
The slope of a distance-time graph of a moving body gives its
A. Speed
B. Displacement
C. Velocity
D. Acceleration
Answer
607.5k+ views
Hint: Slope of a graph between two variables $p$ on y-axis and $q$ on x-axis is $\dfrac{{\Delta p}}{{\Delta q}}$. Here $p$ is distance and $q$ is time. Speed is the distance covered by a body divided by the time taken.
Complete answer:
Two physical quantities are plotted on a graph with $d$ as the distance covered by a moving body in time $t$. Consider the graph given below:
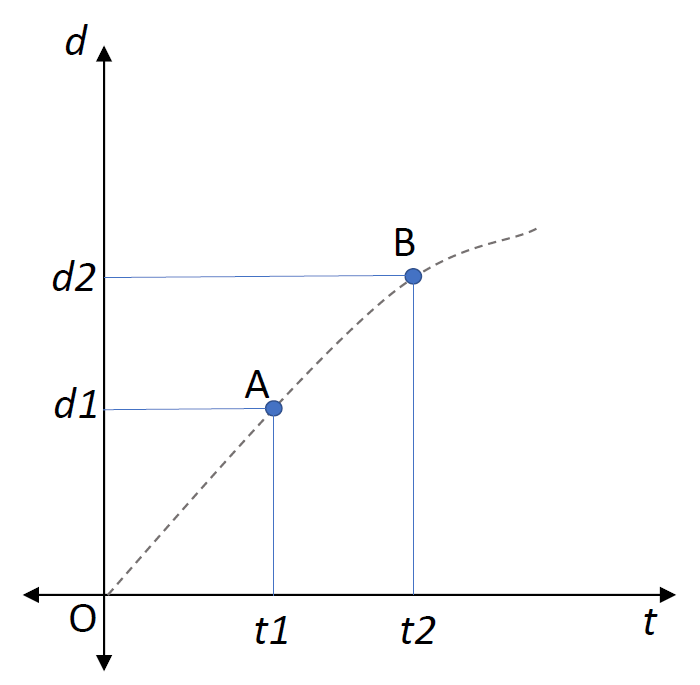
Let us consider an object started moving at $t = 0$ and the distance covered is plotted as variable $d$ on y-axis. Above graph shows an example of two points A and B. Let the distance covered when the object reaches A be $d1$ in time $t1$ and distance covered when the object reaches B be $d2$ in time $t2$. Slope of the line joining these two points is given as $ = \dfrac{{d2 - d1}}{{t2 - t1}}$, which is equal to the average speed of the object between A and B. When comparing the other choices, we know that A is correct. Other choices are displacement, velocity and acceleration which can be unchecked as correct options because each of these quantities requires direction which is not possible in distance-time graphs.
Note: We mentioned averaged speed because distance covered may be distributed through the time between A and B. Here we gave a simple example of a straight line. But actually, the line may not be straight in most of the cases.
Complete answer:
Two physical quantities are plotted on a graph with $d$ as the distance covered by a moving body in time $t$. Consider the graph given below:

Let us consider an object started moving at $t = 0$ and the distance covered is plotted as variable $d$ on y-axis. Above graph shows an example of two points A and B. Let the distance covered when the object reaches A be $d1$ in time $t1$ and distance covered when the object reaches B be $d2$ in time $t2$. Slope of the line joining these two points is given as $ = \dfrac{{d2 - d1}}{{t2 - t1}}$, which is equal to the average speed of the object between A and B. When comparing the other choices, we know that A is correct. Other choices are displacement, velocity and acceleration which can be unchecked as correct options because each of these quantities requires direction which is not possible in distance-time graphs.
Note: We mentioned averaged speed because distance covered may be distributed through the time between A and B. Here we gave a simple example of a straight line. But actually, the line may not be straight in most of the cases.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

What is the color of ferrous sulphate crystals? How does this color change after heating? Name the products formed on strongly heating ferrous sulphate crystals. What type of chemical reaction occurs in this type of change.

Find the greatest fivedigit number which is a perfect class 9 maths CBSE

Find the mode and median of the data 13 16 12 14 1-class-9-maths-CBSE

Write the 6 fundamental rights of India and explain in detail

On an outline map of India show its neighbouring c class 9 social science CBSE




