
The small bulb-like projection coming out from the yeast cell is called
A. Bud
B. Roots
C. Leaf
D. Stem
Answer
562.8k+ views
Hint: Yeasts are single-celled organisms. They play a very important role in the fermentation process. Yeasts are mostly used in baking factories.
Complete answer: Budding is a type of asexual reproduction in which a new organism emerges from an outgrowth or bud due to the fact of cell division in a particular region. The tiny bulb-like projections from the yeast cell body are recognized as a bud.
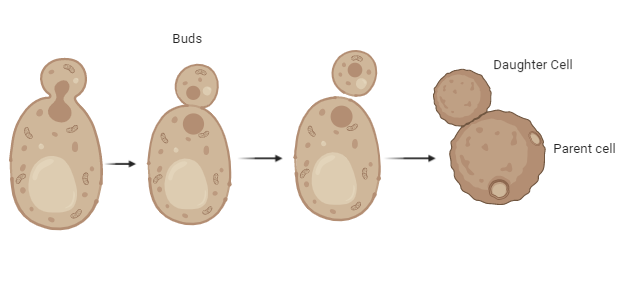
Yeasts may have asexual and sexual reproductive cycles, as with other fungi. Asexual reproduction through budding is the most common mode of reproduction in yeast. The parent cell divides first and then the nucleus migrates to the daughter cell. Then, the bud continues to develop till the cell divides and becomes a new daughter cell. In general, at some stage in the budding process, the daughter cell is smaller than the parent cell. Instead of budding, many yeasts, such as Schizosaccharomyces replicate and therefore create two cells of the identical size. Thus, one can conclude that the key reproductive approach in yeast is budding. After that, the parent cell nucleus splits into the bud and migrates. This outgrowth becomes bigger and breaks down at last.
Thus, choice A is the right answer.
Note: There are about 1,500 unicellular fungal species in the yeast, most of which are in the Ascomycota Phylum. Yeasts are found in soils and on plant surfaces worldwide and in sugar media such as floral nectar and fruit are especially abundant.
Complete answer: Budding is a type of asexual reproduction in which a new organism emerges from an outgrowth or bud due to the fact of cell division in a particular region. The tiny bulb-like projections from the yeast cell body are recognized as a bud.

Yeasts may have asexual and sexual reproductive cycles, as with other fungi. Asexual reproduction through budding is the most common mode of reproduction in yeast. The parent cell divides first and then the nucleus migrates to the daughter cell. Then, the bud continues to develop till the cell divides and becomes a new daughter cell. In general, at some stage in the budding process, the daughter cell is smaller than the parent cell. Instead of budding, many yeasts, such as Schizosaccharomyces replicate and therefore create two cells of the identical size. Thus, one can conclude that the key reproductive approach in yeast is budding. After that, the parent cell nucleus splits into the bud and migrates. This outgrowth becomes bigger and breaks down at last.
Thus, choice A is the right answer.
Note: There are about 1,500 unicellular fungal species in the yeast, most of which are in the Ascomycota Phylum. Yeasts are found in soils and on plant surfaces worldwide and in sugar media such as floral nectar and fruit are especially abundant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




