
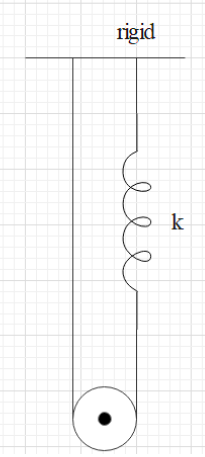
The pulley shown in figure has a moment of inertia $I$ about its axis and mass $m$. Calculate the time period of vertical oscillations of its centre of mass. It has been mentioned that the spring is having a spring constant $k$ and the string does not slip over the pulley.
$\begin{align}
& A.2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{\dfrac{I}{{{r}^{2}}}+m}{4k}} \\
& B.\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{\dfrac{I}{{{r}^{2}}}+m}{4k}} \\
& C.6\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{\dfrac{I}{{{r}^{2}}}+m}{4k}} \\
& D.\text{none of these} \\
\end{align}$

Answer
576.3k+ views
Hint: when we analyse the figure we can understand that the twice of the value of tension will be equivalent to the force of gravity. Apply the conservation of energy in this system and take the derivative of energy which will be zero as it is conservative. The first derivative of the velocity with respect to time will be equivalent to the acceleration. Using this, find the tension. This will help you in answering this question.
Complete step by step solution:
when we analyse the figure we can understand that the twice of the value of tension will be equivalent to the force of gravity. That is,
$2T=mg$
Where the tension can be written as,
$T=ky$
Substituting this in the equation will give,
$\begin{align}
& 2ky=mg \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{mg}{2k} \\
\end{align}$
According to the conservation of energy principle, we can write that,
$U=\dfrac{1}{2}I{{\omega }^{2}}+\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}-mgx+\dfrac{1}{2}{{\left[ \dfrac{mg}{2k}+2x \right]}^{2}}$
Simplifying this equation can be written as,
$U=\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ \dfrac{I}{{{r}^{2}}}+m \right]{{v}^{2}}+\dfrac{{{m}^{2}}{{g}^{2}}}{8k}+2k{{x}^{2}}$
As we already mentioned the system is conservative. Therefore the first derivative of energy with respect to time will be zero.
That is we can write that,
$\dfrac{dU}{dt}=0$
Substituting the value in it will give,
\[0=\dfrac{d}{dt}\left( \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ \dfrac{I}{{{r}^{2}}}+m \right]{{v}^{2}}+\dfrac{{{m}^{2}}{{g}^{2}}}{8k}+2k{{x}^{2}} \right)\]
Now let us perform the differentiation,
That is,
\[0=\left( \left[ \dfrac{I}{{{r}^{2}}}+m \right]\dfrac{vdv}{dt}+4kxv \right)\]
Rearranging this equation in terms of the derivative of velocity can be shown as,
The first derivative of the velocity with respect to time will be equivalent to the acceleration.
\[\dfrac{dv}{dt}=a=\dfrac{-4kx}{\left( \dfrac{I}{{{r}^{2}}}+m \right)}\]
The tension can be found by the equation given as,
\[T=2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{x}{a}}\]
Substituting the values in it will give,
\[T=2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{\left( \dfrac{I}{{{r}^{2}}}+m \right)}{4k}}\]
This is the correct answer.
The answer is mentioned as option A.
Note:
Tension is basically the force itself. It can be explained as the pulling force which has been axially transmitted using the ways of a cable, a string, chain, or similar one-dimensional continuous object or a rope. The unit of tension is the same as that of force itself.
Complete step by step solution:
when we analyse the figure we can understand that the twice of the value of tension will be equivalent to the force of gravity. That is,
$2T=mg$
Where the tension can be written as,
$T=ky$
Substituting this in the equation will give,
$\begin{align}
& 2ky=mg \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{mg}{2k} \\
\end{align}$
According to the conservation of energy principle, we can write that,
$U=\dfrac{1}{2}I{{\omega }^{2}}+\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}-mgx+\dfrac{1}{2}{{\left[ \dfrac{mg}{2k}+2x \right]}^{2}}$
Simplifying this equation can be written as,
$U=\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ \dfrac{I}{{{r}^{2}}}+m \right]{{v}^{2}}+\dfrac{{{m}^{2}}{{g}^{2}}}{8k}+2k{{x}^{2}}$
As we already mentioned the system is conservative. Therefore the first derivative of energy with respect to time will be zero.
That is we can write that,
$\dfrac{dU}{dt}=0$
Substituting the value in it will give,
\[0=\dfrac{d}{dt}\left( \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ \dfrac{I}{{{r}^{2}}}+m \right]{{v}^{2}}+\dfrac{{{m}^{2}}{{g}^{2}}}{8k}+2k{{x}^{2}} \right)\]
Now let us perform the differentiation,
That is,
\[0=\left( \left[ \dfrac{I}{{{r}^{2}}}+m \right]\dfrac{vdv}{dt}+4kxv \right)\]
Rearranging this equation in terms of the derivative of velocity can be shown as,
The first derivative of the velocity with respect to time will be equivalent to the acceleration.
\[\dfrac{dv}{dt}=a=\dfrac{-4kx}{\left( \dfrac{I}{{{r}^{2}}}+m \right)}\]
The tension can be found by the equation given as,
\[T=2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{x}{a}}\]
Substituting the values in it will give,
\[T=2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{\left( \dfrac{I}{{{r}^{2}}}+m \right)}{4k}}\]
This is the correct answer.
The answer is mentioned as option A.
Note:
Tension is basically the force itself. It can be explained as the pulling force which has been axially transmitted using the ways of a cable, a string, chain, or similar one-dimensional continuous object or a rope. The unit of tension is the same as that of force itself.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




