
The reaction \[C{H_3}CN + 4[H]\xrightarrow{{Na/{C_2}{H_5}OH}}C{H_3}C{H_2}N{H_2}\] is known as:
A. Hofmann’s bromamide reaction
B. Mendius reaction
C. Perkin’s reaction
D. Sabatier reaction
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: We have to remember that the reduction reaction is a type of chemical reaction, which involves the gaining of electrons by one of the atoms involved in the reactants. The carbon atom that gains bonds to less electronegative elements, not all time but most commonly hydrogen. The oxidation state of the element that gains electrons is decreased.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us see the options one by one for which option is correct.
Hofmann’s bromamide reaction gives a primary amine
When amide is treated with bromine in an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide the primary amine is called Hofmann’s bromamide reaction. The product amine formed in the reaction contains one carbon atom more than the parent compound.
General chemical reaction is
$RCON{H_2} + B{r_2} + 4NaOH \to RN{H_2} + N{a_2}C{O_3} + 2NaBr + 2{H_2}O$
Nitriles gives primary amine is a Mendius reaction
We need to know that the reduction reaction of nitriles (if a compound containing $ - C \equiv N$ functional group) with sodium $\left( {Na} \right)$ in ethanol gives primary amine is called Mendius reaction.
The general chemical reaction is,
\[R - C \equiv N{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}4[H]{\text{ }}\xrightarrow{{Na/{C_2}{H_5}OH}}{\text{ }}R - C{H_2}N{H_2}\]
$Alkyl \;cyanide \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\; \;\;\; \;\;\;\;\;\; Primary amine$
The product amine formed in the above reaction contains one carbon atom more than the parent compound.
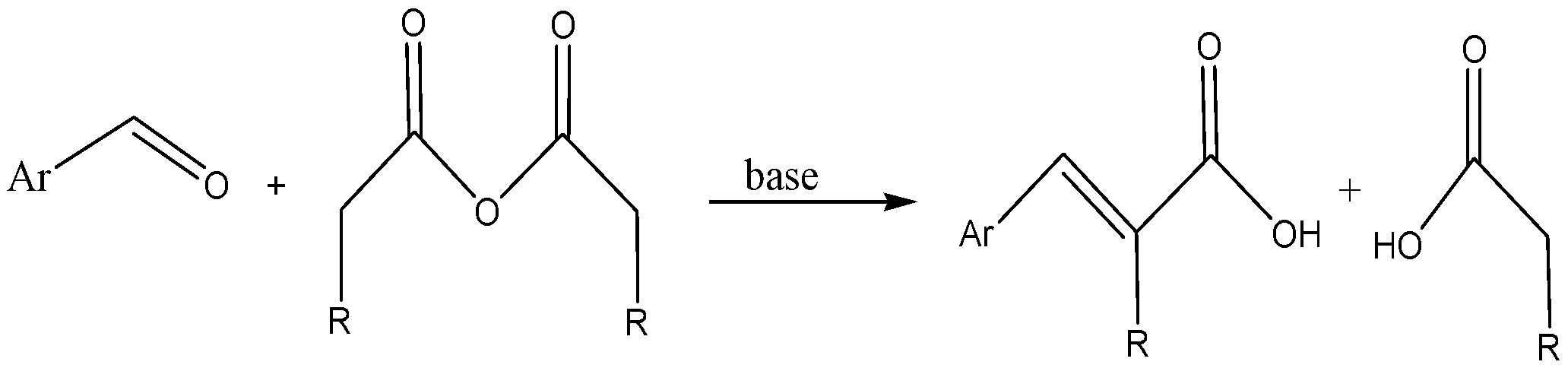
Perkin’s reaction gives that gives an alpha, beta-unsaturated acid
It is a type of condensation reaction that gives an alpha, beta-unsaturated acid
through the aromatic aldehyde and an acid anhydride in the presence of base catalyst.
Perkin reaction is,
$$
Sabatier reaction produce methane of carbon with carbon dioxide at elevated temperatures and pressures
produces methane and water in the presence of a catalyst.
The reaction is
$C{O_2} + 4{H_2}\xrightarrow{{Nickel}}C{H_4} + 2{H_2}O$
From the above information, \[C{H_3}CN + 4[H]\xrightarrow{{Na/{C_2}{H_5}OH}}C{H_3}C{H_2}N{H_2}\] is known as Mendius reaction. Because the nitrile compound, \[C{H_3}CN\], is reduced by nascent hydrogen (atomic hydrogen produced from zinc and dil.${H_2}S{O_4}$) to give primary amine, \[C{H_3}C{H_2}N{H_2}\].
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: We must remember that the primary $({1^0})$amine is one hydrogen atom of ammonia that is replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. For example $C{H_3}N{H_2}$, methyl amine and ${C_6}{H_5}N{H_2}$, aniline. Primary aromatic amines are used for manufacture of azo dyes. Coloured azo-compounds are widely used in dyeing industries. One of the examples is Methyl orange.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us see the options one by one for which option is correct.
Hofmann’s bromamide reaction gives a primary amine
When amide is treated with bromine in an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide the primary amine is called Hofmann’s bromamide reaction. The product amine formed in the reaction contains one carbon atom more than the parent compound.
General chemical reaction is
$RCON{H_2} + B{r_2} + 4NaOH \to RN{H_2} + N{a_2}C{O_3} + 2NaBr + 2{H_2}O$
Nitriles gives primary amine is a Mendius reaction
We need to know that the reduction reaction of nitriles (if a compound containing $ - C \equiv N$ functional group) with sodium $\left( {Na} \right)$ in ethanol gives primary amine is called Mendius reaction.
The general chemical reaction is,
\[R - C \equiv N{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}4[H]{\text{ }}\xrightarrow{{Na/{C_2}{H_5}OH}}{\text{ }}R - C{H_2}N{H_2}\]
$Alkyl \;cyanide \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\; \;\;\; \;\;\;\;\;\; Primary amine$
The product amine formed in the above reaction contains one carbon atom more than the parent compound.
Perkin’s reaction gives that gives an alpha, beta-unsaturated acid
It is a type of condensation reaction that gives an alpha, beta-unsaturated acid
through the aromatic aldehyde and an acid anhydride in the presence of base catalyst.
Perkin reaction is,
$$

Sabatier reaction produce methane of carbon with carbon dioxide at elevated temperatures and pressures
produces methane and water in the presence of a catalyst.
The reaction is
$C{O_2} + 4{H_2}\xrightarrow{{Nickel}}C{H_4} + 2{H_2}O$
From the above information, \[C{H_3}CN + 4[H]\xrightarrow{{Na/{C_2}{H_5}OH}}C{H_3}C{H_2}N{H_2}\] is known as Mendius reaction. Because the nitrile compound, \[C{H_3}CN\], is reduced by nascent hydrogen (atomic hydrogen produced from zinc and dil.${H_2}S{O_4}$) to give primary amine, \[C{H_3}C{H_2}N{H_2}\].
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: We must remember that the primary $({1^0})$amine is one hydrogen atom of ammonia that is replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. For example $C{H_3}N{H_2}$, methyl amine and ${C_6}{H_5}N{H_2}$, aniline. Primary aromatic amines are used for manufacture of azo dyes. Coloured azo-compounds are widely used in dyeing industries. One of the examples is Methyl orange.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




