
The ratio of refractive index of red light to blue light in air is
a) Less than unity
b) equal to unity
Greater than unity
d) less as well as greater than unity depending on the experimental conditions
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: The refractive index depends on the wavelength of light used. The frequency of light does not change as it enters from one medium to another. Hence from the definition of refractive index we can calculate the ratio of the refractive index red light to blue light in air.
Complete solution:
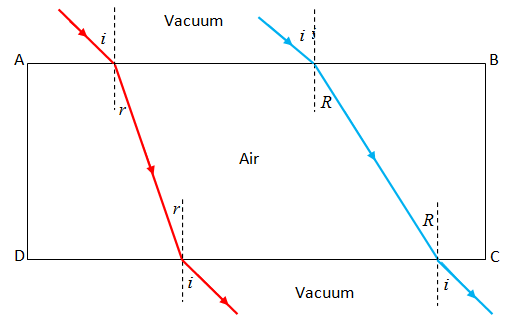
In the above diagram ABCD is a region containing air and it is surrounded by vacuum. The ray of red and blue light are incident on a surface AB at an angle i. The angle of refraction for both the rays of light are as shown in the fig.
From the definition of refractive index,
Refractive index of a medium with respect to vacuum =$\eta =\dfrac{\text{speed of light in vacuum}}{\text{speed of light in medium}}......(1)$
Speed of light is given by $c=\lambda \gamma ....(2)$ where $\lambda $is the wavelength of light used and $\gamma $ is the frequency of light. Substituting equation 2 in one we get,
$\eta =\dfrac{\lambda \gamma }{\overline{\lambda }\gamma }......(1)$ Here $\lambda $is the wavelength of light in vacuum and $\overline{\lambda }$ is the wavelength of light in medium. Since the frequency of light remains the same as it enters from one medium to another the equation for refractive index can be written as $\eta =\dfrac{\lambda }{\overline{\lambda }}......(3)$ .
The wavelength of red light is greater than that of blue light
Hence the ratio of their refractive index is given by, Using Equation 3
$\dfrac{{{\eta }_{RED}}}{{{\eta }_{BLUE}}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{{{\lambda }_{RED}}}{\overline{{{\lambda }_{RED}}}}}{\dfrac{{{\lambda }_{BLUE}}}{\overline{{{\lambda }_{BLUE}}}}}$
Taking the terms in the denominator and multiplying to the numerator we get,
$\dfrac{{{\eta }_{RED}}}{{{\eta }_{BLUE}}}=\dfrac{{{\lambda }_{RED}}\times \overline{{{\lambda }_{BLUE}}}}{\overline{{{\lambda }_{RED}}}\times {{\lambda }_{BLUE}}}$
$\lambda $and $\overline{\lambda }$ in air is approximately the same for any light of given wavelength. Hence,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{\eta }_{RED}}}{{{\eta }_{BLUE}}}=\dfrac{{{\lambda }_{RED}}\times \overline{{{\lambda }_{BLUE}}}}{\overline{{{\lambda }_{RED}}}\times {{\lambda }_{BLUE}}} \\
& \dfrac{{{\eta }_{RED}}}{{{\eta }_{BLUE}}}=1 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the correct answer is option is b.
Note: Refractive index is dimensionless since it is a ratio. The ratio $\dfrac{{{\eta }_{RED}}}{{{\eta }_{BLUE}}}$ is always not equal to 1. Since we have taken the speed of light in vacuum to be approximately equal to speed of light in air hence the ratio becomes unity. In the fig given above R=r for air but for any other material than air it's different.
Complete solution:

In the above diagram ABCD is a region containing air and it is surrounded by vacuum. The ray of red and blue light are incident on a surface AB at an angle i. The angle of refraction for both the rays of light are as shown in the fig.
From the definition of refractive index,
Refractive index of a medium with respect to vacuum =$\eta =\dfrac{\text{speed of light in vacuum}}{\text{speed of light in medium}}......(1)$
Speed of light is given by $c=\lambda \gamma ....(2)$ where $\lambda $is the wavelength of light used and $\gamma $ is the frequency of light. Substituting equation 2 in one we get,
$\eta =\dfrac{\lambda \gamma }{\overline{\lambda }\gamma }......(1)$ Here $\lambda $is the wavelength of light in vacuum and $\overline{\lambda }$ is the wavelength of light in medium. Since the frequency of light remains the same as it enters from one medium to another the equation for refractive index can be written as $\eta =\dfrac{\lambda }{\overline{\lambda }}......(3)$ .
The wavelength of red light is greater than that of blue light
Hence the ratio of their refractive index is given by, Using Equation 3
$\dfrac{{{\eta }_{RED}}}{{{\eta }_{BLUE}}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{{{\lambda }_{RED}}}{\overline{{{\lambda }_{RED}}}}}{\dfrac{{{\lambda }_{BLUE}}}{\overline{{{\lambda }_{BLUE}}}}}$
Taking the terms in the denominator and multiplying to the numerator we get,
$\dfrac{{{\eta }_{RED}}}{{{\eta }_{BLUE}}}=\dfrac{{{\lambda }_{RED}}\times \overline{{{\lambda }_{BLUE}}}}{\overline{{{\lambda }_{RED}}}\times {{\lambda }_{BLUE}}}$
$\lambda $and $\overline{\lambda }$ in air is approximately the same for any light of given wavelength. Hence,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{\eta }_{RED}}}{{{\eta }_{BLUE}}}=\dfrac{{{\lambda }_{RED}}\times \overline{{{\lambda }_{BLUE}}}}{\overline{{{\lambda }_{RED}}}\times {{\lambda }_{BLUE}}} \\
& \dfrac{{{\eta }_{RED}}}{{{\eta }_{BLUE}}}=1 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the correct answer is option is b.
Note: Refractive index is dimensionless since it is a ratio. The ratio $\dfrac{{{\eta }_{RED}}}{{{\eta }_{BLUE}}}$ is always not equal to 1. Since we have taken the speed of light in vacuum to be approximately equal to speed of light in air hence the ratio becomes unity. In the fig given above R=r for air but for any other material than air it's different.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




