
The purine and pyrimidine pairs of complementary strands of DNA are held together by
A. H bonds
B. O bonds
C. C bonds
D. N bonds
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: The term DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid and RNA stands for ribonucleic acid. DNA and RNA are both nucleic acids and either of them is present in the nucleus of the cell. It is the genetic material of an organism.
Complete answer: The structure of DNA is coiled helical in shape which consists of two polynucleotide chains. DNA carries the genetic instruction for the functioning, development, reproduction, and growth of all known organisms and also many viruses. Therefore, DNA is considered the genetic material of an organism. Polynucleotides consist of smaller monomeric units called nucleotides. Each nucleotide is made up of three components: a deoxyribose sugar, a nitrogen-containing nucleobase, and a phosphate group. An organic molecule that contains a nitrogen atom that has chemical properties like the base is called a nitrogenous base. The five types of nitrogenous bases are adenine, guanine, uracil, thymine, and cytosine. The double helix structure of two strands of DNA is due to the hydrogen bonding between the base pairs of purine and pyrimidines. Due to the presence of strong hydrogen bonds between the phosphates the DNA molecule is twisted in shape. In DNA, guanine (G) is paired with cytosine (C) and adenine (A) is paired with thymine (T). These are called complementary base pairs.
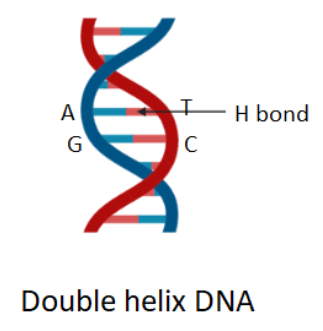
So, option A is the correct option.
Note: Pyrimidine and purine are the two parent compounds from which the nitrogenous bases are derived. Thymine, cytosine, and uracil are included in pyrimidines and have single ring structure. Adenine and guanine are derivatives of purines and have double ring structure. In RNA, the sugar called ribose is present instead of deoxyribose and nitrogenous base uracil is present instead of thymine.
Complete answer: The structure of DNA is coiled helical in shape which consists of two polynucleotide chains. DNA carries the genetic instruction for the functioning, development, reproduction, and growth of all known organisms and also many viruses. Therefore, DNA is considered the genetic material of an organism. Polynucleotides consist of smaller monomeric units called nucleotides. Each nucleotide is made up of three components: a deoxyribose sugar, a nitrogen-containing nucleobase, and a phosphate group. An organic molecule that contains a nitrogen atom that has chemical properties like the base is called a nitrogenous base. The five types of nitrogenous bases are adenine, guanine, uracil, thymine, and cytosine. The double helix structure of two strands of DNA is due to the hydrogen bonding between the base pairs of purine and pyrimidines. Due to the presence of strong hydrogen bonds between the phosphates the DNA molecule is twisted in shape. In DNA, guanine (G) is paired with cytosine (C) and adenine (A) is paired with thymine (T). These are called complementary base pairs.

So, option A is the correct option.
Note: Pyrimidine and purine are the two parent compounds from which the nitrogenous bases are derived. Thymine, cytosine, and uracil are included in pyrimidines and have single ring structure. Adenine and guanine are derivatives of purines and have double ring structure. In RNA, the sugar called ribose is present instead of deoxyribose and nitrogenous base uracil is present instead of thymine.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




