
The soap molecule has a:
A) Hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail
B) Hydrophobic head and a hydrophilic tail
C) Hydrophobic head and a hydrophobic tail
D) Hydrophilic head and a hydrophilic tail
Answer
596.1k+ views
Hint: The soap are water-soluble compounds that are derivative of fatty acid. In aqueous solution, they break down in soap anion and cation. The soap anion has a polar head and the tail is a large hydrocarbon chain. It is non-polar and water-repelling in nature.
Complete step by step answer:
Soaps or detergents are the large hydrocarbon chains. This is a derivative of fatty acid. The soap has a large hydrocarbon tail and a negative charge head.
The soap in solution dissolves into soap anions and sodium cations. For example sodium palmitate
$\text{ }\begin{matrix}
\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{(C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{)}}_{\text{14}}}\text{COO-N}{{\text{a}}^{\text{+}}} & \to & \text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{(C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{)}}_{\text{14}}}\text{COO-} & \text{+} & \text{N}{{\text{a}}^{\text{+}}} \\
\text{(Sodium palmitate)} & {} & \text{Palmitate ion} & {} & \text{Sodium ion} \\
\end{matrix}$
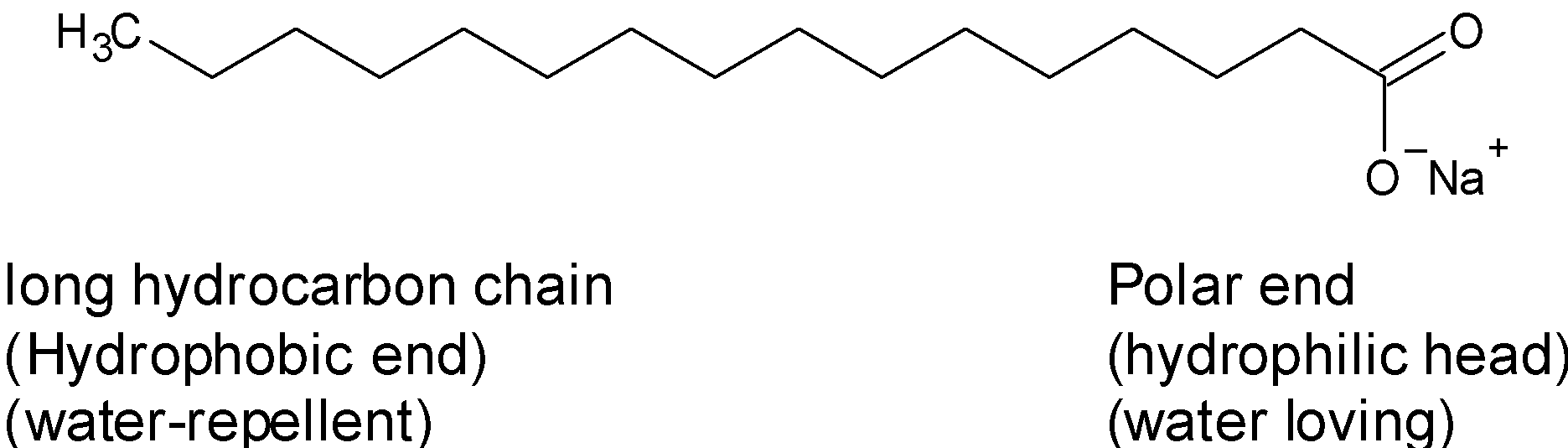
The hydrocarbon tail is made of the long carbon chain and it is nonpolar. Since it is a carbon chain it doesn’t have the affinity towards the water. Therefore, it is also called the hydrophobic end (or water-hating or repelling). It is readily soluble in oil and grease.
The sops are fatty acid derivatives therefore one end of the hydrocarbon chain bonded to the carboxylic acid $\text{(}-\text{CO}{{\text{O}}^{-}}\text{N}{{\text{a}}^{\text{+}}})$ , therefore the negatively charged head is polar. It has a great affinity towards the water. It is also known as the hydrophilic end (water-loving). It is readily soluble in water.
Therefore, the soap molecule has a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail
Hence, (A) is the correct option.
Additional information:
In aqueous solution, water molecules are polar thus they surround the head of the molecule and repel the hydrocarbon tail. Therefore when soap or detergent is dissolved in water, the molecules associate to form a cluster of molecules called as the micelles as shown below,
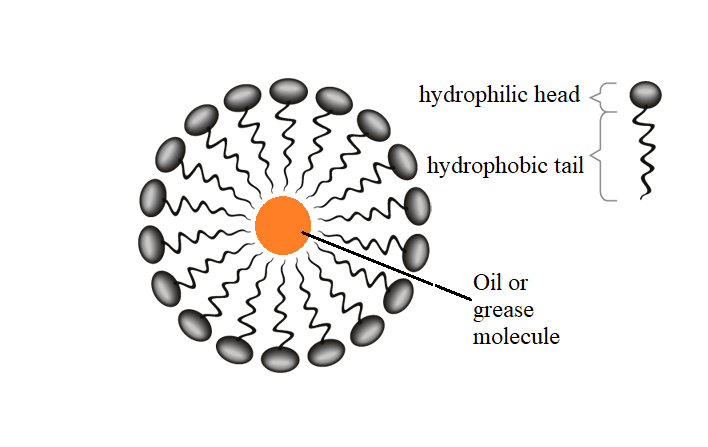
In cleansing, the micelles are arranged in such a way that the hydrophobic tail (hydrocarbon chain) is attached to the oily dirt and the hydrophilic head is moving outward. When the water is shaken vigorously the oily dirt is displaced from the surface and dissociates into the fragments. Thus, more hydrophobic tails can be attached to the oil that prevent the further aggregation of the molecule and removes the dirt from the fabric.
Note: The micelle is a unique capacity of a soap anion to aggregate in solution. They are uniquely oriented such that the hydrophilic head is outward and the hydrophobic tail is inward towards the oil.
Complete step by step answer:
Soaps or detergents are the large hydrocarbon chains. This is a derivative of fatty acid. The soap has a large hydrocarbon tail and a negative charge head.
The soap in solution dissolves into soap anions and sodium cations. For example sodium palmitate
$\text{ }\begin{matrix}
\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{(C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{)}}_{\text{14}}}\text{COO-N}{{\text{a}}^{\text{+}}} & \to & \text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{(C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{)}}_{\text{14}}}\text{COO-} & \text{+} & \text{N}{{\text{a}}^{\text{+}}} \\
\text{(Sodium palmitate)} & {} & \text{Palmitate ion} & {} & \text{Sodium ion} \\
\end{matrix}$

The hydrocarbon tail is made of the long carbon chain and it is nonpolar. Since it is a carbon chain it doesn’t have the affinity towards the water. Therefore, it is also called the hydrophobic end (or water-hating or repelling). It is readily soluble in oil and grease.
The sops are fatty acid derivatives therefore one end of the hydrocarbon chain bonded to the carboxylic acid $\text{(}-\text{CO}{{\text{O}}^{-}}\text{N}{{\text{a}}^{\text{+}}})$ , therefore the negatively charged head is polar. It has a great affinity towards the water. It is also known as the hydrophilic end (water-loving). It is readily soluble in water.
Therefore, the soap molecule has a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail
Hence, (A) is the correct option.
Additional information:
In aqueous solution, water molecules are polar thus they surround the head of the molecule and repel the hydrocarbon tail. Therefore when soap or detergent is dissolved in water, the molecules associate to form a cluster of molecules called as the micelles as shown below,

In cleansing, the micelles are arranged in such a way that the hydrophobic tail (hydrocarbon chain) is attached to the oily dirt and the hydrophilic head is moving outward. When the water is shaken vigorously the oily dirt is displaced from the surface and dissociates into the fragments. Thus, more hydrophobic tails can be attached to the oil that prevent the further aggregation of the molecule and removes the dirt from the fabric.
Note: The micelle is a unique capacity of a soap anion to aggregate in solution. They are uniquely oriented such that the hydrophilic head is outward and the hydrophobic tail is inward towards the oil.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




