
The rate of increase of length of the shadow of man 2 metres in height, due to a lamp at 10 metres height, when he is moving away from it at the rate of 2 m/sec, is
(a) $\dfrac{1}{2}$ m/sec
(b) $\dfrac{2}{5}$ m/sec
(c) $\dfrac{1}{3}$ m/sec
(d) 5 m/sec
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: We will draw a rough figure to understand the given information. We will be able to show that we see similar triangles in the figure. Using the ratio of similar sides of these triangles, we will form an equation that relates the length of the shadow with the distance between the man and the lamp. Then we will differentiate this equation to obtain the required answer.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us draw a rough figure representing the given information. It looks like the following figure,
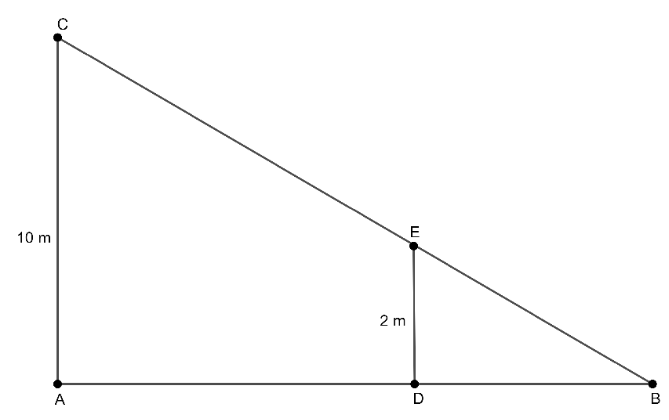
The point C is the lamp and segment ED is the man with height 2 meters. The length of the shadow is the length of segment DB. Let us denote this length of the shadow by $x$. Let the distance between the man and the lamp be $y$ metres.
Now, we can see that we have two right angled triangles, $\Delta \text{CAB}$ and $\Delta \text{EDB}$. In these triangles, we can see that $\angle \text{CAB = }\angle \text{EDB = 90}{}^\circ $ and $\angle \text{CBA = }\angle \text{EBD}$because it is a common angle. Hence, by AA test, we conclude that $\Delta \text{CAB}$ and $\Delta \text{EDB}$ are similar triangles. Now, we will take the ratio of the similar sides in the following manner,
$\dfrac{\text{CA}}{\text{AB}}=\dfrac{\text{ED}}{\text{DB}}$
We know that $\text{CA = 10}$, $\text{AB = AD + DB = }y+x$, $\text{ED = 2}$ and $\text{DB = }x$. Substituting these values in the above equation, we get
$\dfrac{\text{10}}{y+x}=\dfrac{\text{2}}{\text{x}}$
Simplifying this equation, we get
$\begin{align}
& 10x=2y+2x \\
& \Rightarrow 10x-2x=2y \\
& \therefore 8x=2y \\
\end{align}$
Differentiating the above equation with respect to time, we get
$8\dfrac{dx}{dt}=2\dfrac{dy}{dt}$
We are given that the rate of man moving away is 2 m/sec, that is $\dfrac{dy}{dt}=2\text{ m/sec}$. Substituting this value in the above equation, we get
$\begin{align}
& 8\dfrac{dx}{dt}=2\times 2 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dx}{dt}=\dfrac{4}{8} \\
& \therefore \dfrac{dx}{dt}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the rate of increase in the length of shadow of man is $\dfrac{1}{2}\text{ m/sec}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option a”.
Note: It is useful to draw rough diagrams to understand the given information in this type of question. We see that the word ‘rate’ is associated with a differentiation. It is always a rate of some element with respect to another element. Therefore, the differentiation tells us about a particular change in an element with respect to the other element. It is important that we interpret this correctly so that we can substitute the proper values in the differential equation obtained.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us draw a rough figure representing the given information. It looks like the following figure,

The point C is the lamp and segment ED is the man with height 2 meters. The length of the shadow is the length of segment DB. Let us denote this length of the shadow by $x$. Let the distance between the man and the lamp be $y$ metres.
Now, we can see that we have two right angled triangles, $\Delta \text{CAB}$ and $\Delta \text{EDB}$. In these triangles, we can see that $\angle \text{CAB = }\angle \text{EDB = 90}{}^\circ $ and $\angle \text{CBA = }\angle \text{EBD}$because it is a common angle. Hence, by AA test, we conclude that $\Delta \text{CAB}$ and $\Delta \text{EDB}$ are similar triangles. Now, we will take the ratio of the similar sides in the following manner,
$\dfrac{\text{CA}}{\text{AB}}=\dfrac{\text{ED}}{\text{DB}}$
We know that $\text{CA = 10}$, $\text{AB = AD + DB = }y+x$, $\text{ED = 2}$ and $\text{DB = }x$. Substituting these values in the above equation, we get
$\dfrac{\text{10}}{y+x}=\dfrac{\text{2}}{\text{x}}$
Simplifying this equation, we get
$\begin{align}
& 10x=2y+2x \\
& \Rightarrow 10x-2x=2y \\
& \therefore 8x=2y \\
\end{align}$
Differentiating the above equation with respect to time, we get
$8\dfrac{dx}{dt}=2\dfrac{dy}{dt}$
We are given that the rate of man moving away is 2 m/sec, that is $\dfrac{dy}{dt}=2\text{ m/sec}$. Substituting this value in the above equation, we get
$\begin{align}
& 8\dfrac{dx}{dt}=2\times 2 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dx}{dt}=\dfrac{4}{8} \\
& \therefore \dfrac{dx}{dt}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the rate of increase in the length of shadow of man is $\dfrac{1}{2}\text{ m/sec}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option a”.
Note: It is useful to draw rough diagrams to understand the given information in this type of question. We see that the word ‘rate’ is associated with a differentiation. It is always a rate of some element with respect to another element. Therefore, the differentiation tells us about a particular change in an element with respect to the other element. It is important that we interpret this correctly so that we can substitute the proper values in the differential equation obtained.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




