
What will be the reading of the voltmeter which has been shown below?
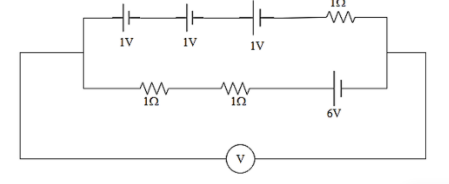
$\begin{align}
& A.0 \\
& B.2V \\
& C.4V \\
& D.6V \\
\end{align}$

Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint: The Kirchhoff’s voltage law is to be used here in order to solve this question. This law says that the total sum of the voltage in a closed circuit will be equivalent to the voltages which have been there in each branch and components in the same closed circuit. According to ohm’s law, the voltage of a circuit will be equivalent to the product of the current in the circuit and the resistance of the circuit. This will help you in answering this question.
Complete step by step solution:
Kirchhoff's voltage law is to be used here in order to solve this question. This law says that the total sum of the voltage in a closed circuit will be equivalent to the voltages which have been there in each branch and components in the same closed circuit.
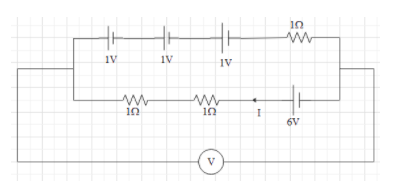
Let us assume that the current in the circuit is $I$.
Therefore we can write that,
$6-\left( 1\times I \right)-\left( 1\times I \right)-1-1-1-\left( 1\times I \right)=0$
Let us simplify this equation in order to obtain the value of current. That is,
$\begin{align}
& 3I=3 \\
& \therefore I=1A \\
\end{align}$
As we can see the voltage will be the same in both the branches as they are parallel in nature. In order to find the voltage shown in the voltmeter, therefore we can consider only one branch. Therefore now the lower branch in the circuit can be shown as,
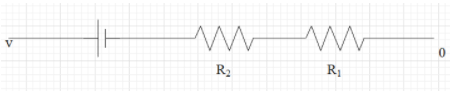
Let us apply Kirchhoff's voltage law in this equation. That is we can write that,
$0+6-1\times 1-1\times 1=4V$
Hence the reading of the voltmeter will be equivalent to $4V$. This has been mentioned as option C.
Note:
Kirchhoff’s Current Law can be otherwise called by several names as Kirchhoff’s First Law and Kirchhoff’s Junction Rule. This junction rule says that, in a circuit, the sum of the currents in a junction will be equal to the sum of currents outside the junction. Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law can be otherwise known as Kirchhoff’s Second Law and Kirchhoff’s Loop Rule.
Complete step by step solution:
Kirchhoff's voltage law is to be used here in order to solve this question. This law says that the total sum of the voltage in a closed circuit will be equivalent to the voltages which have been there in each branch and components in the same closed circuit.

Let us assume that the current in the circuit is $I$.
Therefore we can write that,
$6-\left( 1\times I \right)-\left( 1\times I \right)-1-1-1-\left( 1\times I \right)=0$
Let us simplify this equation in order to obtain the value of current. That is,
$\begin{align}
& 3I=3 \\
& \therefore I=1A \\
\end{align}$
As we can see the voltage will be the same in both the branches as they are parallel in nature. In order to find the voltage shown in the voltmeter, therefore we can consider only one branch. Therefore now the lower branch in the circuit can be shown as,

Let us apply Kirchhoff's voltage law in this equation. That is we can write that,
$0+6-1\times 1-1\times 1=4V$
Hence the reading of the voltmeter will be equivalent to $4V$. This has been mentioned as option C.
Note:
Kirchhoff’s Current Law can be otherwise called by several names as Kirchhoff’s First Law and Kirchhoff’s Junction Rule. This junction rule says that, in a circuit, the sum of the currents in a junction will be equal to the sum of currents outside the junction. Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law can be otherwise known as Kirchhoff’s Second Law and Kirchhoff’s Loop Rule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE

Calculate the equivalent resistance between a and b class 12 physics CBSE

How many states of matter are there in total class 12 chemistry CBSE

Which of the following is the best conductor of electricity class 12 physics CBSE




