.
Note: Always remember that in case of trans-isomerism, if there is a central metal atom then that should have four groups attached to it whether it is a hydrogen or any other functional group with the same functional group on the same side of the carbon chain.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




