
The reaction between \[C{O_2}\] and a Grignard reagent will yield:
A: An alkyl magnesium halide
B: an alcohol
C: magnesium carbonate
D: a carboxylic acid
Answer
549.9k+ views
Hint: A Grignard reagent is a chemical compound having the generic formula of R−Mg−X, while, X refers to a halogen and R refers to an organic group, primarily an alkyl or aryl group. These reagents behave as strong bases and thus react with the protic compounds.
Complete step by step answer:
Grignard reagents are generally used synthetically to produce new carbon–carbon bonds. Grignard reagent reacts with crushed dry ice (i.e. solid carbon dioxide) in order to form salts of carboxylic acids. Now, these salts of carboxylic acids will undergo acidification with mineral acids to finally yield corresponding carboxylic acids. The chemical equations are demonstrated below:
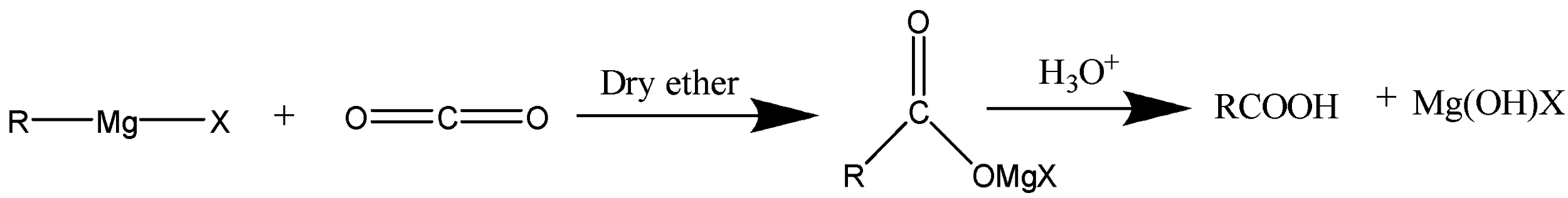
Carbon dioxide is used as a reactant because it is an inert electrophile. Grignard reagent is mainly employed as a strong nucleophile in order to react with \[C{O_2}\] directly and constructs \[C - C\] bonds and lead to the formation of carboxylic acids.
Thus, the reaction between \[C{O_2}\] and a Grignard reagent will yield a carboxylic acid.
Hence, Option D is correct.
Note: Grignard reagent possesses a highly polar carbon–magnesium bond wherein the carbon atom possesses a partial negative charge while metal possesses a partial positive charge. The polarity of carbon–magnesium bond is generally opposite to the carbon–halogen bond of haloalkanes. As the carbon atom of a Grignard reagent possesses a partial negative charge so it resembles a carbanion, thus, it reacts readily with electrophilic centers.
Ether is especially used as a solvent to form Grignard reagents since ethers are non-acidic (aprotic) in nature. On the other hand, water or alcohols have the ability to protonate and would destroy the Grignard reagent, owing to the Grignard carbon being highly nucleophilic.
Complete step by step answer:
Grignard reagents are generally used synthetically to produce new carbon–carbon bonds. Grignard reagent reacts with crushed dry ice (i.e. solid carbon dioxide) in order to form salts of carboxylic acids. Now, these salts of carboxylic acids will undergo acidification with mineral acids to finally yield corresponding carboxylic acids. The chemical equations are demonstrated below:

Carbon dioxide is used as a reactant because it is an inert electrophile. Grignard reagent is mainly employed as a strong nucleophile in order to react with \[C{O_2}\] directly and constructs \[C - C\] bonds and lead to the formation of carboxylic acids.
Thus, the reaction between \[C{O_2}\] and a Grignard reagent will yield a carboxylic acid.
Hence, Option D is correct.
Note: Grignard reagent possesses a highly polar carbon–magnesium bond wherein the carbon atom possesses a partial negative charge while metal possesses a partial positive charge. The polarity of carbon–magnesium bond is generally opposite to the carbon–halogen bond of haloalkanes. As the carbon atom of a Grignard reagent possesses a partial negative charge so it resembles a carbanion, thus, it reacts readily with electrophilic centers.
Ether is especially used as a solvent to form Grignard reagents since ethers are non-acidic (aprotic) in nature. On the other hand, water or alcohols have the ability to protonate and would destroy the Grignard reagent, owing to the Grignard carbon being highly nucleophilic.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE




