
The sides of a triangle are 5, 12, and 13 units. A rectangle of width 10 units is constructed equally in the area to the area of the triangle. Then the perimeter of the rectangle is
(a) 30 units
(b) 26 units
(c) 13 units
(d) 15 units
Answer
593.1k+ views
Hint: Here, first we need to draw the triangle and write down the data is mentioned in the question. Find the area of the triangle = $\dfrac{1}{2}$(base) (height), and use the condition of the area of a triangle equal to the area of the rectangle and find the length of the rectangle using, area of rectangle = $l\times b$. Finally, use the perimeter of the rectangle = $2\left( l+b \right)$ to find the required result.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Let us draw the triangle of sides 5, 12, and 13 units.
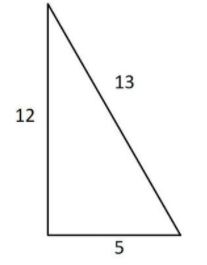
First, let us find the area of the triangle from the given data.
We know,
Area of the triangle = $\dfrac{1}{2}$(base) (height)
From the above diagram, we can see that the height of the triangle is 12 units and the base is 5 units.
Therefore, area of the triangle = $\dfrac{1}{2}$$(5)\times (12)$
= $(5)\times (6)$
= $30$
So, we got the area of the triangle as 30 sq. units
Now, it is given that area of the triangle is equal to the area of the rectangle with a width or breadth of 10 units, hence let us find the length of the rectangle.
Area of triangle = Area of the rectangle
We know, area of rectangle = $l\times b$
We get,
$30 = l\times b$
$\Rightarrow 30 = l\times 10$
Divide by 10 on both the sides of the equation, we get
$\dfrac{30}{10}=l\times \dfrac{10}{10}$
$\Rightarrow 3 = l$
Therefore, we got the length of 3 units.
If we draw the rectangle with a length 3 units and a width 10 units,
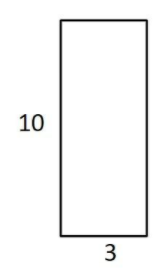
Now, let us find the perimeter of the rectangle
We know,
Perimeter of the rectangle = $2\left( l+b \right)$
= $2 (3 + 10)$
= $2 (13)$
= $26$
Hence, the perimeter of the rectangle is 26 units.
Note: Here, in the above diagram of the triangle, we will use the three sides of the triangle 5, 12 as the two sides of the triangle, and 13 being the longest side. Since it is not given the triangle is a right-angled triangle, we will still use the Pythagoras theorem, and check if it is a right-angled triangle. We have the longest side, 13 which can be considered as the hypotenuse (the longest side in a right-angled triangle) and the other two sides of the triangle. Use the Pythagoras theorem, ${{\left( \text{Hypotenuse} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \text{side}_{1} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \text{side}_{2} \right)}^{2}}$to prove that the given sides of the triangle make a right-angled triangle.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Let us draw the triangle of sides 5, 12, and 13 units.

First, let us find the area of the triangle from the given data.
We know,
Area of the triangle = $\dfrac{1}{2}$(base) (height)
From the above diagram, we can see that the height of the triangle is 12 units and the base is 5 units.
Therefore, area of the triangle = $\dfrac{1}{2}$$(5)\times (12)$
= $(5)\times (6)$
= $30$
So, we got the area of the triangle as 30 sq. units
Now, it is given that area of the triangle is equal to the area of the rectangle with a width or breadth of 10 units, hence let us find the length of the rectangle.
Area of triangle = Area of the rectangle
We know, area of rectangle = $l\times b$
We get,
$30 = l\times b$
$\Rightarrow 30 = l\times 10$
Divide by 10 on both the sides of the equation, we get
$\dfrac{30}{10}=l\times \dfrac{10}{10}$
$\Rightarrow 3 = l$
Therefore, we got the length of 3 units.
If we draw the rectangle with a length 3 units and a width 10 units,

Now, let us find the perimeter of the rectangle
We know,
Perimeter of the rectangle = $2\left( l+b \right)$
= $2 (3 + 10)$
= $2 (13)$
= $26$
Hence, the perimeter of the rectangle is 26 units.
Note: Here, in the above diagram of the triangle, we will use the three sides of the triangle 5, 12 as the two sides of the triangle, and 13 being the longest side. Since it is not given the triangle is a right-angled triangle, we will still use the Pythagoras theorem, and check if it is a right-angled triangle. We have the longest side, 13 which can be considered as the hypotenuse (the longest side in a right-angled triangle) and the other two sides of the triangle. Use the Pythagoras theorem, ${{\left( \text{Hypotenuse} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \text{side}_{1} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \text{side}_{2} \right)}^{2}}$to prove that the given sides of the triangle make a right-angled triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

What is the color of ferrous sulphate crystals? How does this color change after heating? Name the products formed on strongly heating ferrous sulphate crystals. What type of chemical reaction occurs in this type of change.

What is the Full Form of ICSE / ISC ?

Find the mode and median of the data 13 16 12 14 1-class-9-maths-CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it




