
The simplest amino acid is:
A. Glycine
B. Lysine
C. Tyrosine
D. Aspartic acid
Answer
577.2k+ views
Hint: The simplest amino acid will be that amino acid which will have only one amino group and one carboxyl group. It should not have any R or variable groups thus it will be considered as the simplest group among twenty naturally occurring amino acids.
Complete answer:
Amino Acids are the organic compounds generally made up of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen and nitrogen, having amino (-$N{H_2}$) and carboxyl (-COOH) functional group, a side chain (-R group), which differentiates each amino acid from each other.
The basic structure of an amino acid is:
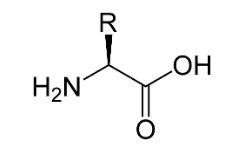
Structure of amino acids differs from each other on the bases of the R-group of the amino acid.
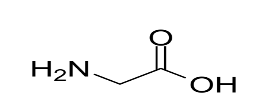
In the given options, the structure of glycine is: Side chain of glycine is a single hydrogen atom.
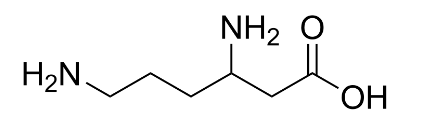
Option ‘B’ is Lysine: Lysine is a long hydro-carbon chain having an amino group at the end of the chain. Thus, in lysine we have two amino groups and one carboxyl group.
Option ‘C’ is tyrosine: Tyrosine is a cyclic compound having one benzene ring, one -OH group, one amino group and one carboxyl group.
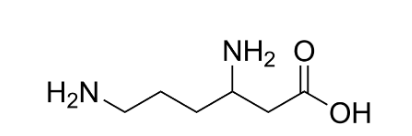
Option ‘D’ is aspartic acid: Aspartic acid is an amino acid in which the R-group is complex, having two carboxyl groups and one amino group. Its structure looks like this:
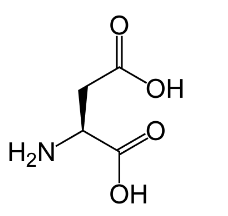
So, after discussing the structure of each given option we can conclude that option ‘A’ that is, Glycine is the correct answer, because of the simplest structure which has an R-group as only one hydrogen atom.
Thus, Option ‘A’ is the correct answer.
Note: Amino acids help in production of proteins inside the organisms. It helps in neurotransmission. They act as precursors for many compounds like glycine and act as a precursor for porphyrins, used in RBCs.
Complete answer:
Amino Acids are the organic compounds generally made up of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen and nitrogen, having amino (-$N{H_2}$) and carboxyl (-COOH) functional group, a side chain (-R group), which differentiates each amino acid from each other.
The basic structure of an amino acid is:

Structure of amino acids differs from each other on the bases of the R-group of the amino acid.
In the given options, the structure of glycine is: Side chain of glycine is a single hydrogen atom.

Option ‘B’ is Lysine: Lysine is a long hydro-carbon chain having an amino group at the end of the chain. Thus, in lysine we have two amino groups and one carboxyl group.

Option ‘C’ is tyrosine: Tyrosine is a cyclic compound having one benzene ring, one -OH group, one amino group and one carboxyl group.

Option ‘D’ is aspartic acid: Aspartic acid is an amino acid in which the R-group is complex, having two carboxyl groups and one amino group. Its structure looks like this:

So, after discussing the structure of each given option we can conclude that option ‘A’ that is, Glycine is the correct answer, because of the simplest structure which has an R-group as only one hydrogen atom.
Thus, Option ‘A’ is the correct answer.
Note: Amino acids help in production of proteins inside the organisms. It helps in neurotransmission. They act as precursors for many compounds like glycine and act as a precursor for porphyrins, used in RBCs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




