
The ratio in case of duplicate dominant epistasis is
a. 15:1
b. 9:3:4
c. 13:3
d. None of the above
Answer
594.6k+ views
Hint: Duplicate dominant epistasis involves the masking of two recessive alleles present at two different loci in the presence of a dominant gene. Complementary gene action is the alternate name of duplicate dominant epistasis.
Complete answer:
The phenomena of duplicate dominant epistasis or duplicate gene action involve a dominant allele (it is an alternative form of a gene) that masks the expression of recessive alleles at two loci (it is a position on a chromosome where a gene is located). Due to this, the same type of phenotypic effect is produced and the ratio becomes 15:1.
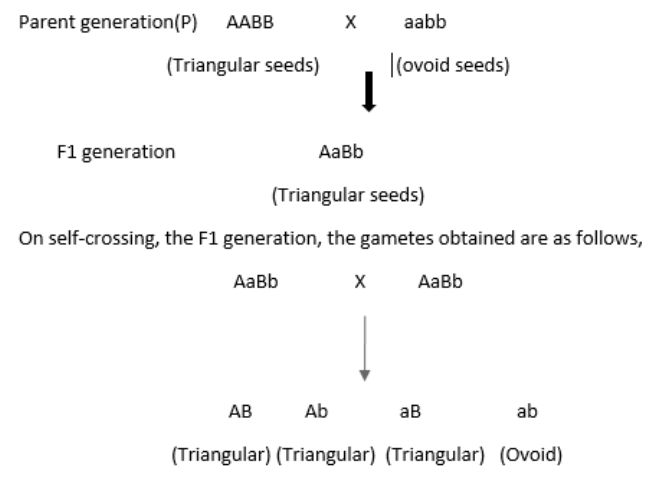
Let us consider an example of Capsella bursa-pastoris (shepherd’s purse) which is a member of Brassicaceae (mustard family) and is famous for its purse-like fruits. It has two types of seed: triangular-shaped seed (let us consider it as a dominant trait) and the oval-shaped seed (let us assume it as a recessive trait).When a cross is made between the triangular seeds (dominant) and the ovoid seeds (recessive), the F1 generation obtained is as follows,
On making a Punnett square, we get,
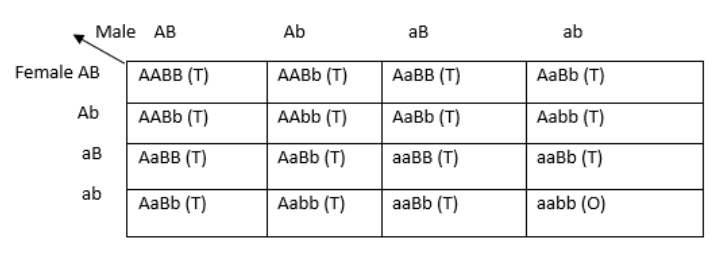
Here, ’T’ represents offspring with triangular seeds and ‘O’ represents offspring with ovoid seeds. It is seen that all the gametes produce the same phenotypic effect, in the presence of a dominant allele, that is, AABB, AaBb, Aabb, aaBB, aaBb. In the absence of dominant genes, the recessive phenotypic trait (aabb), that is, ovoid seeds are produced. Due to this, 15 offspring have triangular seeds and 1 offspring has oval seeds, hence, the ratio becomes 15:1.
Additional information:
- The word epistasis was first used by Bateson to describe the masking effect and is derived from a Greek word which means standing over. In simple words, epistasis deals with the inter-allelic gene interaction. Here, one gene hides the effect of other genes at different loci.
- The gene that masks the other gene is known as the epistatic gene and the gene whose effect is masked is known as the hypostatic gene. Apart from duplicate dominant epistasis, there are five more types. They are dominant epistasis, recessive epistasis, dominant inhibitory epistasis, duplicate recessive epistasis, and polymeric gene interaction.
Note: Duplicate dominant epistasis occurs only in the presence of at least one dominant allele. In the absence of a dominant gene, recessive traits will be expressed and duplicate dominant epistasis won’t take place.
Complete answer:
The phenomena of duplicate dominant epistasis or duplicate gene action involve a dominant allele (it is an alternative form of a gene) that masks the expression of recessive alleles at two loci (it is a position on a chromosome where a gene is located). Due to this, the same type of phenotypic effect is produced and the ratio becomes 15:1.
Let us consider an example of Capsella bursa-pastoris (shepherd’s purse) which is a member of Brassicaceae (mustard family) and is famous for its purse-like fruits. It has two types of seed: triangular-shaped seed (let us consider it as a dominant trait) and the oval-shaped seed (let us assume it as a recessive trait).When a cross is made between the triangular seeds (dominant) and the ovoid seeds (recessive), the F1 generation obtained is as follows,

On making a Punnett square, we get,

Here, ’T’ represents offspring with triangular seeds and ‘O’ represents offspring with ovoid seeds. It is seen that all the gametes produce the same phenotypic effect, in the presence of a dominant allele, that is, AABB, AaBb, Aabb, aaBB, aaBb. In the absence of dominant genes, the recessive phenotypic trait (aabb), that is, ovoid seeds are produced. Due to this, 15 offspring have triangular seeds and 1 offspring has oval seeds, hence, the ratio becomes 15:1.
Additional information:
- The word epistasis was first used by Bateson to describe the masking effect and is derived from a Greek word which means standing over. In simple words, epistasis deals with the inter-allelic gene interaction. Here, one gene hides the effect of other genes at different loci.
- The gene that masks the other gene is known as the epistatic gene and the gene whose effect is masked is known as the hypostatic gene. Apart from duplicate dominant epistasis, there are five more types. They are dominant epistasis, recessive epistasis, dominant inhibitory epistasis, duplicate recessive epistasis, and polymeric gene interaction.
Note: Duplicate dominant epistasis occurs only in the presence of at least one dominant allele. In the absence of a dominant gene, recessive traits will be expressed and duplicate dominant epistasis won’t take place.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




