
The refractive index of the material of a concave lens is \[\mu \]. It is immersed in a medium of refractive index \[{\mu _1}\]. A parallel beam of light is incident on the lens. The path of the emergent rays when \[{\mu _1} > \mu \] is:
A.
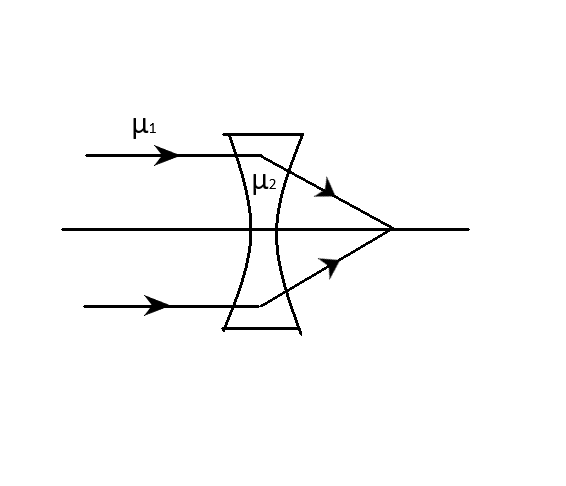
B.
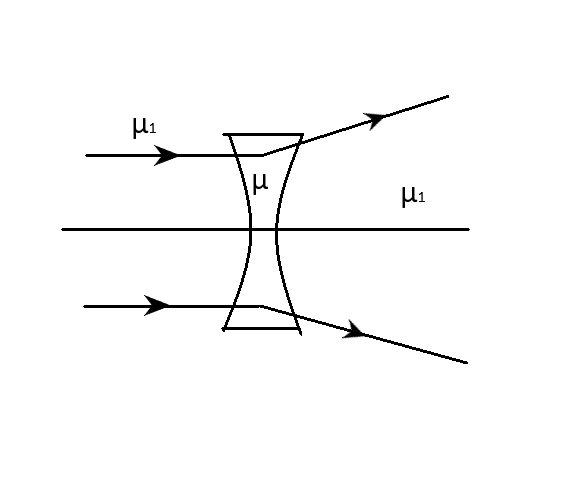
C.
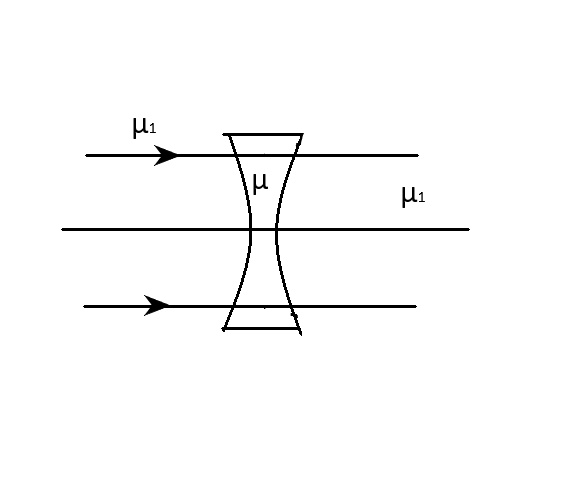
D.
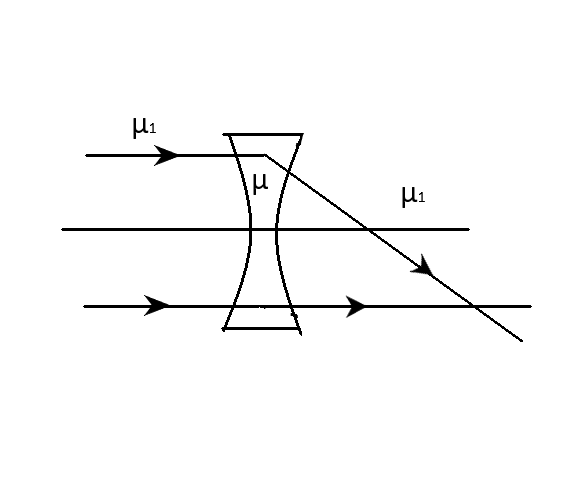




Answer
560.7k+ views
Hint: When it is placed in the air, the concave acts as a diverging lens. This is because air has a lower refractive index than the lens. If the lens is placed in a medium with a higher refractive index, the situation reverses.
Complete step by step answer:
We are told that a concave lens is immersed in a medium of refractive index which is higher than the refractive index of the lens, itself. We are to choose the correct diagram for the emergent ray from the lens.
Generally, a concave lens when placed in air behaves as a diverging lens, hence the reason it is sometimes called a diverging lens. However, this is because air is a medium that has a lower refractive index than that of the material of the lens. When placed in a medium that has a higher refractive index, the refraction becomes the other way around. Hence, the concave lens behaves like a diverging lens. Thus, the emergent ray (refracted light) will diverge from one another as in B.
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: For clarity, the emergent ray usually is the ray that comes out of a lens or block after been refracted, at least twice. For thin lenses, however, the refracted ray is the emergent ray, because that the light does not travel far enough to create a reasonable difference between first refraction and second refraction. In some cases, emergent ray is in the same direction as the incident ray, as in the case of a rectangular block.
Complete step by step answer:
We are told that a concave lens is immersed in a medium of refractive index which is higher than the refractive index of the lens, itself. We are to choose the correct diagram for the emergent ray from the lens.
Generally, a concave lens when placed in air behaves as a diverging lens, hence the reason it is sometimes called a diverging lens. However, this is because air is a medium that has a lower refractive index than that of the material of the lens. When placed in a medium that has a higher refractive index, the refraction becomes the other way around. Hence, the concave lens behaves like a diverging lens. Thus, the emergent ray (refracted light) will diverge from one another as in B.
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: For clarity, the emergent ray usually is the ray that comes out of a lens or block after been refracted, at least twice. For thin lenses, however, the refracted ray is the emergent ray, because that the light does not travel far enough to create a reasonable difference between first refraction and second refraction. In some cases, emergent ray is in the same direction as the incident ray, as in the case of a rectangular block.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




