
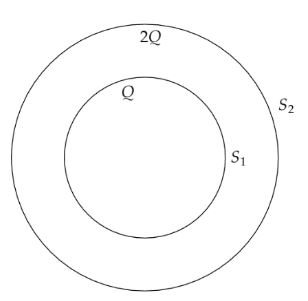
The ${S_1}$ and ${S_2}$ are two hollow concentric sphere enclosing charges $Q$ and $2Q$, respectively, as shown in fig. What is the ratio of the electric flux leaving through the surface of ${S_2}$ and ${S_1}$?

Answer
493.8k+ views
Hint:Here, two hollow spherical shells are given in the figure. We have to find the total electric flux that is leaving through each shell. The smaller shell has a charge within it. While for the bigger shell it is the accumulation of both smaller and larger shells.
Formula used:
Electric flux has the formula of $\phi = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$
The variables are defined as, $\phi = $ electric flux and $q = $ charge enclosed by the particle or body.
Complete step by step answer:
Electric flux is defined as the number of electric lines of force that passes through a given segment of area.Electric flux has the formula,
$\phi = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$
Now, the total charge enclosed by the hollow spherical shell ${S_1}$ is $Q$.
The electric flux through that shell is,
${\phi _1} = \dfrac{Q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$
The total charge enclosed by the hollow spherical shell ${S_2}$ is $\left( {Q + 2Q} \right) = 3Q$
The electric flux through that shell is,
${\phi _2} = \dfrac{{3Q}}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$
Therefore, the ratio of electric flux through the shell ${S_2}$ to ${S_1}$ is,
$\dfrac{{{\phi _2}}}{{{\phi _1}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{3Q}}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}}}{{\dfrac{Q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}}} \\
\therefore \dfrac{{{\phi _2}}}{{{\phi _1}}}= \dfrac{3}{1}$
Therefore, the ratio of electric flux leaving through the surface ${S_2}:{S_1} = 3:1$.
Note:It must be noted that electric field lines originate on positive electric charges and stop on negative charges. Field lines that are directed into a closed surface are considered to be negative while those which are directed out of a closed surface are considered as positive. If there is no net charge within a closed surface, every field line is directed into the surface, enters into the interior or is directed outward elsewhere on the surface. The mathematical relation between electric flux and enclosed charge is known as Gauss’s law for the electric field which is one of the fundamental laws of electromagnetism.
Formula used:
Electric flux has the formula of $\phi = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$
The variables are defined as, $\phi = $ electric flux and $q = $ charge enclosed by the particle or body.
Complete step by step answer:
Electric flux is defined as the number of electric lines of force that passes through a given segment of area.Electric flux has the formula,
$\phi = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$
Now, the total charge enclosed by the hollow spherical shell ${S_1}$ is $Q$.
The electric flux through that shell is,
${\phi _1} = \dfrac{Q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$
The total charge enclosed by the hollow spherical shell ${S_2}$ is $\left( {Q + 2Q} \right) = 3Q$
The electric flux through that shell is,
${\phi _2} = \dfrac{{3Q}}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$
Therefore, the ratio of electric flux through the shell ${S_2}$ to ${S_1}$ is,
$\dfrac{{{\phi _2}}}{{{\phi _1}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{3Q}}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}}}{{\dfrac{Q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}}} \\
\therefore \dfrac{{{\phi _2}}}{{{\phi _1}}}= \dfrac{3}{1}$
Therefore, the ratio of electric flux leaving through the surface ${S_2}:{S_1} = 3:1$.
Note:It must be noted that electric field lines originate on positive electric charges and stop on negative charges. Field lines that are directed into a closed surface are considered to be negative while those which are directed out of a closed surface are considered as positive. If there is no net charge within a closed surface, every field line is directed into the surface, enters into the interior or is directed outward elsewhere on the surface. The mathematical relation between electric flux and enclosed charge is known as Gauss’s law for the electric field which is one of the fundamental laws of electromagnetism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




