
The resistances of the four arms P, Q, R, and S in a Wheatstone’s bridge are $10\Omega $, $30\Omega $, $30\Omega $ and $90\Omega $, respectively. The e.m.f. and the internal resistance of the cell are $7V$ and $5\Omega $ respectively. If the resistance of the galvanometer is $50\Omega $, the current drawn from the cell will be
(a). $1.0A$
(b). $0.2A$
(c). $0.1A$
(d). $2.0A$
Answer
606.3k+ views
- Hint: Draw the circuit diagram for the question, apply the principle of Wheatstone bridge, resolve the circuit and find its equivalent resistance to find the value of current drawn.
Formulae used: Formulae for finding the equivalent resistance in a circuit:
\[\begin{align}
& \text{For series }\Rightarrow \text{ }{{\text{R}}_{eq}}={{\text{R}}_{1}}+{{\text{R}}_{2}} \\
& \text{For parallel }\Rightarrow \text{ }{{\text{R}}_{eq}}=\dfrac{{{\text{R}}_{1}}{{\text{R}}_{2}}}{{{\text{R}}_{1}}+{{\text{R}}_{2}}} \\
\end{align}\]
Formula for Ohm’s law:
$V=IR$
Complete step-by-step solution -
Wheatstone bridge is an instrument which is used to measure the unknown resistance connected in a circuit. It consists of four resistors of which two resistors are known resistors, one resistor which can be varied and the unknown resistor. It also consists of a galvanometer. Refer to the connections from the figure.
It works on the principle that when the value of resistors follows the relation
$\dfrac{P}{Q}=\dfrac{R}{S}$
the voltages at point b and d become the same and the current in the galvanometer G becomes zero.
In this question we have
$\begin{align}
& P=10\Omega \\
& Q=30\Omega \\
& R=30\Omega \\
& S=90\Omega \\
\end{align}$
Therefore,
\[\dfrac{P}{Q}=\dfrac{10}{30}=\dfrac{R}{S}=\dfrac{30}{90}=\dfrac{1}{3}\]
Thus, no current flows in the galvanometer. And the effective circuit looks like this.
We know,
\[\begin{align}
& \text{For series }\Rightarrow \text{ }{{\text{R}}_{eq}}={{\text{R}}_{1}}+{{\text{R}}_{2}} \\
& \text{For parallel }\Rightarrow \text{ }{{\text{R}}_{eq}}=\dfrac{{{\text{R}}_{1}}{{\text{R}}_{2}}}{{{\text{R}}_{1}}+{{\text{R}}_{2}}} \\
\end{align}\]
Equivalent resistance of the circuit is calculated as follows:
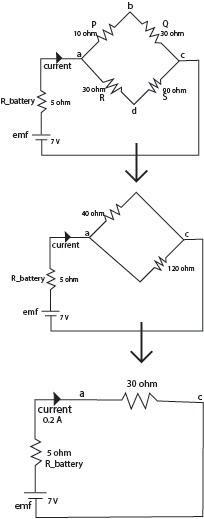
\[\begin{align}
& {{R}_{eq\_up}}=P+Q=40\Omega \\
& {{R}_{eq\_down}}=R+S=120\Omega \\
& {{R}_{eq}}=\dfrac{{{R}_{eq\_up}}{{R}_{eq\_down}}}{{{R}_{eq\_up}}+{{R}_{eq\_down}}}=\dfrac{40\times 120}{40+120}=\dfrac{4800}{160}=30\Omega \\
\end{align}\]
From the relation of voltage, current and resistance in a circuit
$V=IR$
The current can be calculated as
$I=\dfrac{V}{{{R}_{battery}}+{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{7}{30+5}=\dfrac{7}{35}=0.2A$
Therefore, the answer to this question is option B. $0.2 A$.
Note: The value of the resistance in the galvanometer is redundant. Do not use that value and complicate the question. Since, in a Wheatstone’s bridge no current flows through the branch with the galvanometer there is no voltage difference because of the resistance in the galvanometer.
Formulae used: Formulae for finding the equivalent resistance in a circuit:
\[\begin{align}
& \text{For series }\Rightarrow \text{ }{{\text{R}}_{eq}}={{\text{R}}_{1}}+{{\text{R}}_{2}} \\
& \text{For parallel }\Rightarrow \text{ }{{\text{R}}_{eq}}=\dfrac{{{\text{R}}_{1}}{{\text{R}}_{2}}}{{{\text{R}}_{1}}+{{\text{R}}_{2}}} \\
\end{align}\]
Formula for Ohm’s law:
$V=IR$
Complete step-by-step solution -
Wheatstone bridge is an instrument which is used to measure the unknown resistance connected in a circuit. It consists of four resistors of which two resistors are known resistors, one resistor which can be varied and the unknown resistor. It also consists of a galvanometer. Refer to the connections from the figure.
It works on the principle that when the value of resistors follows the relation
$\dfrac{P}{Q}=\dfrac{R}{S}$
the voltages at point b and d become the same and the current in the galvanometer G becomes zero.
In this question we have
$\begin{align}
& P=10\Omega \\
& Q=30\Omega \\
& R=30\Omega \\
& S=90\Omega \\
\end{align}$
Therefore,
\[\dfrac{P}{Q}=\dfrac{10}{30}=\dfrac{R}{S}=\dfrac{30}{90}=\dfrac{1}{3}\]
Thus, no current flows in the galvanometer. And the effective circuit looks like this.
We know,
\[\begin{align}
& \text{For series }\Rightarrow \text{ }{{\text{R}}_{eq}}={{\text{R}}_{1}}+{{\text{R}}_{2}} \\
& \text{For parallel }\Rightarrow \text{ }{{\text{R}}_{eq}}=\dfrac{{{\text{R}}_{1}}{{\text{R}}_{2}}}{{{\text{R}}_{1}}+{{\text{R}}_{2}}} \\
\end{align}\]
Equivalent resistance of the circuit is calculated as follows:

\[\begin{align}
& {{R}_{eq\_up}}=P+Q=40\Omega \\
& {{R}_{eq\_down}}=R+S=120\Omega \\
& {{R}_{eq}}=\dfrac{{{R}_{eq\_up}}{{R}_{eq\_down}}}{{{R}_{eq\_up}}+{{R}_{eq\_down}}}=\dfrac{40\times 120}{40+120}=\dfrac{4800}{160}=30\Omega \\
\end{align}\]
From the relation of voltage, current and resistance in a circuit
$V=IR$
The current can be calculated as
$I=\dfrac{V}{{{R}_{battery}}+{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{7}{30+5}=\dfrac{7}{35}=0.2A$
Therefore, the answer to this question is option B. $0.2 A$.
Note: The value of the resistance in the galvanometer is redundant. Do not use that value and complicate the question. Since, in a Wheatstone’s bridge no current flows through the branch with the galvanometer there is no voltage difference because of the resistance in the galvanometer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




