
The ratio of the areas of the incircle and circumcircle of square is:
A) \[1:\sqrt 2 \]\[\]
B) \[1:\sqrt 3 \]
C) \[1:4\]
D) \[1:2\]
Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: A Square circumscribing a circle and another square is inscribed in a circle with one vertex at the point of contact indicates that the one square is circumscribed to a circle and another one is inscribed.
Area of square\[ = {a^2}\]\[ = sid{e^2}\]
Diagonal of square \[ = \sqrt {2\,\,} a\]
Complete step-by -step solution:
Given that a square circumscribed a circle and another square is inscribed in the circle with one vertex at the point of contact let the radius of the circle\[ = r\]
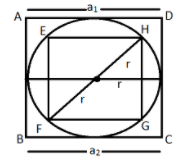
Now in square EFGH, we have:
Diagonal of square \[ = \sqrt {2\,\,} a\]
Diagonal of circle = \[2r\]
In EFGH, \[a = {a_2}\]
As here in the diagram, diagonal of the square is equal to diagonal of the circle. We have:
\[2r = \sqrt 2 \,{a_2}\]
\[{a_2} = \dfrac{{2r}}{{\sqrt 2 }} = \sqrt 2 r........(1)\]
Area of square EAGH is:
\[
{A_{EAGH}} = \left( {{a_2}} \right){}^2 \\
= {(\sqrt 2 r)^2} \\
= 2{r^2}.......(2) \\
\]
Now, considering the square ABCD:
Diagonal of square \[ = \sqrt {2\,\,} a\]
Diagonal of circle = \[2r\]
In EFGH, \[a = {a_1}\]
As here in the diagram, diagonal of the square is equal to diagonal of the circle. We have:
\[{a_1} = 2r\]
Area of square ABCD is:
\[
{A_{ABCD}} = {({a_1})^2} \\
= {(2r)^2} \\
= 4{r^2}.......(3) \\
\]
Now Ratio of Area of square EFGH and area of square ABCD is:
\[
\dfrac{{{A_{EFGH}}}}{{{A_{ABCD}}}} = \dfrac{{2{r^2}}}{{4{r^2}}} \\
= \dfrac{1}{2} \\
\] (from \[e{q^n}\](2) & (3))
Hence, the areas of the inscribed and circumscribed squares are $1:2$
Hence the correct answer is option D.
Note:In geometry, the circumscribed circle or circumcircle of a polygon is a circle that passes through all the vertices of the polygon. The centre of this circle is called the circumcenter, and its radius is called the circumradius. A circumscribed square of a circle is a square surrounding a circle such that the circumference of the circle touches the midpoints of the four sides of the square. The diameter of the circle is equal to the side length of the square.

Area of square\[ = {a^2}\]\[ = sid{e^2}\]
Diagonal of square \[ = \sqrt {2\,\,} a\]
Complete step-by -step solution:
Given that a square circumscribed a circle and another square is inscribed in the circle with one vertex at the point of contact let the radius of the circle\[ = r\]

Now in square EFGH, we have:
Diagonal of square \[ = \sqrt {2\,\,} a\]
Diagonal of circle = \[2r\]
In EFGH, \[a = {a_2}\]
As here in the diagram, diagonal of the square is equal to diagonal of the circle. We have:
\[2r = \sqrt 2 \,{a_2}\]
\[{a_2} = \dfrac{{2r}}{{\sqrt 2 }} = \sqrt 2 r........(1)\]
Area of square EAGH is:
\[
{A_{EAGH}} = \left( {{a_2}} \right){}^2 \\
= {(\sqrt 2 r)^2} \\
= 2{r^2}.......(2) \\
\]
Now, considering the square ABCD:
Diagonal of square \[ = \sqrt {2\,\,} a\]
Diagonal of circle = \[2r\]
In EFGH, \[a = {a_1}\]
As here in the diagram, diagonal of the square is equal to diagonal of the circle. We have:
\[{a_1} = 2r\]
Area of square ABCD is:
\[
{A_{ABCD}} = {({a_1})^2} \\
= {(2r)^2} \\
= 4{r^2}.......(3) \\
\]
Now Ratio of Area of square EFGH and area of square ABCD is:
\[
\dfrac{{{A_{EFGH}}}}{{{A_{ABCD}}}} = \dfrac{{2{r^2}}}{{4{r^2}}} \\
= \dfrac{1}{2} \\
\] (from \[e{q^n}\](2) & (3))
Hence, the areas of the inscribed and circumscribed squares are $1:2$
Hence the correct answer is option D.
Note:In geometry, the circumscribed circle or circumcircle of a polygon is a circle that passes through all the vertices of the polygon. The centre of this circle is called the circumcenter, and its radius is called the circumradius. A circumscribed square of a circle is a square surrounding a circle such that the circumference of the circle touches the midpoints of the four sides of the square. The diameter of the circle is equal to the side length of the square.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




