
The shapes of \[I{F_5}\] and \[I{F_7}\] are respectively:
A.Square pyramidal and pentagonal bipyramidal
B.Octahedral and pyramidal
C.Trigonal bipyramidal and square antiprismatic
D.Distorted square planar and distorted octahedral
Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint: To be able to predict the shape of molecules, we need to know about the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory, also known as the VSEPR Theory. This theory provides a simple procedure to predict the shape of molecules. The geometrical shapes of molecules predicted by the VSEPR theory focuses mainly on the number of bond pairs and lone pairs. In addition, it provides several postulates which are kept in mind while predicting the shape of molecules.
Complete step by step answer:
The main postulates of VSEPR theory are as follows:
(i) The shape of a molecule depends upon the number of valence shell electron pairs (bonded or non-bonded) around the central atom.
(ii) Pairs of electrons in the valence shell repel one another since their electron clouds are negatively charged.
(iii) These pair of electrons tend to occupy such positions that minimize repulsion and thus maximize distance between them.
(iv) The valence shell is taken as a sphere with the electron pairs localizing on the spherical surface at maximum distance from one another.
(v) A multiple bond is treated as if it is a single electron pair and the two or three electron pairs of a multiple bond are treated as a single super pair.
(vi) Where two or more resonance structures can represent a molecule, the VSEPR model is applicable to any such structure.
The repulsive interactions of electron pairs decrease in the order: Lone Pair-Lone pair>Lone pair-Bond pair>Bond pair-Bond pair.
For the prediction of geometrical shapes of molecules with the help of VSEPR theory, it is convenient to divide molecules into two categories as: (i) Molecules in which the central atom has no lone pair and (ii) molecules in which the central atom has one or more lone pairs.
Now we can predict the shape of $I{F_5}$ : The central atom $I$ has valence electrons in its valence shell. 5 of the valence electrons will be occupied by the 5 $F$ atoms leaving a pair of electrons. Hence, there are 5 bond pairs and 1 lone pair. Hence the shape will be as follows:

The shape of this molecule is square pyramidal.
Now we can predict the shape of $I{F_7}$ : The central atom $I$ has 7 valence electrons in its valence shell. All the valence electrons are occupied by the 7 $F$ atoms. Hence there are 7 bonding pairs and no lone pairs. Hence the shape will be as follows:
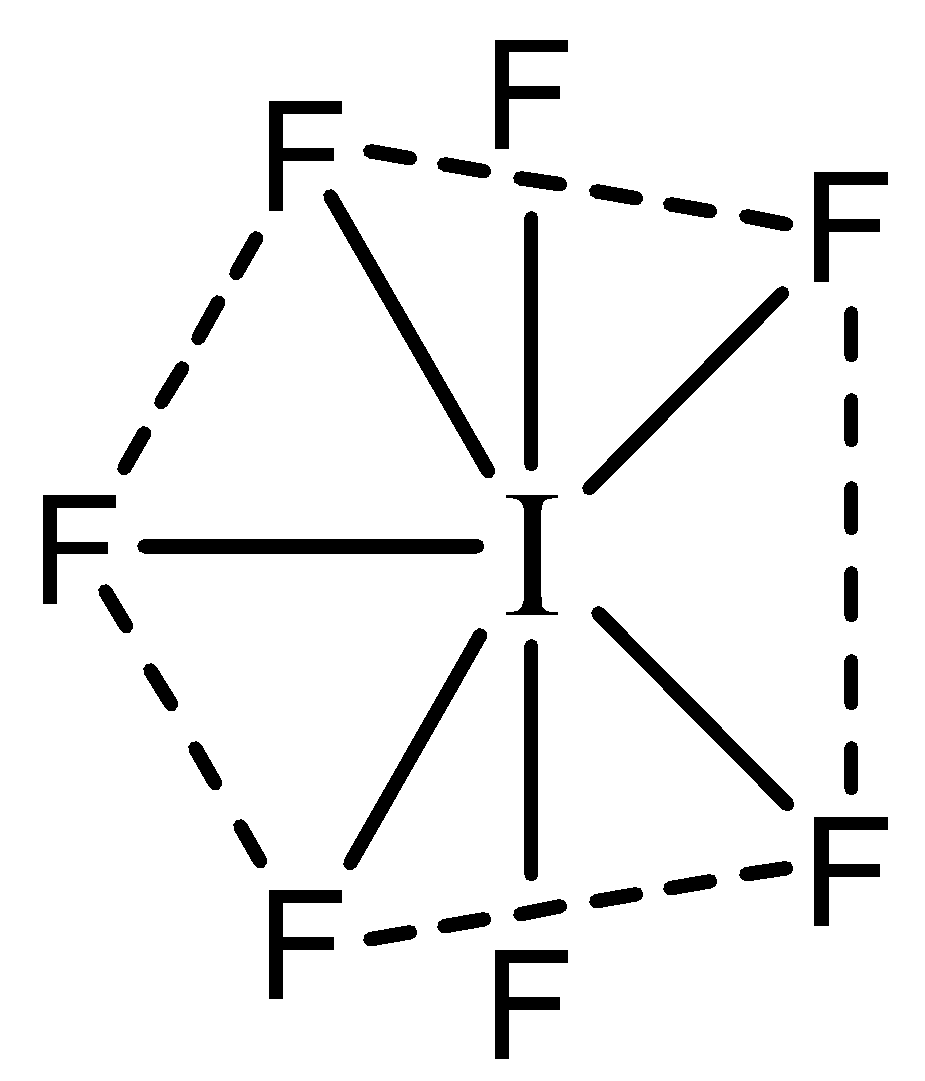
The shape of this molecule is pentagonal Bipyramidal.
Hence the correct option is option (A).
Note:
We must be noted that the key aspects of the VSEPR theory is important to predict the geometry of a large number of molecules, especially the compounds of p-block elements accurately. It must also be noted that the lone pair electrons occupy more space as compared to the bonding pairs of electrons. Calculating the number of lone pairs and bond pairs using the valency of the central atom and its bonded molecule and understanding the priorities each one of them in contributing to the shape is sufficient to predict the shape of a large number of molecules.
Complete step by step answer:
The main postulates of VSEPR theory are as follows:
(i) The shape of a molecule depends upon the number of valence shell electron pairs (bonded or non-bonded) around the central atom.
(ii) Pairs of electrons in the valence shell repel one another since their electron clouds are negatively charged.
(iii) These pair of electrons tend to occupy such positions that minimize repulsion and thus maximize distance between them.
(iv) The valence shell is taken as a sphere with the electron pairs localizing on the spherical surface at maximum distance from one another.
(v) A multiple bond is treated as if it is a single electron pair and the two or three electron pairs of a multiple bond are treated as a single super pair.
(vi) Where two or more resonance structures can represent a molecule, the VSEPR model is applicable to any such structure.
The repulsive interactions of electron pairs decrease in the order: Lone Pair-Lone pair>Lone pair-Bond pair>Bond pair-Bond pair.
For the prediction of geometrical shapes of molecules with the help of VSEPR theory, it is convenient to divide molecules into two categories as: (i) Molecules in which the central atom has no lone pair and (ii) molecules in which the central atom has one or more lone pairs.
Now we can predict the shape of $I{F_5}$ : The central atom $I$ has valence electrons in its valence shell. 5 of the valence electrons will be occupied by the 5 $F$ atoms leaving a pair of electrons. Hence, there are 5 bond pairs and 1 lone pair. Hence the shape will be as follows:

The shape of this molecule is square pyramidal.
Now we can predict the shape of $I{F_7}$ : The central atom $I$ has 7 valence electrons in its valence shell. All the valence electrons are occupied by the 7 $F$ atoms. Hence there are 7 bonding pairs and no lone pairs. Hence the shape will be as follows:

The shape of this molecule is pentagonal Bipyramidal.
Hence the correct option is option (A).
Note:
We must be noted that the key aspects of the VSEPR theory is important to predict the geometry of a large number of molecules, especially the compounds of p-block elements accurately. It must also be noted that the lone pair electrons occupy more space as compared to the bonding pairs of electrons. Calculating the number of lone pairs and bond pairs using the valency of the central atom and its bonded molecule and understanding the priorities each one of them in contributing to the shape is sufficient to predict the shape of a large number of molecules.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




