
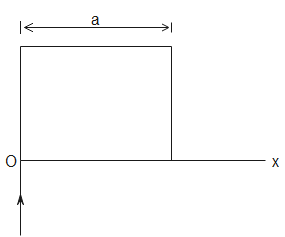
The refractive index of an anisotropic medium varies as $\mu ={{\mu }_{0}}\sqrt{x+1}$, where $0\le x\le a$. A ray of light is incident at the origin just along the y-axis (shown in figure). Find the equation of ray in the medium.

Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: We are given the variation of refractive index. Use Snell’s law to obtain the value of sine and cosine of angle of refraction. The equation of the light ray can be obtained by using slope of the line which is also equivalent to tangent of angle of refraction.
Complete step by step answer:
The variation of refractive index of the anisotropic medium is given as $\mu ={{\mu }_{0}}\sqrt{x+1}$
It can be noted that the value of refractive index at $x=0$ is $\mu=\mu_0$
The relationship of angle of incidence and angle of refraction at the interface of two media is given by Snell’s law. Snell’s law states that the ratio of the sines of the angles of incidence and refraction is equal to the reciprocal of the ratio of the indices of refraction.
At interface of the media, we apply Snell’s law or law of refraction, and get
${{\mu }_{0}}\sin i=\mu \sin r$
It is given that, the ray of light is incident at the origin just along y-axis which implies $i={{90}^{{}^\circ }}$ which further implies that $\sin i=\sin {{90}^{{}^\circ }}=1$
Substituting the value in above equation, we have
${{\mu }_{0}}={{\mu }_{0}}\sin r\sqrt{x+1}$
On solving, we have
$\sin r=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x+1}}$
We know that, $\sqrt{1-{{\sin }^{2}}r}=\cos r$ and substituting the value of $\sin r=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x+1}}$, we get
$\cos r=\sqrt{1-{{\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x+1}} \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{x}{x+1}}$
The tangent to refracted ray can be written as
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\tan r=\dfrac{\sin r}{\cos r}$
Substituting the values, we get
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{1/\sqrt{x+1}}{\sqrt{x/(x+1)}}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}}$
$\Rightarrow dy=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}}dx$
On integrating, we get
$y=\int{\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}}dx}=2\sqrt{x}$
$y=\int{\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}}dx}=2\sqrt{x}$.
This is the required equation of the light ray in the medium.
Note: Anisotropic medium is the medium in which the properties vary in all the directions. Anisotropic medium has many refractive indexes. The equation of tangent to any straight line is the equation of the straight line itself.
Complete step by step answer:
The variation of refractive index of the anisotropic medium is given as $\mu ={{\mu }_{0}}\sqrt{x+1}$
It can be noted that the value of refractive index at $x=0$ is $\mu=\mu_0$
The relationship of angle of incidence and angle of refraction at the interface of two media is given by Snell’s law. Snell’s law states that the ratio of the sines of the angles of incidence and refraction is equal to the reciprocal of the ratio of the indices of refraction.
At interface of the media, we apply Snell’s law or law of refraction, and get
${{\mu }_{0}}\sin i=\mu \sin r$
It is given that, the ray of light is incident at the origin just along y-axis which implies $i={{90}^{{}^\circ }}$ which further implies that $\sin i=\sin {{90}^{{}^\circ }}=1$
Substituting the value in above equation, we have
${{\mu }_{0}}={{\mu }_{0}}\sin r\sqrt{x+1}$
On solving, we have
$\sin r=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x+1}}$
We know that, $\sqrt{1-{{\sin }^{2}}r}=\cos r$ and substituting the value of $\sin r=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x+1}}$, we get
$\cos r=\sqrt{1-{{\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x+1}} \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{x}{x+1}}$
The tangent to refracted ray can be written as
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\tan r=\dfrac{\sin r}{\cos r}$
Substituting the values, we get
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{1/\sqrt{x+1}}{\sqrt{x/(x+1)}}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}}$
$\Rightarrow dy=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}}dx$
On integrating, we get
$y=\int{\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}}dx}=2\sqrt{x}$
$y=\int{\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}}dx}=2\sqrt{x}$.
This is the required equation of the light ray in the medium.
Note: Anisotropic medium is the medium in which the properties vary in all the directions. Anisotropic medium has many refractive indexes. The equation of tangent to any straight line is the equation of the straight line itself.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




