
The reaction
$C{{H}_{2}}=CH-C{{H}_{3}}+HBr\to C{{H}_{3}}CHBr-C{{H}_{3}}$ is
A. Nucleophilic addition
B. Electrophilic addition
C. Electrophilic substitution
D. Free radical addition
Answer
357k+ views
Hint: When an alkene reacts with hydrogen halide there is always an addition reaction occurs. The negative halide ion gets attached to one of the carbon atoms of the double bond, and the positive hydrogen ion goes to other carbon atoms. The overall mechanism is governed by Markownikoff’s rule.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
The addition of hydrogen halide reacts with asymmetric alkene according to Markownikoff’s rule. It is the simplest electrophilic addition reaction as this reaction uses the smallest electrophile ${{H}^{+}}$. An electrophilic addition reaction in which an electrophile (Electron deficient species) accepts an electron.
Here the reagent hydrogen bromide provides both the nucleophile ( Electron rich species) bromide ion ($B{{r}^{-}}$) and electrophile proton(${{H}^{+}}$).
In the first step, the electrophile proton accepts a set of electrons from a double bond, and the pi electrons of alkene act as nucleophiles. Here the pi electrons of the alkenes move towards the hydrogen, and the bond between and bromine $H-Br$breaks and $B{{r}^{-}}$moves away. Thereby generating a positive charge on one of the carbon atoms of the double bond, called carbocation.
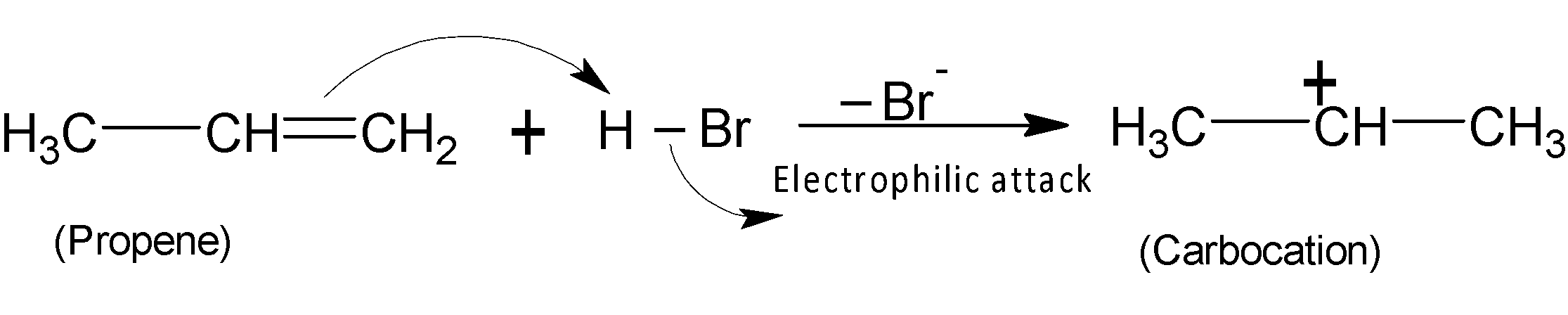
In the next step the nucleophile, bromide ion ($B{{r}^{-}}$) attacks the electrophilic positive centre to form $2-bromopropane$ the major product.
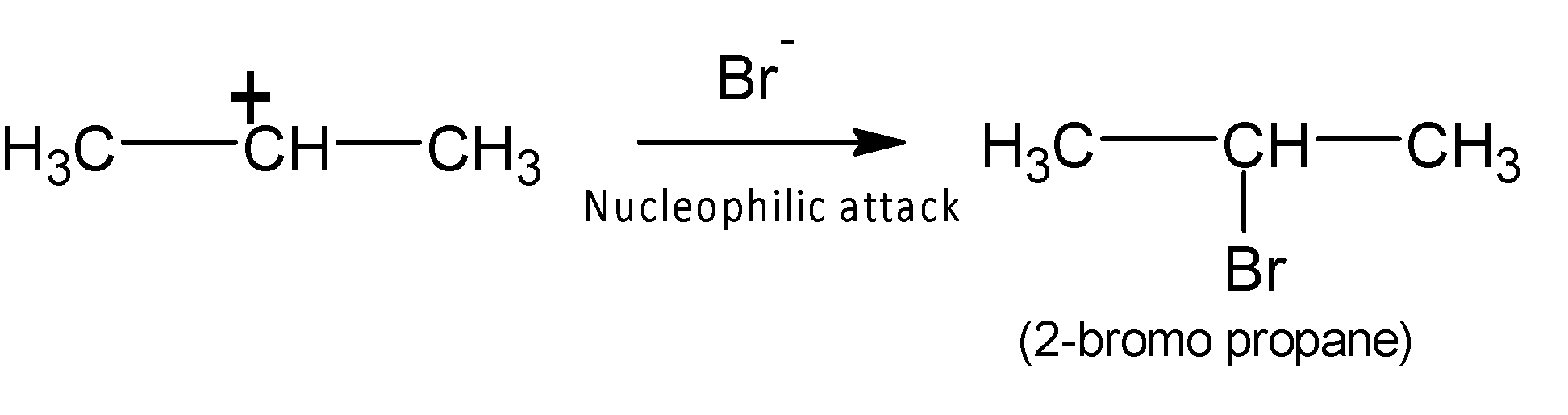
Therefore propene reacts with hydrogen bromide to form $2-bromopropane$ an electrophilic addition reaction.
Thus, option (B) is correct.
Note: Markovnikoff’s rule provides us with an empirical rule to determine the regioselectivity of alkenes and alkynes. According to this rule when hydrogen halide reacts with asymmetric alkene the negative halide ion gets linked to the carbon with the least number of hydrogen atoms of carbon-carbon double bond.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
The addition of hydrogen halide reacts with asymmetric alkene according to Markownikoff’s rule. It is the simplest electrophilic addition reaction as this reaction uses the smallest electrophile ${{H}^{+}}$. An electrophilic addition reaction in which an electrophile (Electron deficient species) accepts an electron.
Here the reagent hydrogen bromide provides both the nucleophile ( Electron rich species) bromide ion ($B{{r}^{-}}$) and electrophile proton(${{H}^{+}}$).
In the first step, the electrophile proton accepts a set of electrons from a double bond, and the pi electrons of alkene act as nucleophiles. Here the pi electrons of the alkenes move towards the hydrogen, and the bond between and bromine $H-Br$breaks and $B{{r}^{-}}$moves away. Thereby generating a positive charge on one of the carbon atoms of the double bond, called carbocation.

In the next step the nucleophile, bromide ion ($B{{r}^{-}}$) attacks the electrophilic positive centre to form $2-bromopropane$ the major product.

Therefore propene reacts with hydrogen bromide to form $2-bromopropane$ an electrophilic addition reaction.
Thus, option (B) is correct.
Note: Markovnikoff’s rule provides us with an empirical rule to determine the regioselectivity of alkenes and alkynes. According to this rule when hydrogen halide reacts with asymmetric alkene the negative halide ion gets linked to the carbon with the least number of hydrogen atoms of carbon-carbon double bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE




