
The resistivity of a semiconductor
A. increases as the temperature increases.
B. decreases as the temperature increases.
C. remains constant even when the temperature varies
D. none of the above
Answer
591k+ views
Hint: The resistivity of a substance is dependable on the type of material and the temperature of the conductor, but does not depend on its shape and size. A good conductor is having less resistivity. By the way, a bad conductor or insulator is having high resistivity. Increasing the length will increase the resistance.
Complete step by step answer:
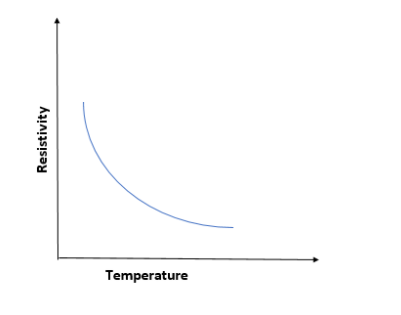
Resistivity of metallic conductors commonly increases with a rise in temperature. But resistivity of semiconductors like carbon and silicon decreases generally with temperature rise. Good insulators, or dielectrics, have high resistivities and also low conductivities. Anyway semiconductors are having intermediate values of both. As the temperature gets increased, more electrons will get the energy to jump out from the conduction band to valence band, and hence increases the conductivity of the semiconductor. At lower temperatures the charge carriers move more slowly, so there will be more time for them to interact with charged impurities. Therefore, as the temperature decreases, the impurity scattering also increases, and the mobility decreases. This is just the opposite of the process of lattice scattering. So as the temperature gets higher, the resistivity of semiconductors will be reduced. Hence the correct answer is option B.
Note:
Resistivity does not actually depend on length and area but it depends on type or the nature of material. It is constant which is used to calculate the resistance of a material. Where l is the length of material, A is the area of the material. Resistivity and Resistance are different.
Complete step by step answer:
Resistivity of metallic conductors commonly increases with a rise in temperature. But resistivity of semiconductors like carbon and silicon decreases generally with temperature rise. Good insulators, or dielectrics, have high resistivities and also low conductivities. Anyway semiconductors are having intermediate values of both. As the temperature gets increased, more electrons will get the energy to jump out from the conduction band to valence band, and hence increases the conductivity of the semiconductor. At lower temperatures the charge carriers move more slowly, so there will be more time for them to interact with charged impurities. Therefore, as the temperature decreases, the impurity scattering also increases, and the mobility decreases. This is just the opposite of the process of lattice scattering. So as the temperature gets higher, the resistivity of semiconductors will be reduced. Hence the correct answer is option B.

Note:
Resistivity does not actually depend on length and area but it depends on type or the nature of material. It is constant which is used to calculate the resistance of a material. Where l is the length of material, A is the area of the material. Resistivity and Resistance are different.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




