
The reagent used in the Wolff-Kushner reduction is :
(A). \[{{H}_{2}}N-N{{H}_{2}}/KOH\]
(B). \[{{H}_{2}}/Ni\]
(C). \[Sn/HCI\]
(D). \[LiAI{{H}_{4}}\]
Answer
546.3k+ views
Hint: Wolff Kushner reduction is a type of reduction in which a carbonyl group is converted into a methyl group . This reduction was discovered by N- Kushner in \[1911\] and Ludwig Wolff in \[1912\] . That’s why this reduction process is known as Wolff Kushner reduction.
Complete step by step answer:
Wolff Kushner reduction is a reduction process used in organic chemistry to convert the carbonyl functionalities into methyl groups. In this reaction, the carbonyl group is treated with hydrogen to give the initial product as nitrogen. The hydrogen is reacted with \[KOH/glycal\] to remove \[{{N}_{2}}\] and to give the final methylene group as the product.
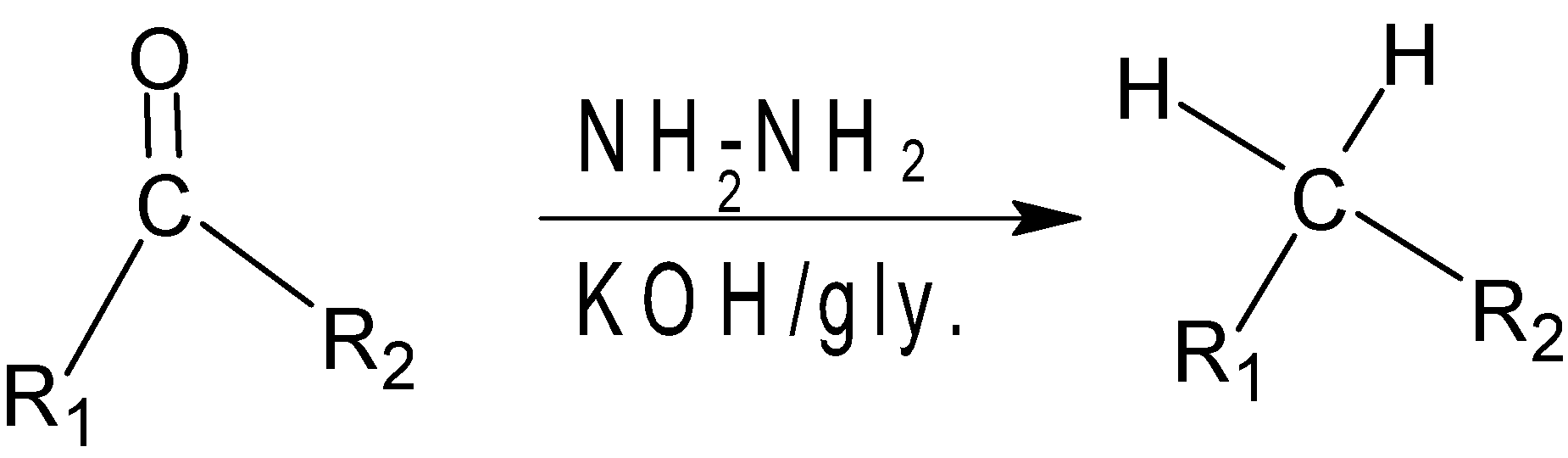
Mechanism of the reaction:-
Step A :-
The carbonyl compound such as aldehyde or ketone is treated with hydrazine which results in information of hydrazine.
That is,
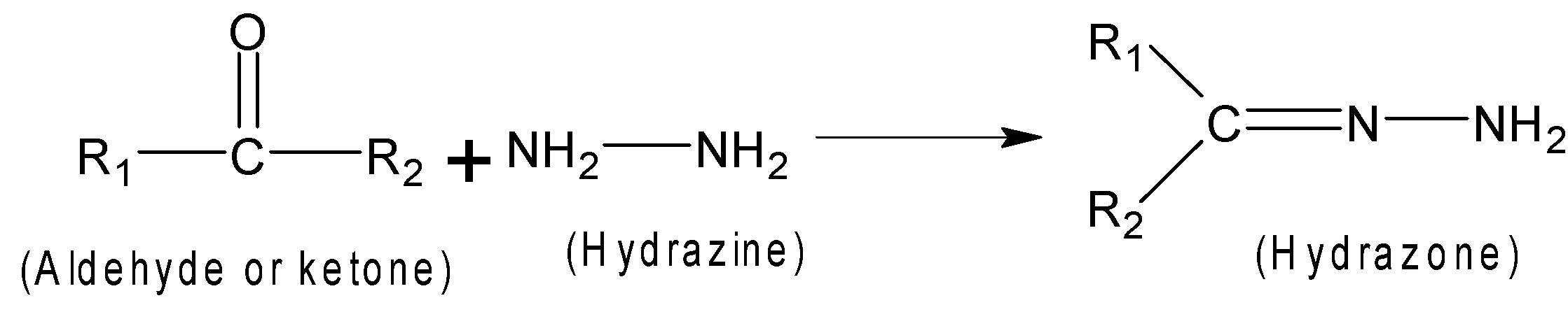
Here \[{{R}_{1}}\] and \[{{R}_{2}}\] can be any alkyl group .
Step B :-
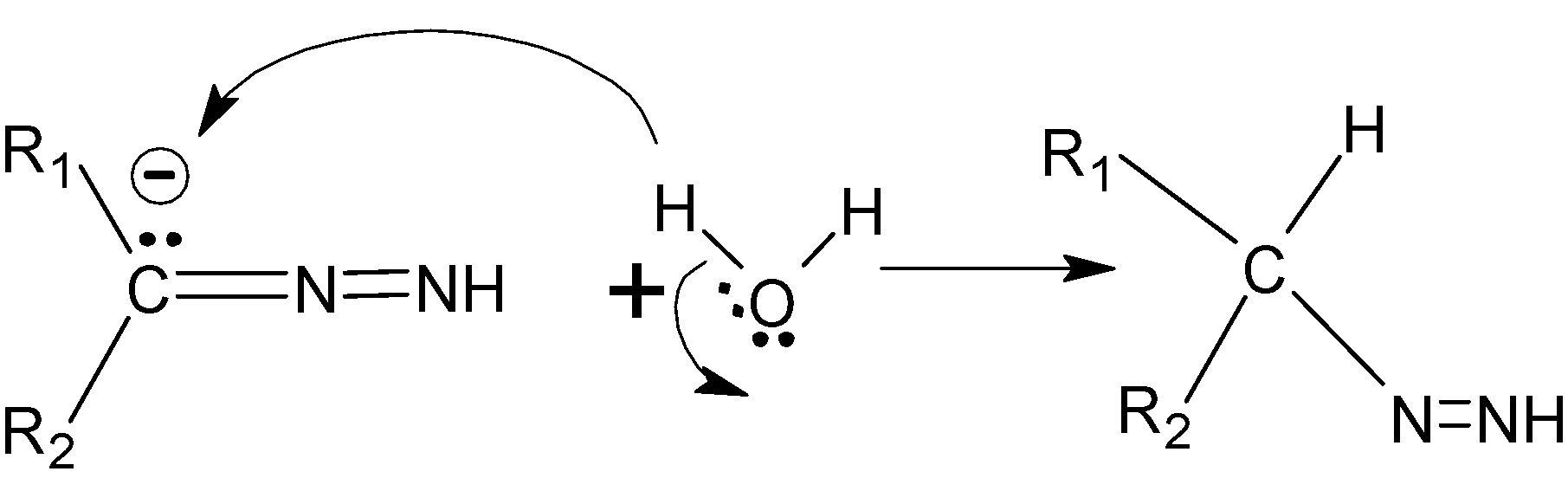
Now the hydrazone is treated with \[KOH\] , which releases \[O{{H}^{-}}\]ions which deprotonates the hydrazone. Due to this a double bond is formed between two adjacent nitrogen atoms. The released proton combines with \[O{{H}^{-}}\] to form water.

(hydrazone )
Step C : The oxygen is more electronegative and withdraw electrons towards it than carbon, so the carbon gets protonated.
Step D :- The nitrogen groups are deprotonated again by the effect of \[KOH\], and this time it forms triple bond with nitrogen atom which leads to the removal of \[{{N}_{2}}\] from the compound.
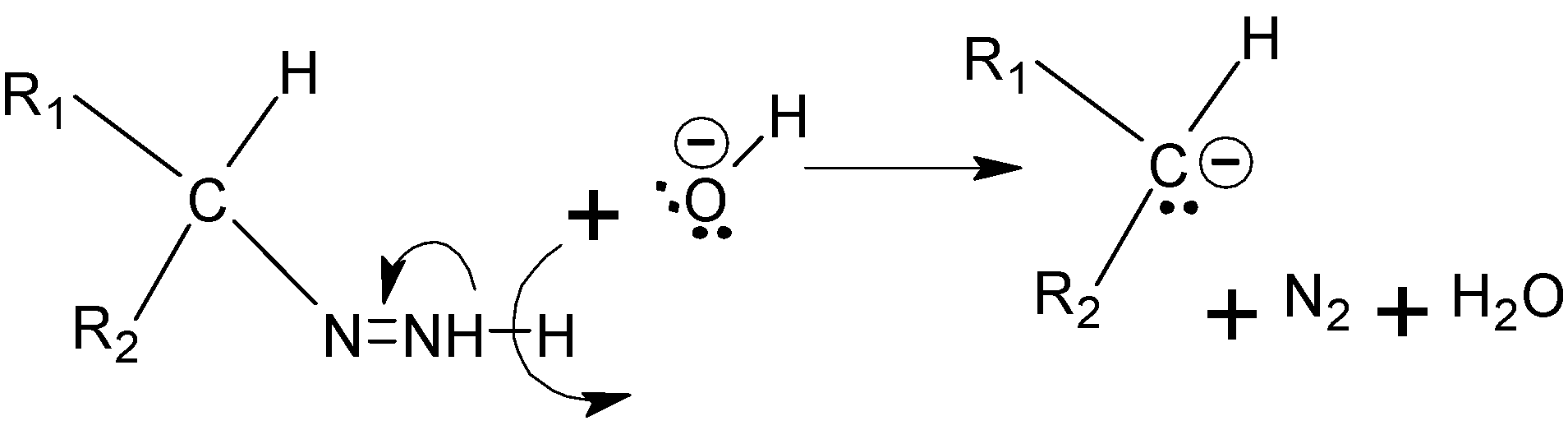
Step E :- Now the carbon again gets protonated from the water to give the final alkane.
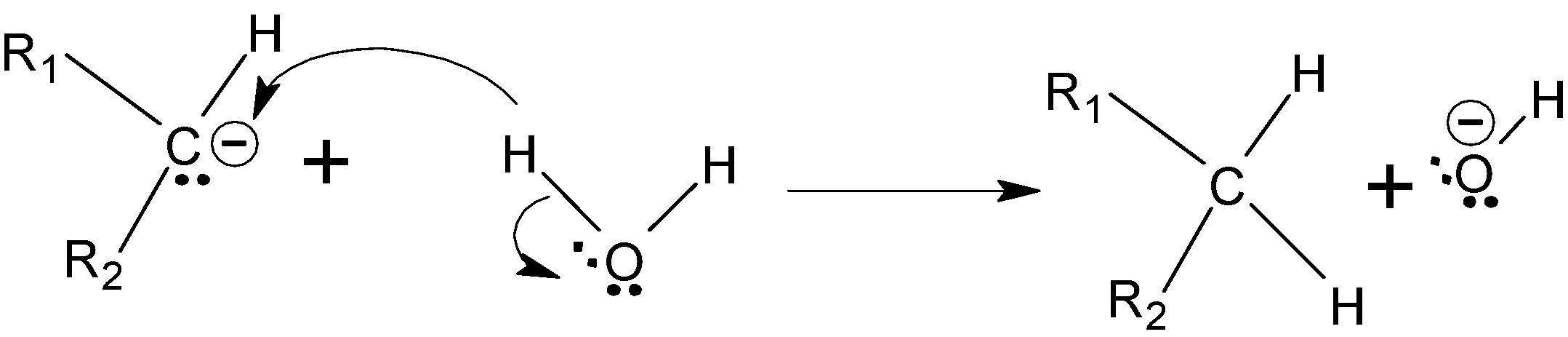
Hence we got to know that \[{{H}_{2}}N-N{{H}_{2}}\] and \[KOH\] is used in wolff Kushner reduction.
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Note: We can use any base other than \[KOH\] in this Wolff Kushner reduction because we only needs \[O{{H}^{-}}\] ion in its mechanism which can be given by any base. The Wolff Kushner reduction has been modified into various techniques such as the Huang Minlon modification that offer reduced reaction time and the achievement of higher temperatures but requires distillation.
Complete step by step answer:
Wolff Kushner reduction is a reduction process used in organic chemistry to convert the carbonyl functionalities into methyl groups. In this reaction, the carbonyl group is treated with hydrogen to give the initial product as nitrogen. The hydrogen is reacted with \[KOH/glycal\] to remove \[{{N}_{2}}\] and to give the final methylene group as the product.
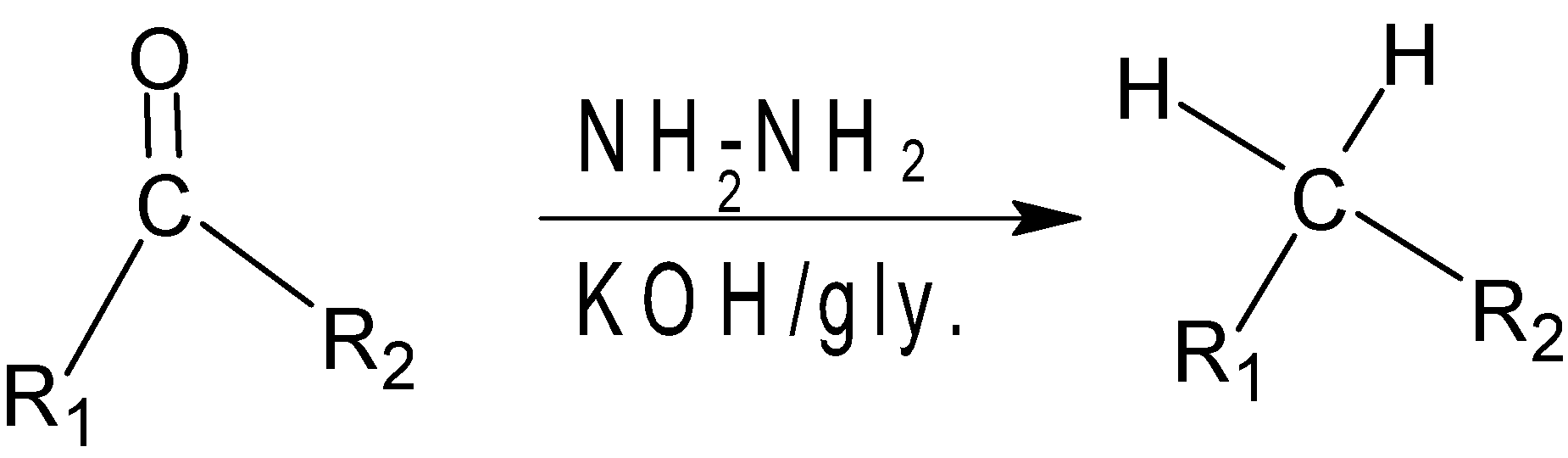
Mechanism of the reaction:-
Step A :-
The carbonyl compound such as aldehyde or ketone is treated with hydrazine which results in information of hydrazine.
That is,

Here \[{{R}_{1}}\] and \[{{R}_{2}}\] can be any alkyl group .
Step B :-
Now the hydrazone is treated with \[KOH\] , which releases \[O{{H}^{-}}\]ions which deprotonates the hydrazone. Due to this a double bond is formed between two adjacent nitrogen atoms. The released proton combines with \[O{{H}^{-}}\] to form water.

(hydrazone )
Step C : The oxygen is more electronegative and withdraw electrons towards it than carbon, so the carbon gets protonated.

Step D :- The nitrogen groups are deprotonated again by the effect of \[KOH\], and this time it forms triple bond with nitrogen atom which leads to the removal of \[{{N}_{2}}\] from the compound.

Step E :- Now the carbon again gets protonated from the water to give the final alkane.

Hence we got to know that \[{{H}_{2}}N-N{{H}_{2}}\] and \[KOH\] is used in wolff Kushner reduction.
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Note: We can use any base other than \[KOH\] in this Wolff Kushner reduction because we only needs \[O{{H}^{-}}\] ion in its mechanism which can be given by any base. The Wolff Kushner reduction has been modified into various techniques such as the Huang Minlon modification that offer reduced reaction time and the achievement of higher temperatures but requires distillation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




