
The shape of equipotential surface for an infinite line charge is
Answer
522k+ views
Hint: It has two or more three-dimensional linear forms sharing a common axis. Thus, it is concentric in three-dimensional, linear forms.
Formula used:
\[C\prime = \dfrac{{2\pi \varepsilon }}{{\ln (b/a)}}\]
Complete step by step solution:
The shape of equipotential surface for an infinite line charge is coaxial cylindrical
The radii of the inner and outer cylinders a and b, and the permittivity between them is ϵ .
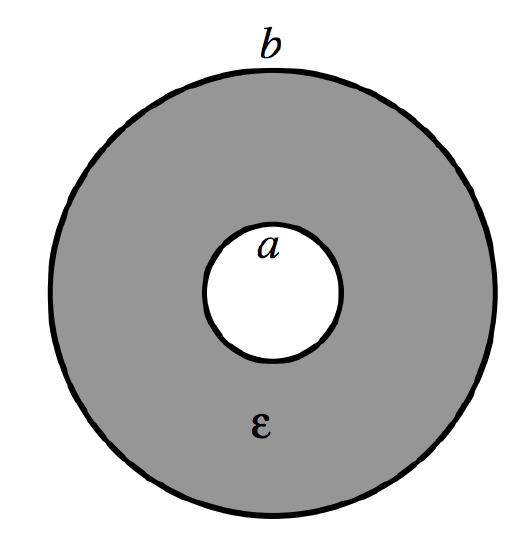
Suppose that the two cylinders are connected to a battery so that the potential difference between them is V , and the charge per unit length on the inner cylinder is \[ + \lambda C{\text{ }}{m^{ - 1}}\], and on the outer cylinder is \[ + \lambda C{\text{ }}{m^{ - 1}}\]. We have seen that the potential difference between the cylinders under such circumstances is λ2πϵln(b/a) . Therefore the capacitance per unit length, \[C\prime \], is
\[C\prime = \dfrac{{2\pi \varepsilon }}{{\ln (b/a)}}\]
This is by no means solely of academic interest. The capacitance per unit length of coaxial cable is an important property of the cable, and this is the formula used to calculate it.
For example The coaxial cylinder viscometer is a popular rotational device for measuring rheological properties. The instrument is designed to shear fluid located in the annulus between two concentric cylinders, one of which is held stationary while the other rotates. A cylindrical bob of radius Ri is suspended in sample fluid held in a stationary cylindrical cup of radius Ro. Liquid covers the bob to a height h from the bottom of the outer cup. As the inner cylinder rotates and the fluid undergoes steady laminar flow, the angular velocity $\Omega $ and torque M are measured. In some designs the outer cylinder rather than the inner bob rotates; in either case the motion is relative with angular velocity $\Omega $
Note: The coaxial cylinder viscometer is a popular rotational device for measuring rheological properties.The instrument is designed to shear fluid located in the annulus between two concentric cylinders, one of which is held stationary while the other rotates.
Formula used:
\[C\prime = \dfrac{{2\pi \varepsilon }}{{\ln (b/a)}}\]
Complete step by step solution:
The shape of equipotential surface for an infinite line charge is coaxial cylindrical
The radii of the inner and outer cylinders a and b, and the permittivity between them is ϵ .

Suppose that the two cylinders are connected to a battery so that the potential difference between them is V , and the charge per unit length on the inner cylinder is \[ + \lambda C{\text{ }}{m^{ - 1}}\], and on the outer cylinder is \[ + \lambda C{\text{ }}{m^{ - 1}}\]. We have seen that the potential difference between the cylinders under such circumstances is λ2πϵln(b/a) . Therefore the capacitance per unit length, \[C\prime \], is
\[C\prime = \dfrac{{2\pi \varepsilon }}{{\ln (b/a)}}\]
This is by no means solely of academic interest. The capacitance per unit length of coaxial cable is an important property of the cable, and this is the formula used to calculate it.
For example The coaxial cylinder viscometer is a popular rotational device for measuring rheological properties. The instrument is designed to shear fluid located in the annulus between two concentric cylinders, one of which is held stationary while the other rotates. A cylindrical bob of radius Ri is suspended in sample fluid held in a stationary cylindrical cup of radius Ro. Liquid covers the bob to a height h from the bottom of the outer cup. As the inner cylinder rotates and the fluid undergoes steady laminar flow, the angular velocity $\Omega $ and torque M are measured. In some designs the outer cylinder rather than the inner bob rotates; in either case the motion is relative with angular velocity $\Omega $
Note: The coaxial cylinder viscometer is a popular rotational device for measuring rheological properties.The instrument is designed to shear fluid located in the annulus between two concentric cylinders, one of which is held stationary while the other rotates.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




