
The reaction conditions leading to the best yield of ${ C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 5 }Cl$ are:
(a) ${ C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 6 }(excess)+{ Cl }_{ 2 }\xrightarrow { U.V.\quad light }$
(b) ${ C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 6 }{ Cl }_{ 2 }(excess)+{ Cl }_{ 2 }\xrightarrow { Dark\quad room\quad Temperature } $
(c) ${ C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 6 }{ Cl }_{ 2 }+{ Cl }_{ 2 }(excess)\xrightarrow { U.V.\quad light } $
(d) ${ C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 6 }{ Cl }_{ 2 }+{ Cl }_{ 2 }\xrightarrow { U.V.\quad light } $
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: ${ C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 5 }Cl$ can be obtained by the chlorination of ${ C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 6 }$ which is an alkane and hence involves a free radical mechanism which is photochemical in nature.
Complete step by step answer:
We need the following reaction:
${ C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 6 }(excess)+{ Cl }_{ 2 }\rightarrow { C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 5 }-Cl\quad (major\quad product)\quad $
${ C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 6 }$ is an alkane. For their chlorination reaction, the mechanism is a free radical mechanism which requires U.V. light. It happens in three steps:
Step 1: Initiation step
The atoms in the halogen molecule will separate into radical due to U.V. light:

Step 2: Propagation steps:
(a) First the abstraction of a hydrogen atom will take place:
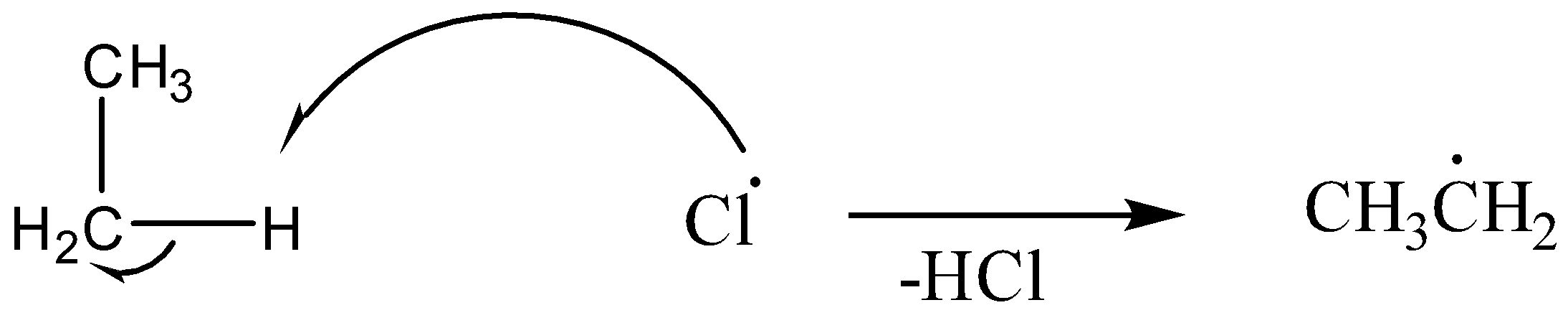
(b) The ethyl radical formed reacts with another chlorine molecule to form Chloroethane:
Step 3: Termination steps
Two radicals combine together to give stable compounds:
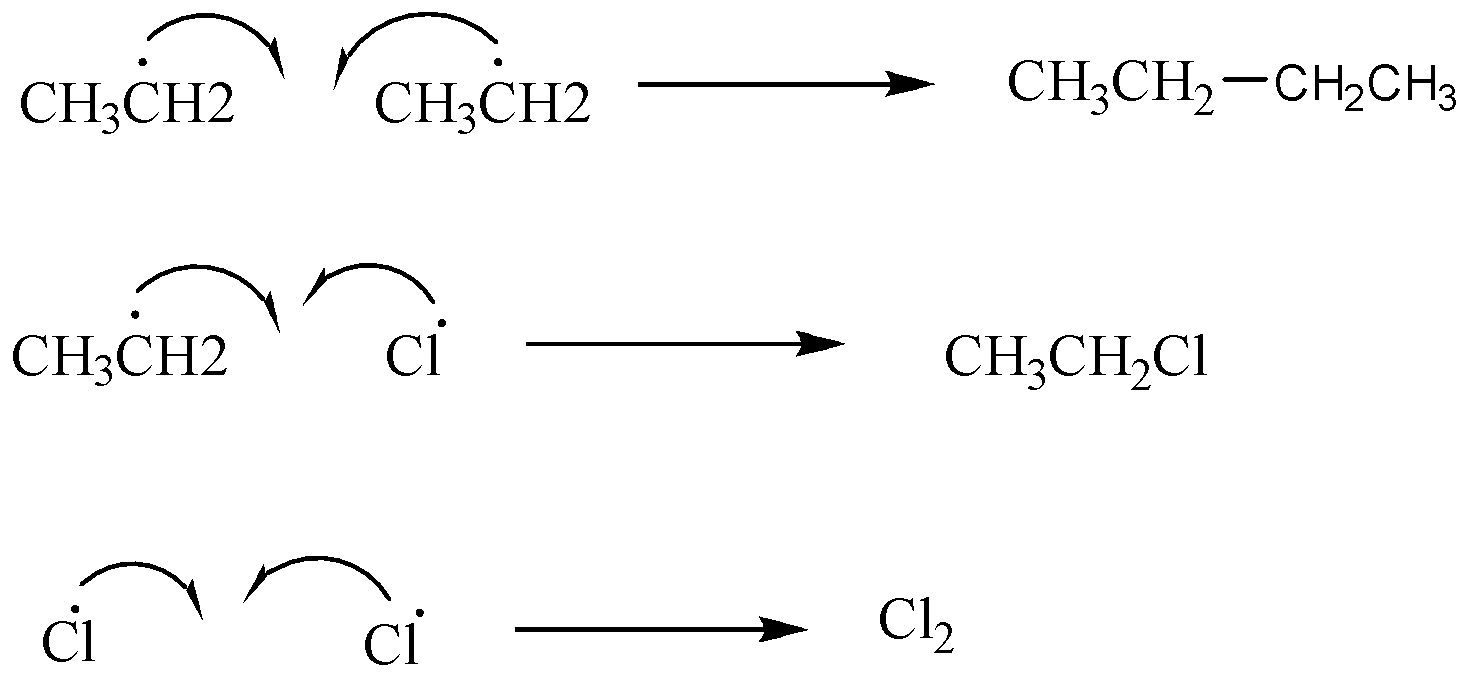
If we take ethane in excess in this reaction then a monosubstituted product will be the major product. Similarly if we take chlorine in excess then trichloro and dichloro derivatives will be the major products.
When ethane is in excess the chlorine radicals will collide with the ethane molecules with higher probability which will result in the formation of ${ C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 5 }Cl$ as the major product.
Hence the correct answer is ${ C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 6 }(excess)+{ Cl }_{ 2 }\xrightarrow { U.V.\quad light }$.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Please remember that during the propagation step, the hydrogen attached to the more substituted carbon is abstracted by the halogen radical more preferably. This is because tertiary alkyl/aryl radicals are more stable followed by secondary alkyl/aryl radicals with primary alkyl/aryl radicals being the least stable. This trend is governed by the inductive effect observed in the alkyl/aryl hydrocarbons. Also note that there are a variety of side products that are formed in a halogenation reaction of alkanes but the number of side products formed in chlorination is more than bromination because bromination is more selective than chlorination. The bromine radical is more stable than the chlorine radical (HCl has higher bond energy than HBr) and hence the bromination reaction is slower and more selective.
Complete step by step answer:
We need the following reaction:
${ C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 6 }(excess)+{ Cl }_{ 2 }\rightarrow { C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 5 }-Cl\quad (major\quad product)\quad $
${ C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 6 }$ is an alkane. For their chlorination reaction, the mechanism is a free radical mechanism which requires U.V. light. It happens in three steps:
Step 1: Initiation step
The atoms in the halogen molecule will separate into radical due to U.V. light:

Step 2: Propagation steps:
(a) First the abstraction of a hydrogen atom will take place:
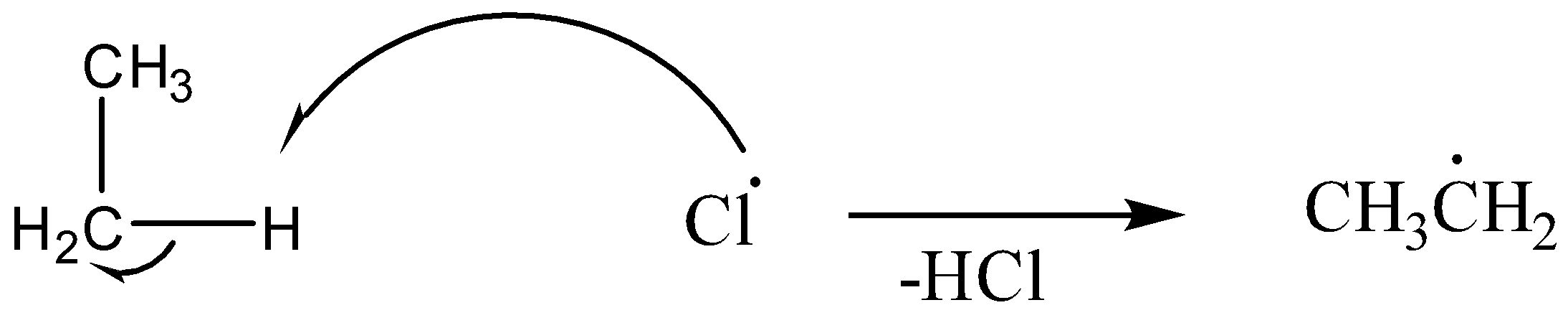
(b) The ethyl radical formed reacts with another chlorine molecule to form Chloroethane:
Step 3: Termination steps
Two radicals combine together to give stable compounds:

If we take ethane in excess in this reaction then a monosubstituted product will be the major product. Similarly if we take chlorine in excess then trichloro and dichloro derivatives will be the major products.
When ethane is in excess the chlorine radicals will collide with the ethane molecules with higher probability which will result in the formation of ${ C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 5 }Cl$ as the major product.
Hence the correct answer is ${ C }_{ 2 }{ H }_{ 6 }(excess)+{ Cl }_{ 2 }\xrightarrow { U.V.\quad light }$.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Please remember that during the propagation step, the hydrogen attached to the more substituted carbon is abstracted by the halogen radical more preferably. This is because tertiary alkyl/aryl radicals are more stable followed by secondary alkyl/aryl radicals with primary alkyl/aryl radicals being the least stable. This trend is governed by the inductive effect observed in the alkyl/aryl hydrocarbons. Also note that there are a variety of side products that are formed in a halogenation reaction of alkanes but the number of side products formed in chlorination is more than bromination because bromination is more selective than chlorination. The bromine radical is more stable than the chlorine radical (HCl has higher bond energy than HBr) and hence the bromination reaction is slower and more selective.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




